SNLA388 June 2021 DS160PR410
2 Signal Conditioners
High speed data and video links in industrial application must be reliable and robust for efficient operation with seamless and consistent data throughput. The links often suffer from too much loss, low margin, susceptibility to environmental condition such as supply voltage and temperature variation, internal and external noise. High speed signal conditioners when used in a data or video link improve overall signal integrity by eliminating loss and jitter.
A signal conditioning element such as a redriver or retimer in a high speed industrial link provides equalization to eliminate inter symbol interference (ISI) effectively, increasing overall link reach and SI margin. Additionally a retimer component has clock and data recovery circuits (CDR) that can eliminate SI impairments such as random jitter, cross-talk and reflection. For addional differences between a redriver and retimer see TI Precision lab video. Figure 2-1 shows what redrivers, retimers and active muxs can provide in a link.
| Redriver | Retimer | Active Mux |
|---|---|---|
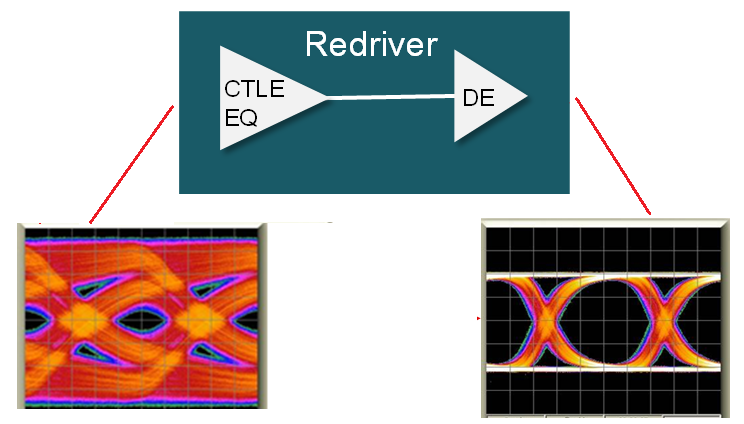 |
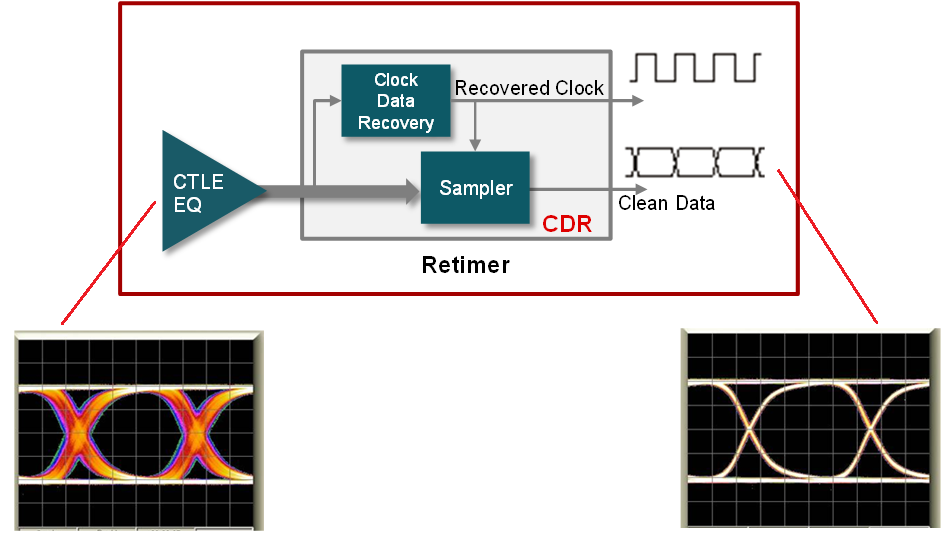 |
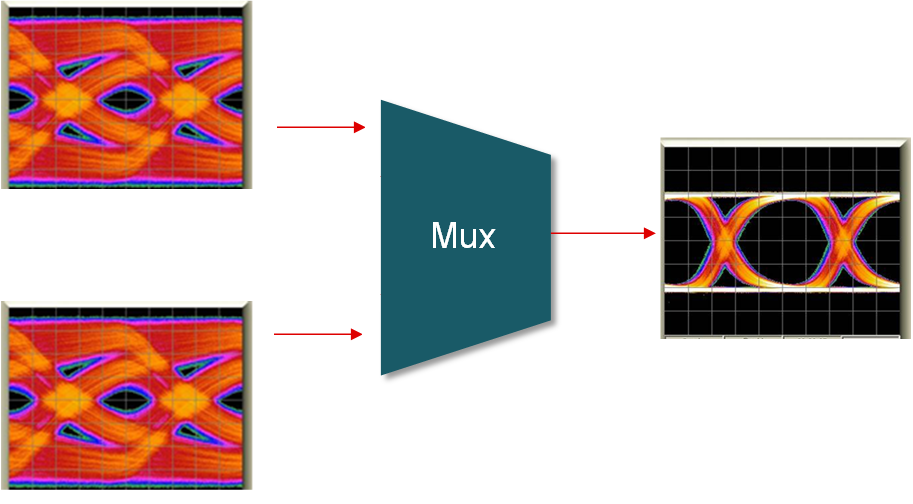 |
|
|
|
Industrial PCs likely use the most diverse set of high speed interface links in industrial applications. These systems can be considered as the brain of industrial automation. They process and analyze vast amount of data to implement critical functions, interface with human operators, and display the results in to industrial monitors. Mutliple CPUs are often connected together to form a powerful compute cluster in an industrial PC. Multiple systems are also connected together over a back plane or network to implement a complex function. Figure 2-2 shows the most commonly used interfaces inside a industrial PC system. In this article, industrial PC system is used an example to discuss different high speed interfaces. However this can be extended into other relevant industrial applications also.
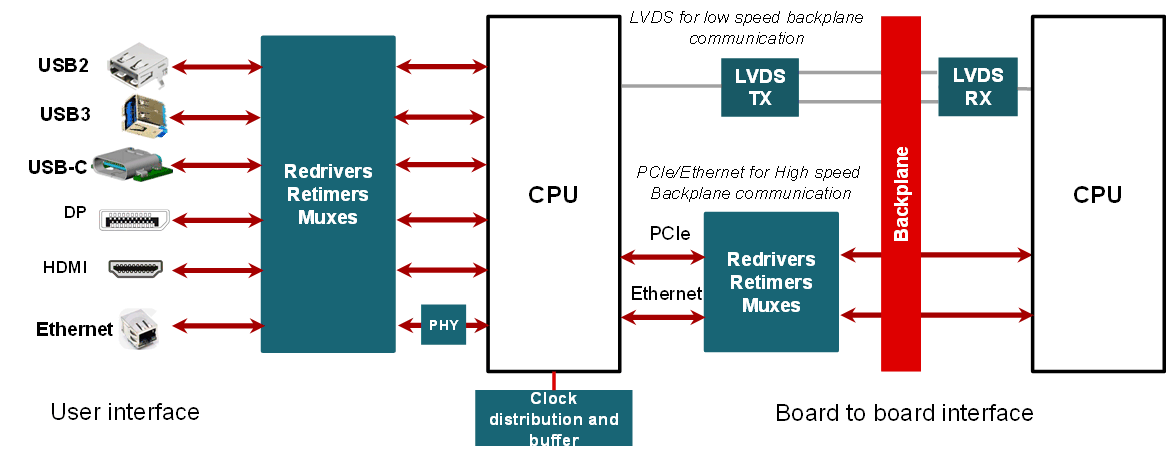 Figure 2-2 High speed interfaces inside an
industrial PC system
Figure 2-2 High speed interfaces inside an
industrial PC systemUser interfaces include USB, Display Port, HDMI and Ethernet which are external interfaces that provide access for operators and allow connectivity to additional functional end equipment such as display monitors, Ethernet networks, USB disks etc. Board to board interfaces illustrate system connectivity between different boards through a back plane. LVDS are typically used for lower speed data, while PCIe and Ethernet are used for high bandwidth data connections in back plane application.
A user interface port typically needs to meet industry compliance so that it can inter-operate and communicate with any device connecting to it. Compliance tests require a signal to meet certain eye-opening margin and jitter performance criteria which can be challenging since signal degradation can occur for high speed data after traversing along PCB traces and connectors. The same signal integrity challenge can also be imposed for signals traveling through a back plane for board to board communications. Long PCB traces and connectors can degrade signal quality causing compliance issues, downgrade of data throughput and even resulting in communication failure. By adding signal conditioners, such as redrivers, retimers and active muxes, in a CPU system, the designer can ensure compliance at the connectors per standard specifications, while also improving the signal quality at the receiver side to enable a more robust communication system.
Now let’s look at more detailed examples on how to use signal conditioners to solve signal impairment problems for USB, PCIe, Display Port, HDMI, and Ethernet interfaces.