SLVS974F September 2009 – May 2020 TPS54218
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation and Output Current
- 7.3.3 Bootstrap Voltage (Boot) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Soft-Start Pin
- 7.3.9 Sequencing
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.12 Frequency Shift
- 7.3.13 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.14 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.15 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.16 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Step One: Select the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Step Two: Select the Output Inductor
- 8.2.2.3 Step Three: Choose the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Step Four: Select the Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Step Five: Minimum Load DC COMP Voltage
- 8.2.2.6 Step Six: Choose the Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Step Seven: Select the Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Step Eight: Undervoltage Lockout Threshold
- 8.2.2.9 Step Nine: Select Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors
- 8.2.2.10 Step 10: Select Loop Compensation Components
- 8.2.2.11 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.8 Soft-Start Pin
The TPS54218 device regulates to the lower of the SS pin and the internal reference voltage. A capacitor on the SS pin to ground implements a soft-start time. The TPS54218 device has an internal pullup current source of 2.07 μA that charges the external soft-start capacitor. Equation 4 calculates the required soft-start capacitor value where tSS is the desired soft-start time in ms, ISS is the internal soft-start charging current of 2.07 μA, and 0.9 V is the SS pin voltage at the SS to reference crossover point. Equation 4 represents a first order linear approximation of the SS time using the well-known relationship I = C × dV / dt. A constant current charging a capacitor results in a fixed value for dV / dt and a linear charge from 0 V to the 0.9 V SS to reference crossover voltage. In use, there are two factors that cause the actual output voltage to deviate from this linear ideal ramp. At the initial start, the COMP pin voltage can be below the minimum skip voltage. The TPS54218 does not begin to switch and the output voltage does not start to rise until the RC compensation network from COMP to GND has charged above the skip threshold. At the end of the SS time, when the output has reached 90% of its final regulated value, a “soft handoff” occurs to transition from the SS pin voltage to the internal reference at the non-inverting terminal of the error amplifier. When the SS pin voltage is at 0.9 V, the output voltage is defined to be within 98% typical of the final regulated voltage.
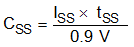
where
- CSS is in nF
- tSS is in ms
- ISS is in µA
It is recommended to maintain the soft-start time in the range between 1 msec and 10 msec.
There are two conditions that can cause the SS pin to be intentionally discharged. If a fault condition occurs that results in the COMP pin voltage reaching its maximum voltage as during an overcurrent condition, the comp pin is discharged to below 20 mV. Only the discharge voltage is specified, not the discharge current. This allows the TPS54218 to gracefully recover from an overcurrent condition that can reduce the output voltage. If during normal operation, the input voltage goes below the UVLO, the EN pin is pulled below 1.2 V, or a thermal shutdown event occurs, the TPS54218 stops switching and the SS capacitor is discharged before reinitiating a powering up sequence. See Figure 46 for an example of this discharge behavior.