SLVUC46D March 2021 – November 2023
2.4 Headers and Connectors (Hardware Device Variant)
Figure 2-8 shows all configuration jumpers for the DRV824xH-Q1 hardware variant. DRV814xH-Q1 features the same jumpers, with the exception of MODE. Each LVL silkscreen label directly corresponds to the data sheet description. Changing the jumper within MODE allows the user to use the driver in PH/EN, PWM, and Independent Half-Bridge mode. Please refer to the device data sheet for more information regarding pin LVL settings and associated configuration.
Note: IPROPI is common to both hardware
and SPI EVM/ device variants and performs the same function.
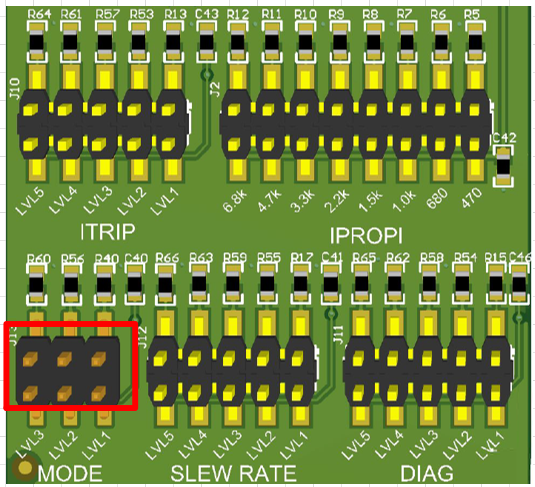 Figure 2-8 DRV824x and DRV814x Hardware
Variant Configuration Jumpers
Figure 2-8 DRV824x and DRV814x Hardware
Variant Configuration Jumpers