SLAAE67 December 2022 MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1518 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3518 , MSPM0G3518-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0G3519-Q1 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346
Abstract
One of the main features of the MSPM0 platform is its scalability. Every device with the MSPM0 prefix that has the same package and pin-count is pin-to-pin compatible for drop-in replacements. This provides a high level of flexibility, as when you begin designing with a particular MCU, you can always swap it out if your MCU requirements change further on in the design phase without having to make any changes to the board. Additionally, if the next generation of your product requires more features in the MCU, you can upgrade it and just drop it on to your new board.
Now, this scalability presents a considerable amount of options. How do you pick the right one for your application? Let’s start with some basic MCU features. The main difference between MSPM0L and MSPM0G is the CPU speed:
- M0L devices have a max frequency of 32 MHz
- M0G devices have a max frequency of 80 MHz
If your application requires the MCU to be faster than 32 MHz, then an M0G device is where you want to start. The following figure and table provide a quick comparison of some of the different offerings.
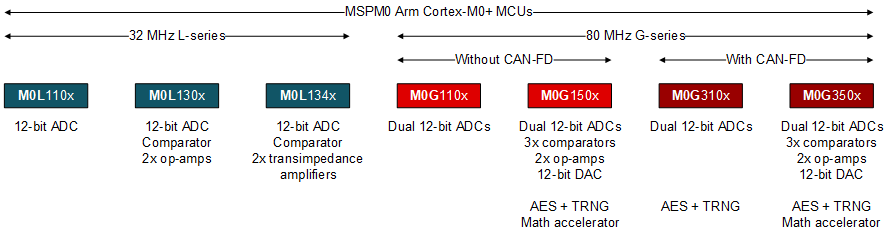 Figure 1-1 MSPM0 Microcontrollers
Figure 1-1 MSPM0 Microcontrollers| Device | CPU Speed [MHz] | Flash [KB] | SRAM [KB] | Analog Level | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSPM0L110x | 32 | 32, 64 | 4 | Low | |
| MSPM0L130x(1) | 32 | 8, 16, 32, 64 | 2, 4 | Low | Zero-drift op-amps |
| MSPM0L134x | 32 | 8, 16, 32, 64 | 2, 4 | Medium | Dual transimpedance amplifiers, zero-drift op-amps |
| MSPM0G110x | 80 | 32, 64, 128 | 16, 32 | Low | |
| MSPM0G150x | 80 | 32, 64, 128 | 16, 32 | High | Zero-drift op-amps |
| MSPM0G310x(1) | 80 | 32, 64, 128 | 16, 32 | Low | CAN-FD, zero-drift op-amps |
| MSPM0G350x(1) | 80 | 32, 64, 128 | 16, 32 | High | CAN-FD, zero-drift op-amps |