SCEA140 October 2023 CD4009UB , CD4009UB-MIL , CD40109B , CD40109B-MIL , CD40109B-Q1 , CD4010B , CD4010B-MIL , CD4010B-Q1 , CD4504B , CD4504B-MIL , TXH0137D-Q1
Introduction
High voltage level shifting are faced with challenges where high voltage peripherals must communicate with low voltage processors. A question that can be asked is: How high is high-voltage?
Texas Instruments has offered high voltage level shifters up to 18 V for several decades. However, the voltage trend is increasing as peripherals are starting to require translation less than 1.8 V and greater than 18 V. See Table 1 for high-voltage level shifter families.
| TXH Family | Existing CD4000 Family | |
|---|---|---|
| Drive strength | 100 mA | 36 mA |
| VCC and translation range | 1.5 V – 30 V | 3 V - 18 V |
| Inverted outputs | Yes | No |
| Maximum bit and Ch count | 7 | 6 |
| Output type | Open-drain | Push-pull |
| Q100 qualified | Yes | Yes |
| Packages | TSSOP-16 | TSSOP-16 |
System designers can leverage the TXH device family for typical 24-V PLC modules, motor drivers, LED and LCD, circuit breakers, ECG monitors, protection relays, fast charging stations, solar grids and high multivoltage applications as shown as subsystems in Figure 1.
 Figure 1 Simple Application Schematic
of TXH0137D-Q1
Figure 1 Simple Application Schematic
of TXH0137D-Q1Key applications for TXH includes open-drain applications or GND switches where high sinking current is required (up to 100-mA per channel), such as high voltage PLC modules. For such high voltage and current applications, the device also supports low power consumption of approximately 30 µA maximum for the power supply and 10 nA maximum for the I/O pins. For automotive end equipment, TXH is typically used where MCU and peripherals communicate with mismatched IO voltages up to 30 V. For industrial end equipment, TXH can be leveraged with high and low side switches, which enables communication up to 30 V.
See Figure 2 for additional use-cases in automotive and industrial applications.
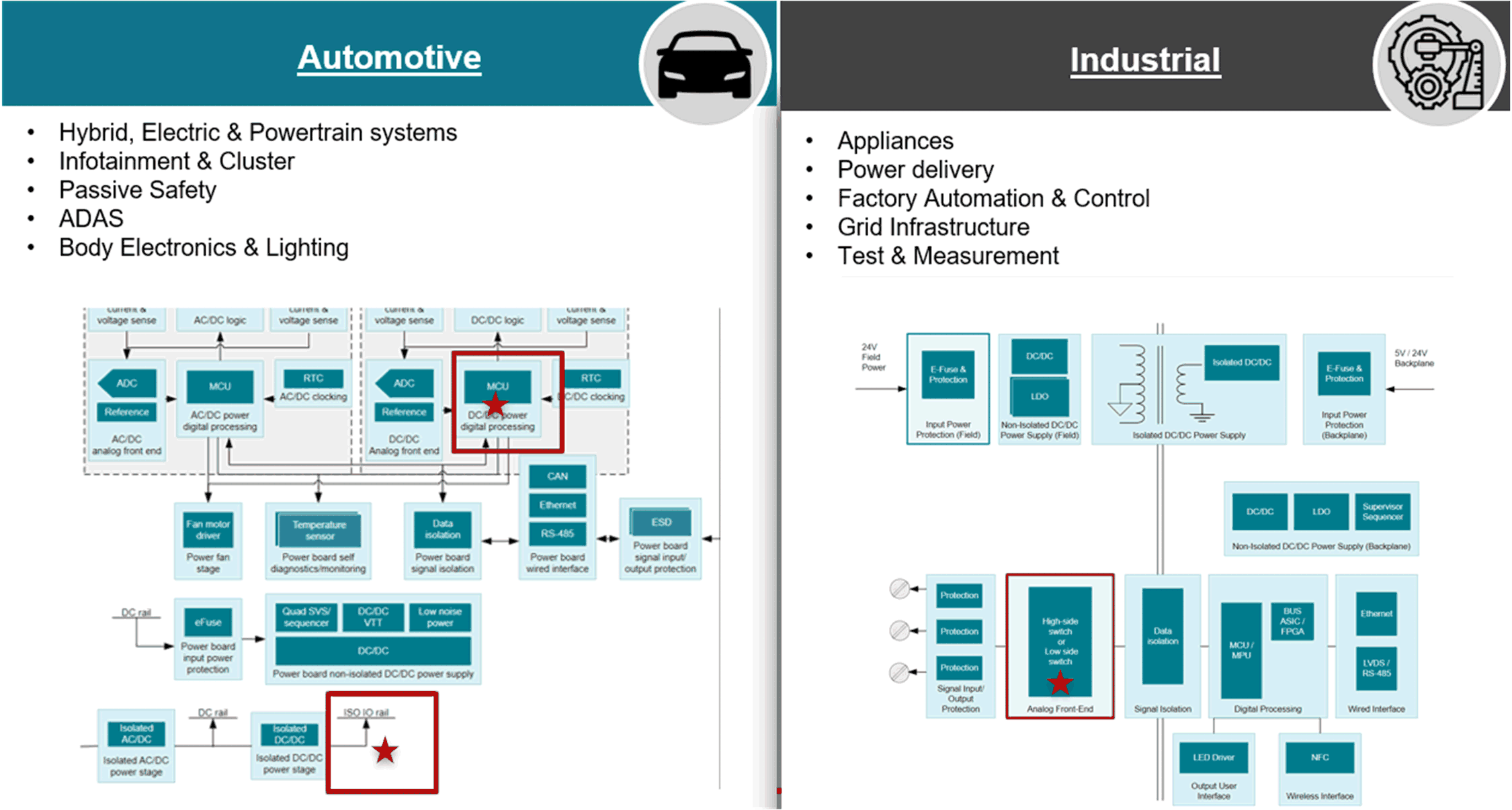 Figure 2 Examples of TXH End
Equipment
Figure 2 Examples of TXH End
EquipmentWith existing peripheral technologies developed for higher voltages and new microprocessor technologies being developed for lower voltages, the TXH0137D-Q1 for example, can be used in designs for a wide variety of voltage ranges as low as 1.5 V and as high as 30 V.
Figure 3 shows the internal structure of the TXH device equipped with 1-MΩ pull-downs, 50-kΩ series resistors, and overvoltage protection Zener diodes at the inputs, as well as internal diodes between the VCC supply pin and output pins.
 Figure 3 Internal Structure of
TXH0137D
Figure 3 Internal Structure of
TXH0137DTXH inputs
The weak pull-downs of 1-MΩ at the input pulls high-impedance drivers low, remaining in the OFF position and as a result, the input logic can be Hi-Z to make sure only one peripheral can translate data on the bus at a time. This is useful where more than one peripherals share the same bus.
In addition to the internal pull-downs, the inputs are equipped with 50-kΩ series resistors in parallel with the 5-pF input capacitance of the device (as stated in the data sheet), which prevents limits inrush current from voltage spikes or ringing due to noise coupling on the input pins. The circuitry behaves as an RC snubber, minimizing noise and further preventing false logic states. The overvoltage protection Zener clamp circuitry adds extra robustness in clamping voltages to help avoid overvoltage breakdown of the driver.
TXH outputs
With the device rated for high voltage outputs, the device can also be used in lower voltage applications as a form of high voltage tolerance for higher power supply modules to protect against high voltage spikes.
Such examples are observed with DC motors or solenoids with 12-V power supplies. The output voltage of the 12-V supply can rise to twice the normal voltage operation of approximately 24 V immediately after the 12-V supply is turned off. If the downstream devices cannot tolerate 24 V, the outcome can be detrimental to the system. With the TXH internal output diodes, the supply and the outputs are protected from voltage spikes that can fly back.
Summary
To conclude, TXH can be leveraged for high voltage applications up to 30 V requiring high sinking current capabilities, Hi-Z IO capabilities, high voltage fly back protection, low output leakage, and applications with slow inputs or with noisy environments, while protecting against overshoot in both high and low voltage level shifting applications.