SLLSEA0I February 2012 – January 2021 SN6501
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.3 Diode Selection
A rectifier diode should always possess low-forward voltage to provide as much voltage to the converter output as possible. When used in high-frequency switching applications, such as the SN6501 however, the diode must also possess a short recovery time. Schottky diodes meet both requirements and are therefore strongly recommended in push-pull converter designs. A good choice for low-volt applications and ambient temperatures of up to 85°C is the low-cost Schottky rectifier MBR0520L with a typical forward voltage of 275 mV at 100-mA forward current. For higher output voltages such as ±10 V and above use the MBR0530 which provides a higher DC blocking voltage of 30 V.
Lab measurements have shown that at temperatures higher than 100°C the leakage currents of the above Schottky diodes increase significantly. This can cause thermal runaway leading to the collapse of the rectifier output voltage. Therefore, for ambient temperatures higher than 85°C use low-leakage Schottky diodes, such as RB168M-40.
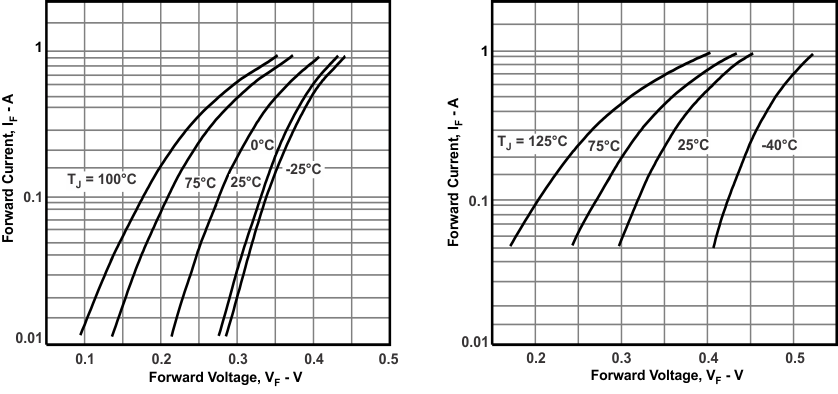 Figure 8-4 Diode Forward Characteristics for MBR0520L (Left) and MBR0530 (Right)
Figure 8-4 Diode Forward Characteristics for MBR0520L (Left) and MBR0530 (Right)