SLUAAR3 December 2023 BQ27426 , BQ27427 , BQ27Z561 , BQ27Z746 , BQ28Z610 , BQ34Z100 , BQ40Z50 , BQ40Z80
7 Algorithm Comparisons
For this comparison, a robot vacuum cleaner was used to collect voltage and current data during normal operating use. The test environment involved the robot using a 4S2P battery to vacuum and mop at room temperature. Two tests were conducted, showcasing two different load profiles. For the first test, the robot vacuumed low pile carpet. Figure 7-1 shows the voltage and current profile for the test.
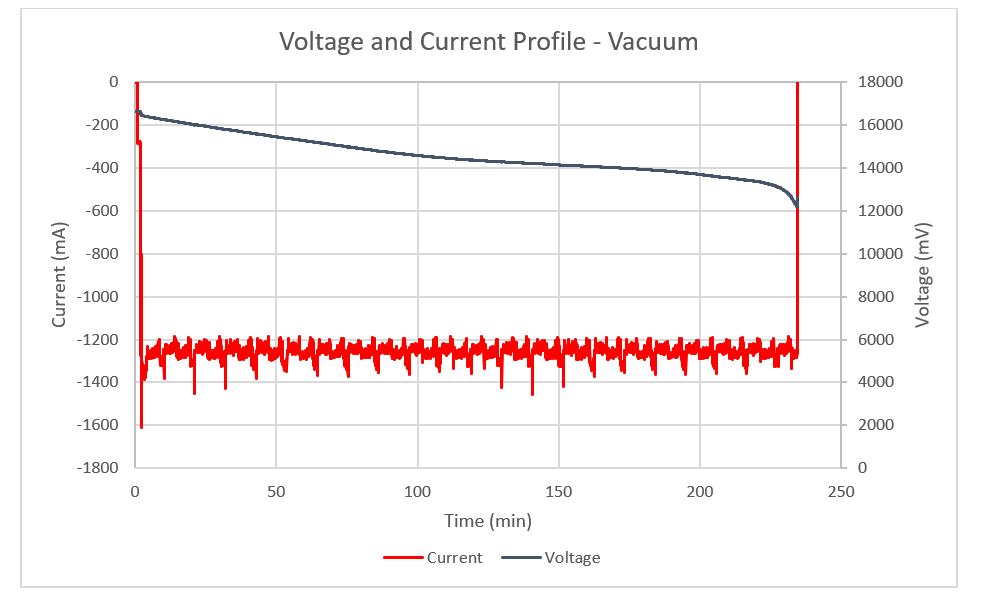 Figure 7-1 Voltage and Current Profile
for Test 1
Figure 7-1 Voltage and Current Profile
for Test 1During the second test, the robot mopped tile floors. The robot can return to the base to re-wet the mops and charge the battery for a short period. Figure 7-2 shows the voltage and current profile for this test.
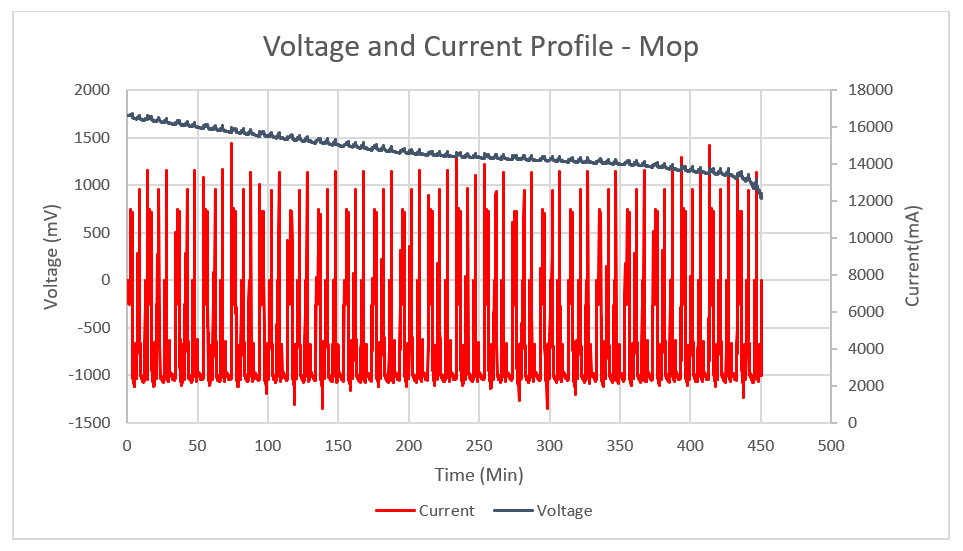 Figure 7-2 Voltage and Current Profile
for Test 2
Figure 7-2 Voltage and Current Profile
for Test 2