JAJS436D December 2009 – December 2019 BQ24610 , BQ24617
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 9.3.2 Battery Current Regulation
- 9.3.3 Input Adapter Current Regulation
- 9.3.4 Precharge
- 9.3.5 Charge Termination, Recharge, and Safety Timer
- 9.3.6 Power Up
- 9.3.7 Enable and Disable Charging
- 9.3.8 System Power Selector
- 9.3.9 Automatic Internal Soft-Start Charger Current
- 9.3.10 Converter Operation
- 9.3.11 Synchronous and Nonsynchronous Operation
- 9.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Undercurrent Protection
- 9.3.13 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 9.3.14 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.15 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 9.3.16 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Overcurrent Protection
- 9.3.17 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 9.3.18 Temperature Qualification
- 9.3.19 Timer Fault Recovery
- 9.3.20 PG Output
- 9.3.21 CE (Charge Enable)
- 9.3.22 Charge Status Outputs
- 9.3.23 Battery Detection
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.3.3 Input Adapter Current Regulation
The total input from an AC adapter or other DC source is a function of the system supply current and the battery charging current. System current normally fluctuates as portions of the systems are powered up or down. Without DPM, the source must be able to supply the maximum system current and the maximum charger input current simultaneously. By using DPM, the battery charger reduces the charging current when the input current exceeds the input current limit set by ACSET. The current capability of the AC adapter can be lowered, reducing system cost.
Similar to setting battery regulation current, adapter current is sensed by resistor RAC connected between ACP and ACN. Its maximum value is set by ACSET using Equation 3:
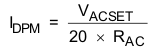
VACSET, the input voltage range of ACSET, is from 0 V to 2 V. The ACP and ACN pins are used to sense voltage across RAC with default value of 10 mΩ. However, resistors of other values can also be used. A larger the sense resistor gives a larger sense voltage and a higher regulation accuracy, but at the expense of higher conduction loss.