JAJSHT7 August 2019 DRV5057-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.1.2.2 Decoding a PWM (Analog)
If an analog signal is needed at the end of a large travel distance, first use a microcontroller to digitally decode the PWM, then use a DAC to produce the analog signal. If an analog signal is needed after a short signal travel distance, use an analog output device, such as the DRV5055-Q1.
If an analog signal is needed at the end of a large travel distance and a microcontroller is unavailable, use a low-pass filter to convert the PWM signal into an analog voltage, as shown in Figure 17. When using this method, note the following:
- A ripple appears at the analog voltage output, causing a decrease in accuracy. The ripple intensity and frequency depend on the values chosen for R and C in the filter.
- The minimum and maximum voltages of the PWM must be known to calculate the magnetic field strength from the analog voltage. Thus, if the signal is traveling a large distance, then the minimum and maximum values must be either measured or buffered back to a known value.
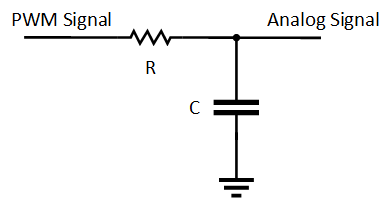 Figure 17. Low-Pass RC Filter
Figure 17. Low-Pass RC Filter