SNOA943 January 2016 FDC2112 , FDC2112-Q1 , FDC2114 , FDC2114-Q1 , FDC2212 , FDC2212-Q1 , FDC2214 , FDC2214-Q1
- Power Reduction Techniques for the FDC2214/2212/2114/2112 in Capacitive Sensing Applications
3 Test Setup
Duty-cycling the FDC2x1x was tested on the Noise-immune Capacitive Proximity Sensor System Reference Design (TIDA-00466) with only one channel (Channel 0, proximity sensor) enabled. The current flowing through the FDC2214 was measured using a digital multi-meter. The test setup is shown in Figure 4 and the testing conditions are given in Figure 4.
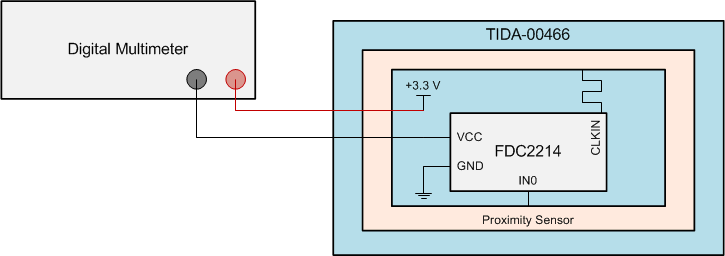 Figure 4. Test Setup
Figure 4. Test Setup Table 1. Testing Conditions
| CHANNEL 0 | |
|---|---|
| Reference Frequency (MHz) | 40 |
| Sensor Frequency (MHz) | 5.3 |
| Amplitude (V_PP) | 1.22 |
| SETTLECOUNT | 30 |
| Current Drive Setting (mA) | 0.069 |
The reference frequency was set by an external crystal oscillator and the current drive was set to achieve the recommended voltage amplitude for the oscillation waveform, which is between 1.2 and 1.8 VPP.