TIDUC99 August 2022 TPSM82903
3.3.6 Thermal Performance
Thermal performances measured at 2.5-A and 2-A loads. The TPSM82903 is designed for maximum junction temperature of 125°C. These images were captured under room temperature, which is approximately 27°C. The measurements were taken with no air flow present and the thermal camera placed horizontally at a distance of 5-inches from the camera. The peak temperature typically occurs at the center of the board where the inductor and the converter are located.
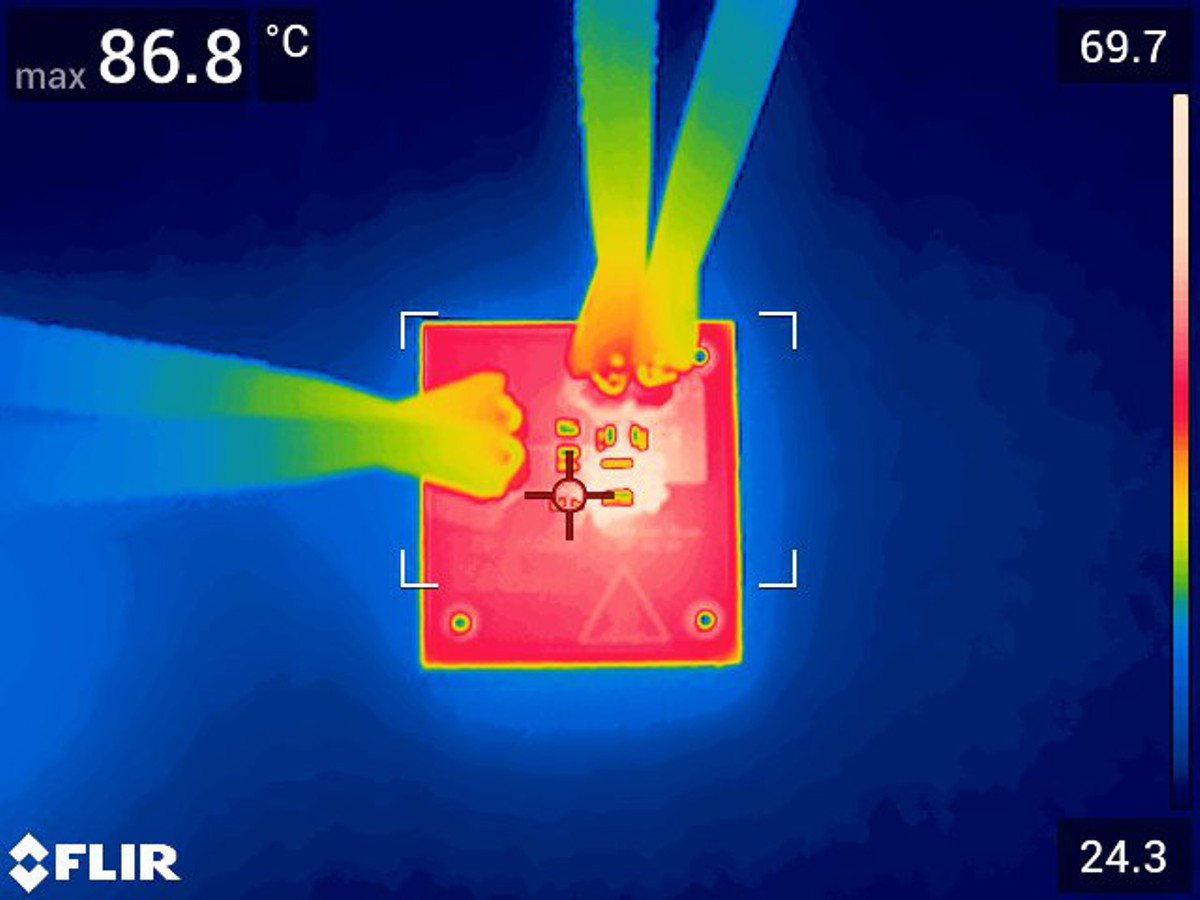 Figure 3-10 Thermal Image at Room
Temperature with 12-Vin, 1.2-Vo, 2.5-A
Figure 3-10 Thermal Image at Room
Temperature with 12-Vin, 1.2-Vo, 2.5-A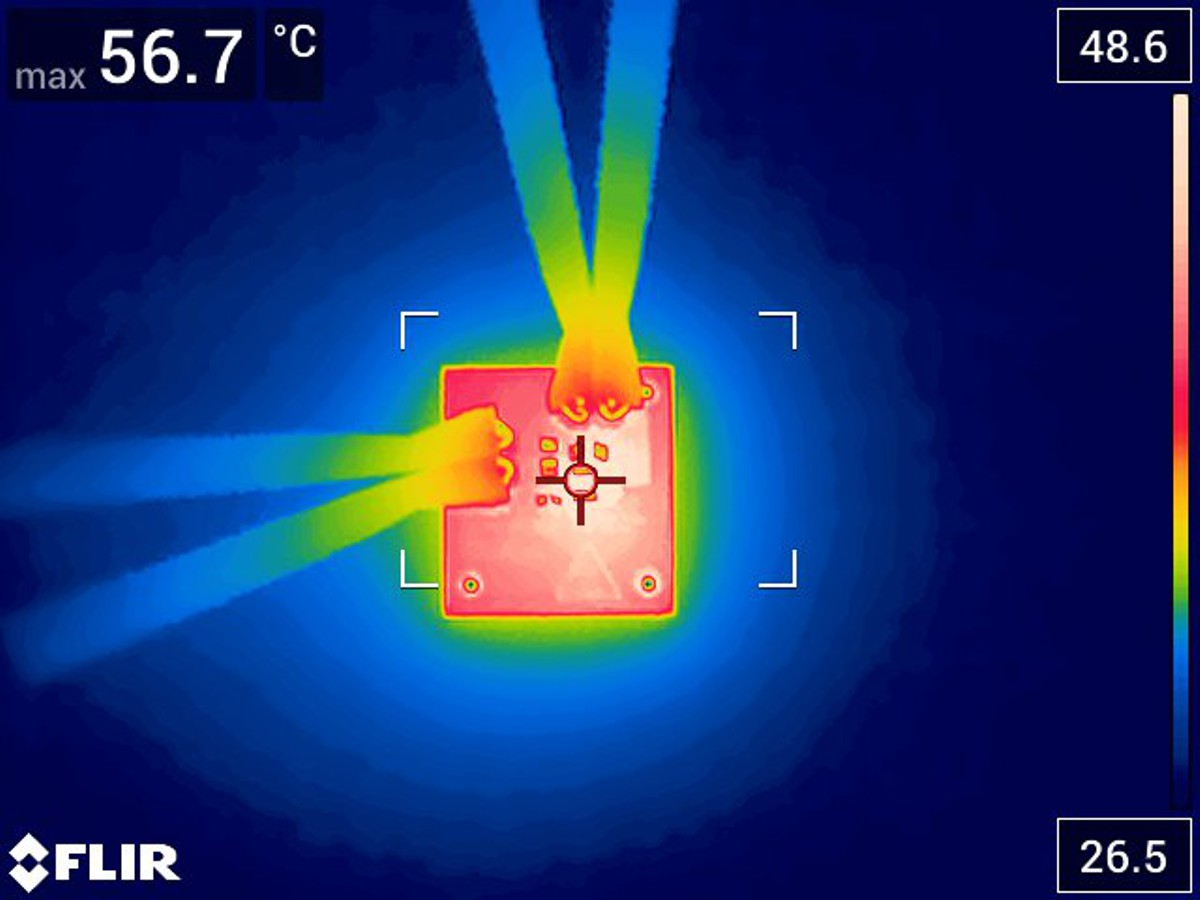 Figure 3-11 Thermal Image at Room
Temperature with 12-Vin, 1.2-Vo, 2-A
Figure 3-11 Thermal Image at Room
Temperature with 12-Vin, 1.2-Vo, 2-A