SPRUJ66A February 2023 – December 2023
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1EVM Revisions and Assembly Variants
- 2Inside the Box
- 3EMC, EMI, and ESD Compliance
-
4System Description
- 4.1 Key Features
- 4.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 4.3 AM62A Low Power SK EVM Interface Mapping
- 4.4 Power ON/OFF Procedures
- 4.5
Peripheral and Major Component Description
- 4.5.1 Clocking
- 4.5.2 Reset
- 4.5.3 CSI Interface
- 4.5.4 Audio Codec Interface
- 4.5.5 HDMI Display Interface
- 4.5.6 JTAG Interface
- 4.5.7 Test Automation Header
- 4.5.8 UART Interface
- 4.5.9 USB Interface
- 4.5.10 Memory Interfaces
- 4.5.11 Ethernet Interface
- 4.5.12 GPIO Port Expander
- 4.5.13 GPIO Mapping
- 4.5.14 Power
- 4.5.15 AM62A Low Power SK EVM User Setup and Configuration
- 4.5.16 Expansion Headers
- 4.5.17 I2C Address Mapping
- 5Revision History
4.5.8 UART Interface
The four UART ports of the SOC (MCU UART0, WKUP UART0, SOC UART0 and SOC UART1) are interfaced with an FTDI Bridge FT4232HL for UART-to-USB functionality and then terminated on a USB micro-B connector (J17) on board. When the AM62A Low Power SK EVM is connected to a Host using USB cable, the computer can establish a Virtual COM Port which can be used with any terminal emulation application. The FT4232HL device is bus powered.
Since the circuit is powered through the USB BUS, the connection to the COM port will not be lost when the SKEVM power is removed.
| UART Port | USB to UART Bridge | USB Connector | COM Port |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOC_UART0 | FT4232HL | J17 | COM1 |
| SOC_UART1 | COM2 | ||
| WKUP_UART0 | COM3 | ||
| MCU_UART0 | COM4 |
The FT4232 chip is configured to operate in ‘Single chip USB to four channel UART’ mode using the configuration file from an external SPI EEPROM connected to it. The EEPROM (93LC46B) supports 1 Mbit/s clockrate. The EEPROM is programmable in-circuit over USB using a utility program called FT_PROG available from FTDI's web site. The FT_PROG is also used for programming the board serial number for users to identify the connected COM port with board serial number when one or more boards are connected to the computer.
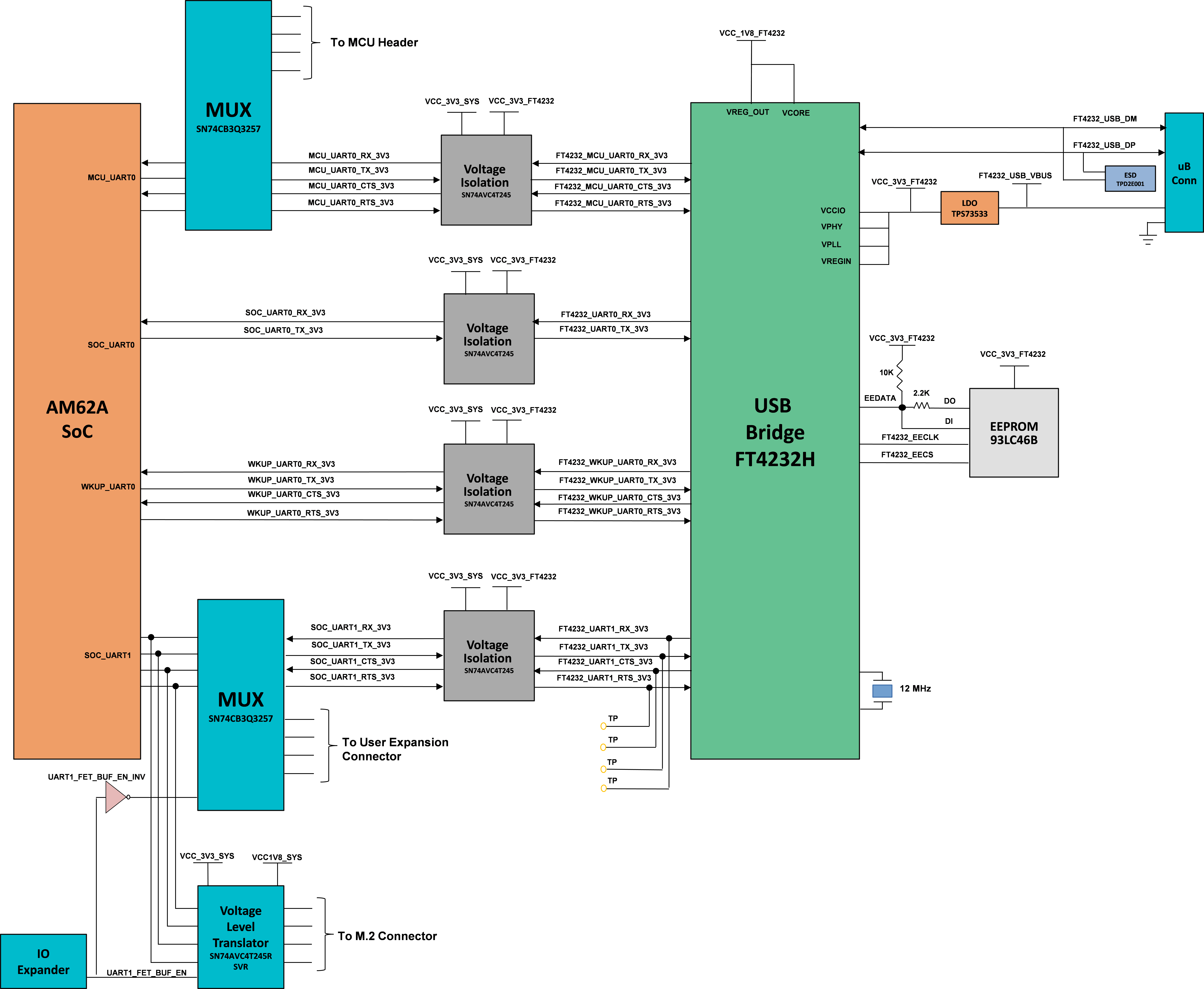 Figure 4-17 UART Interface block diagram
Figure 4-17 UART Interface block diagram