SLUA748A December 2015 – April 2016 BQ25120 , BQ51003 , TPS61046 , TPS61240 , TPS62743
- Trademarks
- Power Management Reference Design for a Wearable Device with Wireless Charging Using the bq51003 and bq25120
- AExperimental Results
- Revision History
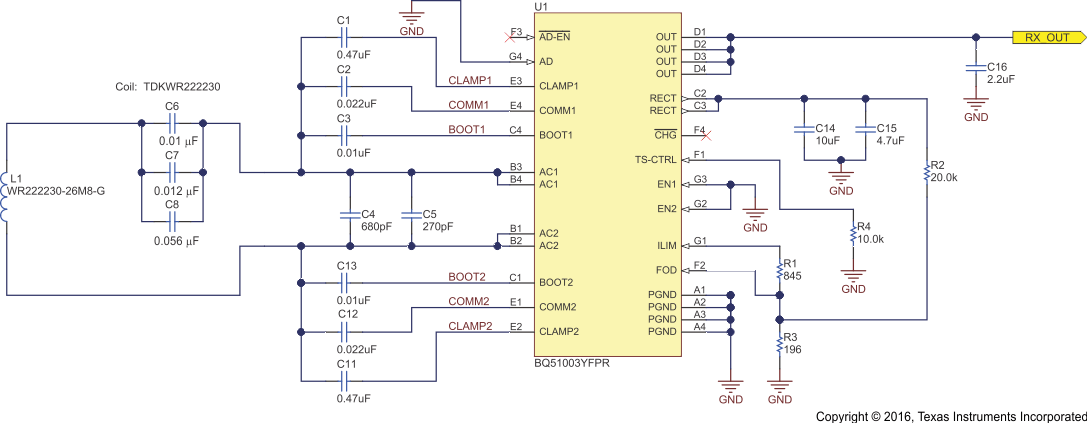
1.1 Wireless Charging Input
A large number of low-power wearable devices such as smart watches, fitness wrist bands and headphones are adopting wireless charging. The BQ51003 is an advanced, integrated receiver tailored for wearable applications. A standard Qi-compliant design will deliver 5W with a 50-mm coil. Figure 3 is modified from a Qi-compliant design with a smaller 30-mm coil and adjustable 500 mW to 1500 mW capabilities. When used with a Qi-compliant wireless transmitter, the RX_OUT supplies the input to a Li-Ion charger, in this case the bq25120. This better matches the wearable form factor and battery requirements, and is optimized for the device to stay cooler during power transfer.