SLUAAR3 December 2023 BQ27426 , BQ27427 , BQ27Z561 , BQ27Z746 , BQ28Z610 , BQ34Z100 , BQ40Z50 , BQ40Z80
2 Voltage Correlation
Voltage correlation is a very basic method for gauging batteries. This algorithm takes the OCV (Open Circuit Voltage) of the battery and references this value to a look-up table of voltages, where each voltage corresponds to a different SOC (State of Charge).
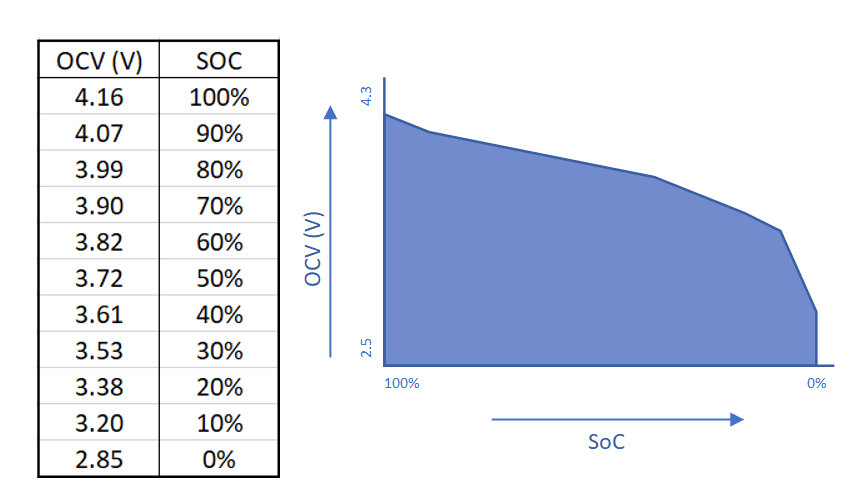 Figure 2-1 OCV Look-up Table and
Graph
Figure 2-1 OCV Look-up Table and
GraphFor example, Figure 2-1 shows what a voltage look-up table can look like for a lithium-ion battery. Using the voltage correlation method, if the OCV of the battery is 3.72 volts, then the gauge can predict that the SOC at that given time is 50%.
While voltage correlation is a very easy method to implement, the correlation does come with many drawbacks. Voltage correlation is only able to report the SOC, and is not be able to report other important data like SoH (State of Health), Remaining Capacity, and Remaining Run Time. Also, SOC is not adjusted for important factors like discharge rate, temperature, and the age of the battery.
Because of this factor, we recommend using voltage correlation for applications where the battery has long periods of rest where the OCV can be taken to accurately determine SOC and or the current is low enough where an OCV is still accurate.