SLTS278J November 2010 – March 2020 PTH08T250W
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1.1.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 9.1.1.2
Capacitor Recommendations for the PTH08T250W Power Module
- 9.1.1.2.1 Capacitor Technologies
- 9.1.1.2.2 Input Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.4 Output Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.6 TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.7 Non-TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.8 Designing for Fast Load Transients
- 9.1.1.2.9 Capacitor Table
- 9.1.1.3 TurboTrans™ Technology
- 9.1.1.4 TurboTrans™ Selection
- 9.1.1.5 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.1.1.6 On/Off Inhibit
- 9.1.1.7 Current Sharing
- 9.1.1.8 Prebias Startup Capability
- 9.1.1.9 SmartSync Technology
- 9.1.1.10 Auto-Track™ Function
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- BCU|22
- ECT|22
- ECU|22
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.1.7 Current Sharing
The PTH08T250W module is capable of being configured in parallel with another PTH08T250W module to share load current. To parallel the two modules, it is necessary to configure one module as the Master and one module as the Slave. To configure a module as the Master, connect the CONFIG pin (pin 1) to GND. The CONFIG pin of the Slave must be connected to VI. In order to share current, pins 2 thru 5 of both the Master and Slave must be connected between the two modules. See Figure 27 for the recommended layout of pins 2 thru 5. The module that is configured as the MASTER is used to control all of the functions of the two modules including Inhibit ON/OFF control, AutoTrack sequencing, TurboTrans, SmartSync, +/- Remote Sense, and Output Voltage Adjust. See the current sharing diagram in Figure 22 for connections. The MASTER and the SLAVE must be powered from the same input voltage supply.
See Figure 22 and Table 8 for a diagram and connection description of each pin when two PTH08T250W modules are being used in a MASTER/SLAVE configuration.
Refer to the application article SLYT320 for more information regarding current sharing PTH08T250W modules.
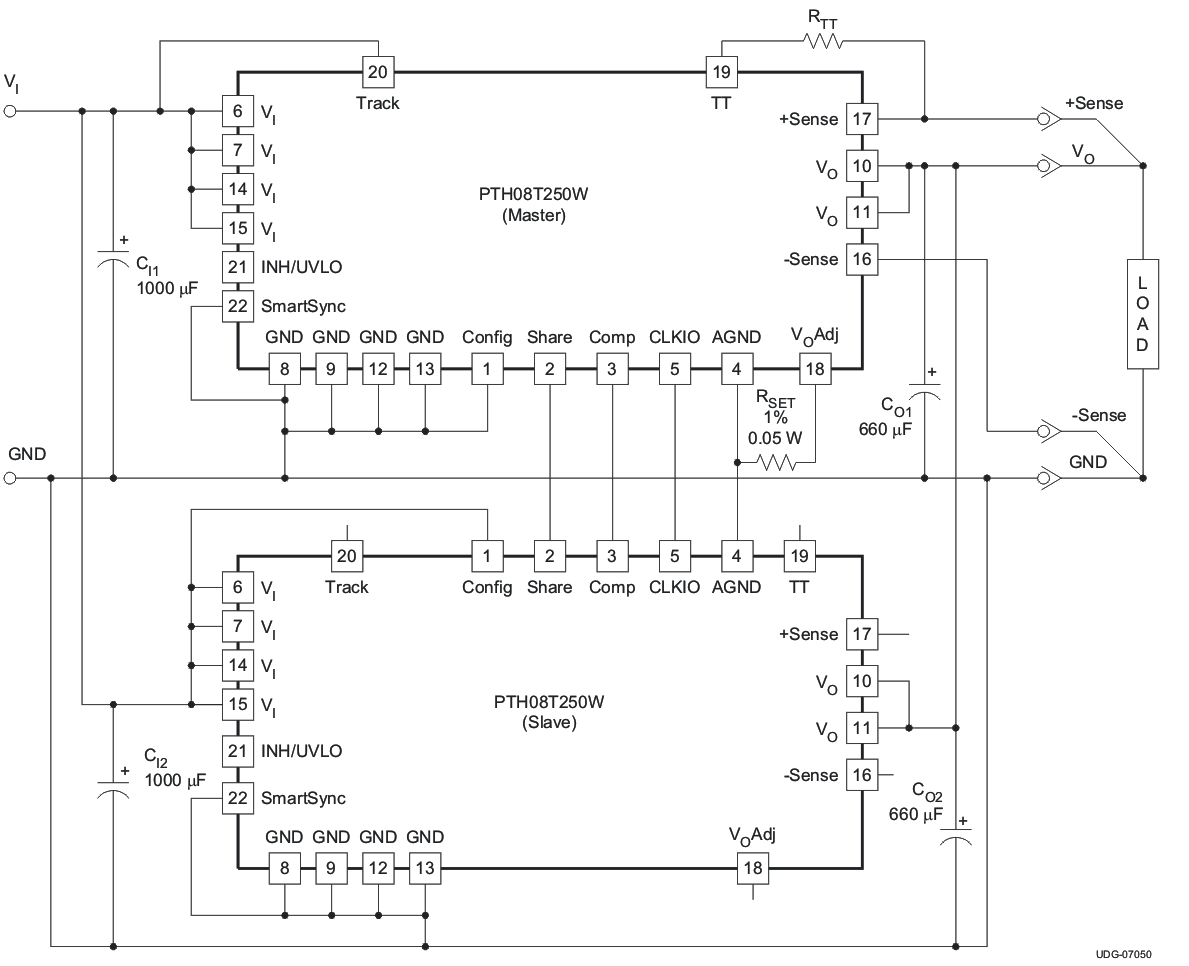 Figure 22. Typical Current Sharing Diagram
Figure 22. Typical Current Sharing Diagram Table 8. Required Connections for Current Sharing(1)
| PIN | MASTER | SLAVE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| VI | 6,7,14,15 | Connect to the Input Bus. | Connect to the Input Bus. | |
| VO | 10,11 | Connect to the Output Bus. | Connect to the Output Bus. | |
| GND | 8,9,12,13 | Connect to Common Power GND. | Connect to Common Power GND. | |
| Inhibit and UVLO | 21 | Use for Inhibit control & UVLO adjustments. If unused leave open-circuit. | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| Vo Adjust | 18 | Use to set the output voltage. Connect RSET resistor between this pin and AGND (pin 4). | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| +Sense | 17 | Connect to the output voltage either at the load or at the module (pin 11). | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| –Sense | 16 | Connect to the output GND either at the load or at the module (pin 13). | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| Track | 20 | Connect to Track control or to VI (pin 15). | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| TurboTrans™ | 19 | Connect TurboTrans resistor, RTT, between this pin and +Sense (pin 17). | No Connection. Leave open-circuit. | |
| SmartSync | 22 | Connect to an external clock. If unused connect to GND. | Connect to Common Power GND. | |
| CONFIG | 1 | Connect to GND. (2) | Connect to the Input Bus. | |
| Share | 2 | Connect to pin 2 of Slave. (2) | Connect to pin 2 of Master. | |
| Comp | 3 | Connect to pin 3 of Slave. (2) | Connect to pin 3 of Master. | |
| AGND | 4 | Connect to pin 4 of Slave. (3) | Connect to pin 4 of Master. | |
| CLKIO | 5 | Connect to pin 5 of Slave. (2) | Connect to pin 5 of Master. | |