SNVS346G November 2007 – November 2023 LM3481
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1
Boost Converter
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 7.2.1.2.2 Power Inductor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.3 Programming the Output Voltage and Output Current
- 7.2.1.2.4 Current Limit With Additional Slope Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.5 Power Diode Selection
- 7.2.1.2.6 Power MOSFET Selection
- 7.2.1.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.8 Output Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.9 Driver Supply Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.10 Compensation
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 7.2.2 Typical SEPIC Converter
- 7.2.1
Boost Converter
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.3.4 Frequency Adjust, Synchronization, and Shutdown
The switching frequency of the LM3481 can be adjusted between 100 kHz and 1 MHz using a single external resistor. This resistor must be connected between the FA/SYNC/SD pin and ground, as shown in Figure 6-8. Refer to the Section 5.6 to determine the value of the resistor required for a desired switching frequency.
Equation 16 can also be used to estimate the frequency adjust resistor.
Where fS is in kHz and RFA in kΩ.
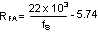
The LM3481 can be synchronized to an external clock. The external clock must be connected between the FA/SYNC/SD pin and ground, as shown in Figure 6-9. The frequency adjust resistor may remain connected while synchronizing a signal, therefore if there is a loss of signal, the switching frequency will be set by the frequency adjust resistor.
It is recommended to have the width of the synchronization pulse wider than the duty cycle of the converter and to have the synchronization pulse width ≥ 300 ns.
The FA/SYNC/SD pin also functions as a shutdown pin. If a high signal (refer to the Electrical CharacteristicsElectrical CharacteristicsElectrical Characteristics section for definition of high signal) appears on the FA/SYNC/SD pin, the LM3481 stops switching and goes into a low current mode. The total supply current of the device reduces to 5 µA, typically, under these conditions.
Figure 6-10 and Figure 6-11 show an implementation of a shutdown function when operating in frequency adjust mode and synchronization mode, respectively. In frequency adjust mode, connecting the FA/SYNC/SD pin to ground forces the clock to run at a certain frequency. Pulling this pin high shuts down the IC. In frequency adjust or synchronization mode, a high signal for more than 30 µs shuts down the device.
 Figure 6-8 Frequency Adjust
Figure 6-8 Frequency Adjust Figure 6-9 Frequency Synchronization
Figure 6-9 Frequency Synchronization Figure 6-10 Shutdown Operation in Frequency Adjust Mode
Figure 6-10 Shutdown Operation in Frequency Adjust Mode Figure 6-11 Shutdown Operation in Synchronization Mode
Figure 6-11 Shutdown Operation in Synchronization Mode