SLVU957A September 2019 – November 2021
- Trademarks
- 1Features
- 2BQ76922EVM Quick Start Guide
- 3Interface Adapter
- 4Battery Management Studio Software
- 5BQ76922EVM Circuit Module Use
- 6BQ76922EVM Circuit Module Physical Construction
- 7Related Documents from Texas Instruments
- 8Revision History
4.6.1 Entering, Saving, and Loading Configuration
Most of the configuration of the BQ76922 is accomplished through setting values in data memory. The data memory locations are accessed using the buttons in the Data Memory view. The Parameter View selection at the top of the pane allows the choice of basic parameters which shows commonly used parameters, or all parameters which shows more configuration parameters. Data values may be changed by selecting and entering a value. Parameter registers which are bit fields may be changed by selecting the bit in the pop up when the register or its value is selected. Data Memory must be written after bit changes, a button is provided under the bit field. Figure 4-6 shows the bit field for the Enabled Protections A which is one of the most basic settings that must typically be changed with the EVM.
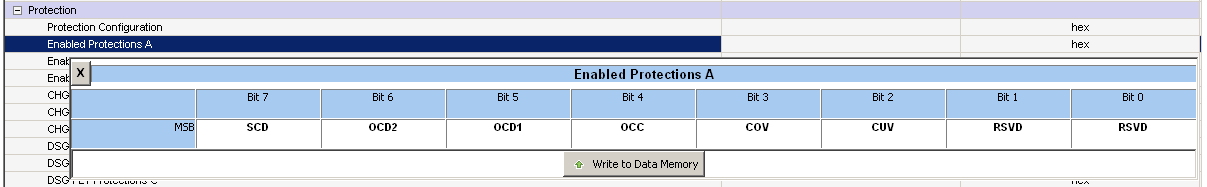 Figure 4-6 Data Memory Bit Field
Change
Figure 4-6 Data Memory Bit Field
ChangeChanges to configuration by memory changes take place immediately, however the FETs are enabled using the Enable_FETs command. Enabling a protection and enabling the protection action on a FET are not sufficient, the FETs must be enabled with the command. BQStudio will enter and exit configuration update mode of the part automatically when data memory is edited. If FETs were on when config update mode was entered they will be turned off during the write and turned on after exit. Exiting config will clear some command settings such as SLEEP_DISABLE, check settings after configuration changes.
Calibration data is also located in data memory. Calibration values may be loaded manually or calculated by a tool.
The data is read from the part when the Data Memory view is opened, but the window does not know when the power may have been cycled so that the data is not current. Data may be read using the Read All tool at the top of the pane. The Export tool in the Data Memory view allows saving the configuration data to a comma-separated-value file format which can be accessed by a spreadsheet program. Reading data before export with the Read All button loads the data from the part rather than values which may be only in the view. Export also has an option to export a Flash Stream format file which can be written to another part by the Command Sequence tool. The FS file can be saved with OTP programming command included. The Import tool allows loading a saved file into the view so that it can be written to the device. The Write All tool writes all values in the view into registers in the device. The gg.csv files should not be edited with a spreadsheet program since those may add characters causing the import to fail.