SNVSAC2A March 2015 – June 2020 LM317A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 1.25-V to 25-V Adjustable Regulator
- 8.2.2 5-V Logic Regulator With Electronic Shutdown
- 8.2.3 Slow Turnon 15-V Regulator
- 8.2.4 Adjustable Regulator With Improved Ripple Rejection
- 8.2.5 High-Stability 10-V Regulator
- 8.2.6 High-Current Adjustable Regulator
- 8.2.7 Emitter-Follower Current Amplifier
- 8.2.8 1-A Current Regulator
- 8.2.9 Common-Emitter Amplifier
- 8.2.10 Low-Cost 3-A Switching Regulator
- 8.2.11 Current-Limited Voltage Regulator
- 8.2.12 Adjusting Multiple On-Card Regulators With Single Control
- 8.2.13 AC Voltage Regulator
- 8.2.14 12-V Battery Charger
- 8.2.15 Adjustable 4-A Regulator
- 8.2.16 Current-Limited 6-V Charger
- 8.2.17 Digitally-Selected Outputs
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.4.2 Protection Diodes
When external capacitors are used with any IC regulator, it is sometimes necessary to add protection diodes to prevent the capacitors from discharging through low-current points into the regulator. Most 10-μF capacitors have low enough internal series resistance to deliver 20-A spikes when shorted. Although the surge is short, there is enough energy to damage parts of the IC.
When an output capacitor is connected to a regulator and the input is shorted, the output capacitor will discharge into the output of the regulator. The discharge current depends on the value of the capacitor, the output voltage of the regulator, and the rate of decrease of VIN. In the LM317A, this discharge path is through a large junction that is able to sustain 15-A surge with no problem. This is not true of other types of positive regulators. For output capacitors of 25 μF or less, there is no need to use diodes.
The bypass capacitor on the adjustment terminal can discharge through a low current junction. Discharge occurs when either the input, or the output, is shorted. Internal to the LM317A is a 50-Ω resistor which limits the peak discharge current. No protection is needed for output voltages of 25 V or less and 10-μF capacitance. Figure 17 shows an LM317A with protection diodes included for use with outputs greater than 25 V and high values of output capacitance.
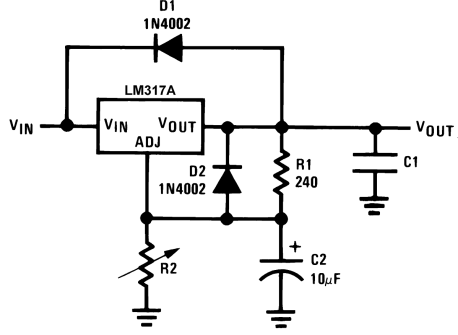
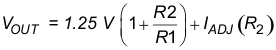 |
||
| D1 protects against C1 | ||
| D2 protects against C2 | ||