SLLSEW9A December 2016 – June 2018 SN65DSI84-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Control and Status Registers Overview
- 8.6.1.1 CSR Bit Field Definitions – ID Registers
- 8.6.1.2 CSR Bit Field Definitions – Reset and Clock Registers
- 8.6.1.3 CSR Bit Field Definitions – DSI Registers
- 8.6.1.4 CSR Bit Field Definitions – LVDS Registers
- 8.6.1.5
CSR Bit Field Definitions – Video Registers
- 8.6.1.5.1 Register 0x20
- 8.6.1.5.2 Register 0x21
- 8.6.1.5.3 Register 0x24
- 8.6.1.5.4 Register 0x25
- 8.6.1.5.5 Register 0x28
- 8.6.1.5.6 Register 0x29
- 8.6.1.5.7 Register 0x2C
- 8.6.1.5.8 Register 0x2D
- 8.6.1.5.9 Register 0x30
- 8.6.1.5.10 Register 0x31
- 8.6.1.5.11 Register 0x34
- 8.6.1.5.12 Register 0x36
- 8.6.1.5.13 Register 0x38
- 8.6.1.5.14 Register 0x3A
- 8.6.1.5.15 Register 0x3C
- 8.6.1.6 CSR Bit Field Definitions – IRQ Registers
- 8.6.1
Control and Status Registers Overview
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PAP|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PAP|64
Orderable Information
3 Description
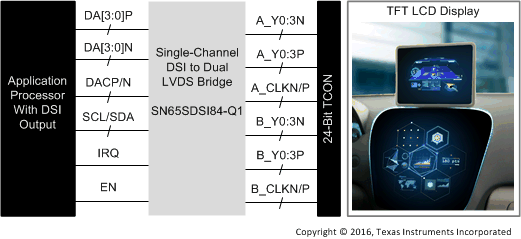
The SN65DSI84-Q1 DSI-to-LVDS bridge features a single-channel MIPI D-PHY receiver front-end configuration with four lanes per channel operating at 1 Gbps per lane and a maximum input bandwidth of 4 Gbps. The bridge decodes MIPI® DSI 18-bpp RGB666 and 24-bpp RGB888 packets and converts the formatted video data-stream to an LVDS output operating at pixel clocks operating from 25 MHz to 154 MHz, offering a dual-link LVDS or single-link LVDS with four data lanes per link.
The SN65DSI84-Q1 device is well suited for WUXGA (1920 × 1080) at 60 frames per second (fps) with up to 24 bits-per-pixel (bpp). Partial line buffering is implemented to accommodate the data stream mismatch between the DSI and LVDS interfaces.
The SN65DSI84-Q1 device is implemented in a small outline 10 mm × 10 mm HTQFP package with a
0.5-mm pitch, and operates across a temperature range from –40°C to 105°C.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN65DSI84-Q1 | HTQFP (64) | 10.00 mm × 10.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
3.1 Typical Application