SLLSEQ7F December 2015 – May 2025 TCAN330 , TCAN330G , TCAN332 , TCAN332G , TCAN334 , TCAN334G , TCAN337 , TCAN337G
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- Device Options
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
- Parameter Measurement Information
- 6Detailed Description
- 7Application Information Disclaimer
- Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Termination is typically a 120Ω resistor at each end of the bus. If filtering and stabilization of the common mode voltage of the bus is desired, then split termination may be used. Split termination uses two 60Ω resistors with a capacitor in the middle of these resistors to ground. Split termination improves the electromagnetic emissions behavior of the network by eliminating fluctuations in the bus common mode voltages at the start and end of message transmissions.
Care should be taken in the power ratings of the termination resistors used. Typically the worst case condition would be if the system power supply was shorted across the termination resistance to ground. In most cases, the current flow through the resistor in this condition is much higher than the transceiver current limit.
 Figure 7-2 Typical CAN Bus
Figure 7-2 Typical CAN Bus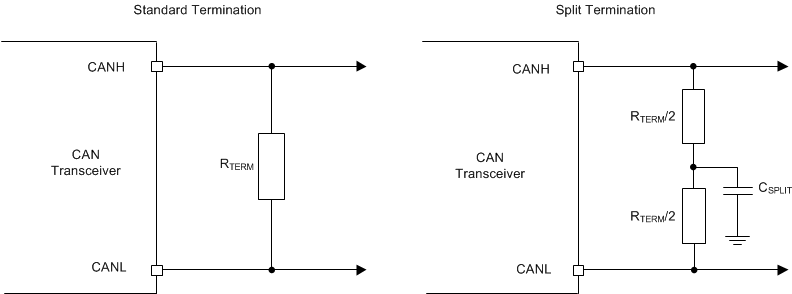 Figure 7-3 CAN Bus Termination Concepts
Figure 7-3 CAN Bus Termination Concepts