SBOU293D November 2022 – January 2024
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2OPTEVM Hardware Overview
- 3OPTEVM Software
- 4Schematic, PCB Layout, and Bill of Materials
- 5Troubleshooting
- 6Revision History
4.2.1 Schematic
Figure 4-6 shows the complete schematic of the OPTMB EVM board. The schematic is split into three sections: connector, MSP430, and socket. A USB type C connector is used to interface with the PC. The MSP430 microcontroller allows the PC to interface with the light sensor through I2C. The coupon board containing the light sensor plugs into the OPTMB EVM board through the socket. The OPTMB EVM board provides easy access to the I2C, INT, VDD, and GND lines. The header J2 is depopulated on the OPTEVM by default and is labeled through hole pads can be used to access the lines. Alternatively, a header can be populated at J2 for easier access.
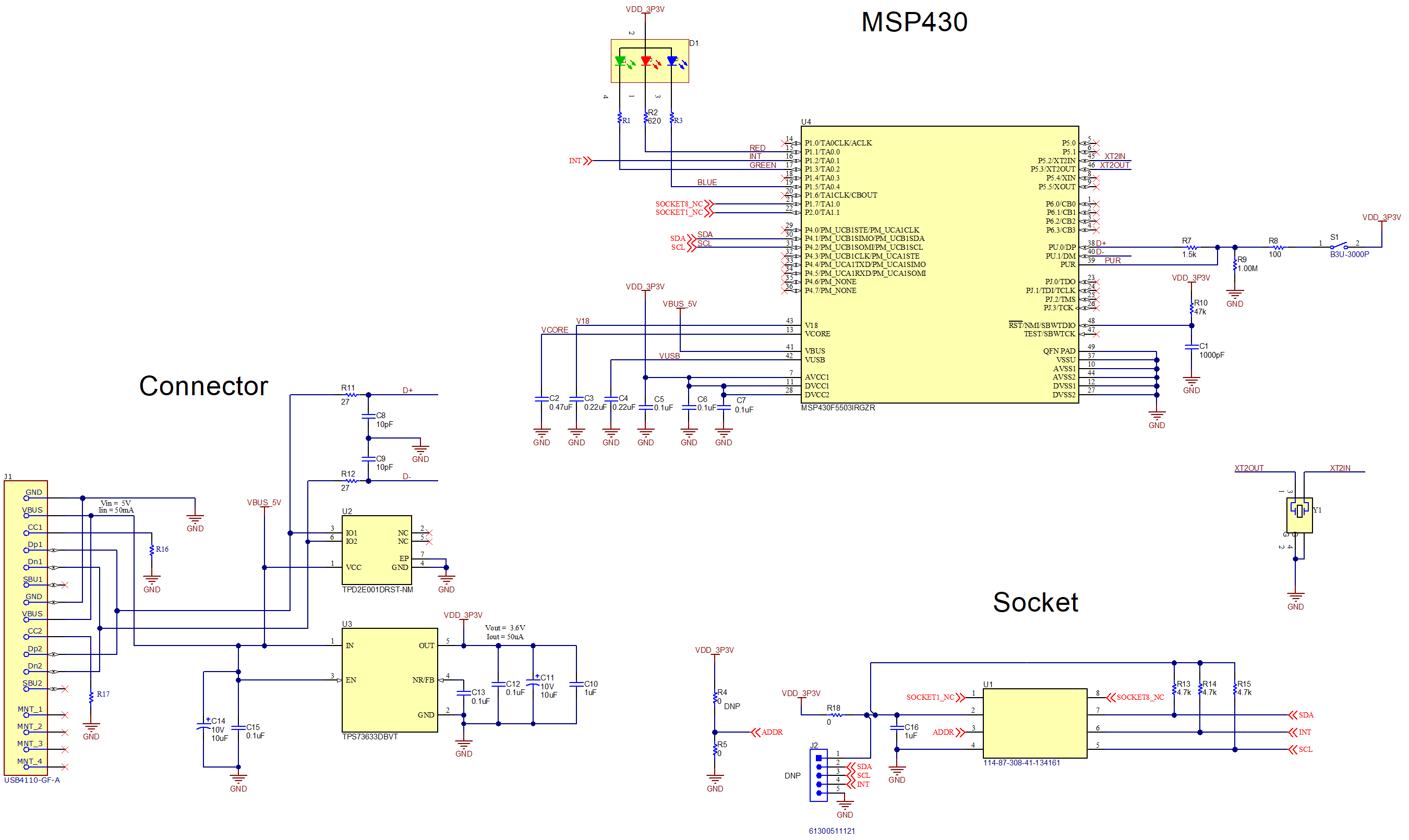 Figure 4-6 OPTMB EVM Board Schematic
Figure 4-6 OPTMB EVM Board Schematic