SLVAEB9A May 2019 – February 2022 TPS1663 , TPS24710 , TPS24711 , TPS24712 , TPS24713 , TPS2660 , TPS2663
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Powering Capacitive Loads with Constant Inrush Current and Output Slew Rate at Start-up
- 3Powering Capacitive Loads with Constant Power Dissipation in Power Switch at Start-up
- 4Powering Capacitive Loads with Thermal Regulation at Start up
- 5Conclusion
- 6References
- 7Revision History
3 Powering Capacitive Loads with Constant Power Dissipation in Power Switch at Start-up
Hot-swap controllers like the TPS2471x can provide the charging of output capacitors with constant power dissipation in power switch. As illustrated in Figure 3-1, resistor RPROG sets the power dissipation limit for power switch M1 and capacitor CT sets the maximum time for power limiting and overcurrent faults.
 Figure 3-1 TPS2471x
Application Circuit for Start up with Constant Power
Dissipation in Power Switch
Figure 3-1 TPS2471x
Application Circuit for Start up with Constant Power
Dissipation in Power SwitchFigure 3-2 shows start-up with capacitance of 1 mF and VIN of 12 V. The inrush current is at its lowest value initially but increases as the drop across the power switch reduces with charging of output capacitor. These devices can provide clean start-up with higher output capacitance and higher input voltage but these devices require external MOSFET to handle the power dissipation during start-up. External MOSFET needs more area on the board and leads to increased solution size.
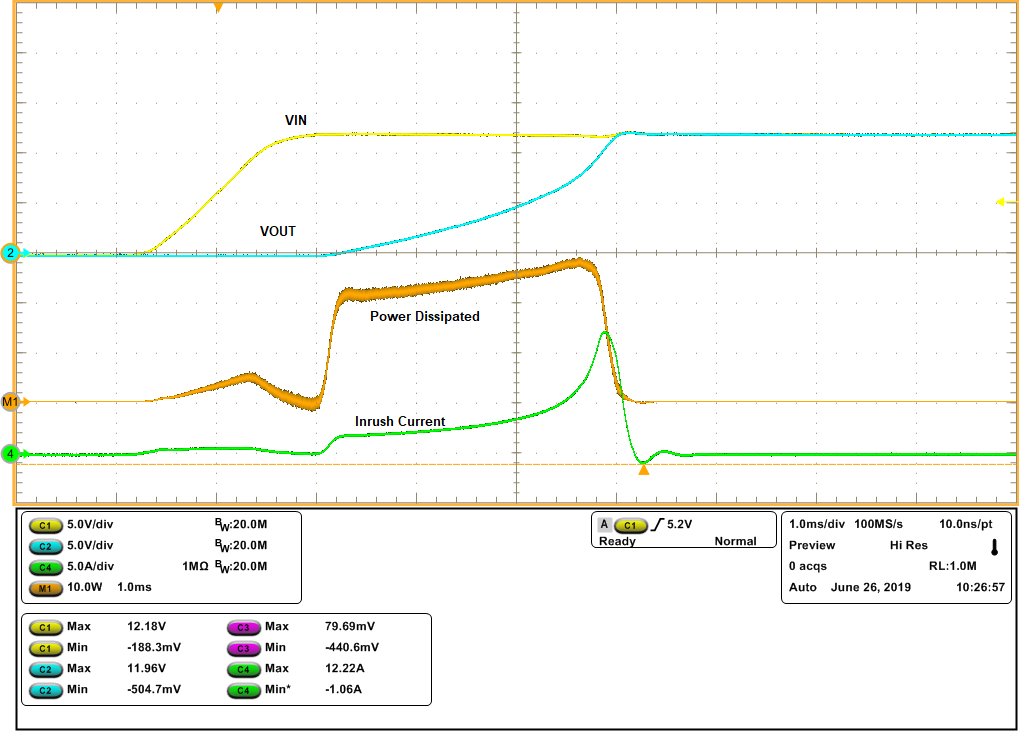 Figure 3-2 Clean Start-up
with Constant Power Dissipation in Power Switch
Figure 3-2 Clean Start-up
with Constant Power Dissipation in Power SwitchWith increased input voltage and load capacitance, the power dissipation in the power switch can go beyond SOA limits of the power switch and can lead to hiccups in start-up. Figure 3-3 shows the hiccup in start-up with the TPS24710 device for VIN of 15 V and COUT of 2.2 mF. The device tries to charge load capacitance up to a time of 8 ms and output reaches up to 7.5 V.
See TPS24710 Design Calculator to design with the TPS24710 device.
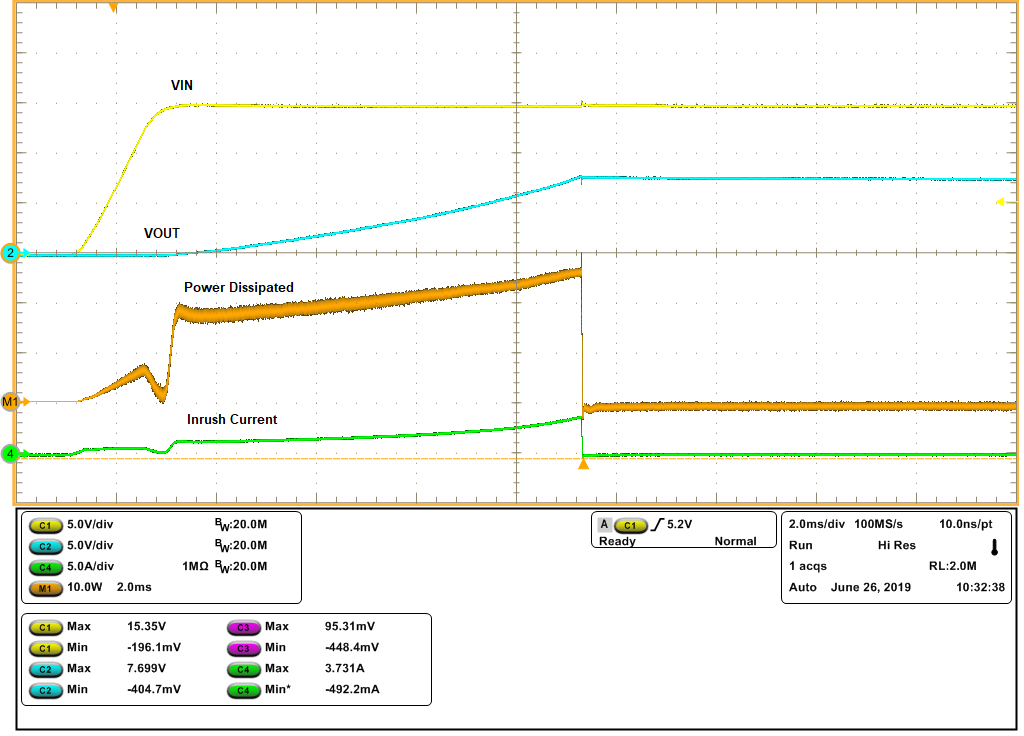 Figure 3-3 Hiccup in
Start-up with Constant Power Dissipation in Power
Switch
Figure 3-3 Hiccup in
Start-up with Constant Power Dissipation in Power
Switch