SLOA011B January 2018 – July 2021 LF347 , LF353 , LM348 , MC1458 , TL022 , TL061 , TL062 , TL071 , TL072 , UA741
- 1Introduction
- 2Non-Inverting Amplifier
- 3Inverting Amplifier
- 4Simplified Op Amp Circuit Diagram
-
5Op Amp Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings and Recommended Operating Condition
- 5.2 Input Offset Voltage
- 5.3 Input Current
- 5.4 Input Common Mode Voltage Range
- 5.5 Differential Input Voltage Range
- 5.6 Maximum Output Voltage Swing
- 5.7 Large Signal Differential Voltage Amplification
- 5.8 Input Parasitic Elements
- 5.9 Output Impedance
- 5.10 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
- 5.11 Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
- 5.12 Supply Current
- 5.13 Slew Rate at Unity Gain
- 5.14 Equivalent Input Noise
- 5.15 Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise
- 5.16 Unity-Gain Bandwidth and Phase Margin
- 5.17 Settling Time
- 6References
- 7Glossary
- 8Revision History
5.9 Output Impedance
Different data sheets list the output impedance under two different conditions. Some data sheets list closed-loop output impedance while others list open loop output impedance, both designated by Zo.
Zo is defined as the small signal impedance between the output terminal and ground (see Amplifiers, Comparators, and Special Functions, pg. 1-40). Data sheet values run from 50Ω to 200Ω.
Common emitter (bipolar) and common source (CMOS) output stages used in rail-to-rail output op amps have higher output impedance than emitter follower output stages.
Output impedance is a design issue when using rail-to-rail output op amps to drive heavy loads. If the load is mainly resistive, the output impedance will limit how close to the rails the output can go. If the load is capacitive, the extra phase shift will erode phase margin. Figure 5-7 shows how output impedance affects the output signal assuming Zo is mostly resistive.
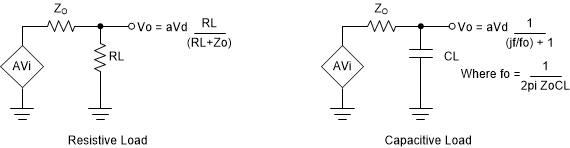 Figure 5-7 Effect Output Impedance
Figure 5-7 Effect Output Impedance