SLUSDD5A April 2019 – December 2020 UC1825B-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- HKT|16
- KGD|0
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2 Synchronization
The oscillator can be synchronized by an external pulse inserted in series with the timing capacitor (see Figure 7-2). Program the free running frequency of the oscillator to be 10% to 15% slower than the desired synchronous frequency. The pulse width must be greater than 10 ns and less than half the discharge time of the oscillator. Figure 7-3 shows how to synchronize two ICs, with one as primary and one as secondary. Figure 7-4 shows the waveforms in a primary and secondary configuration.
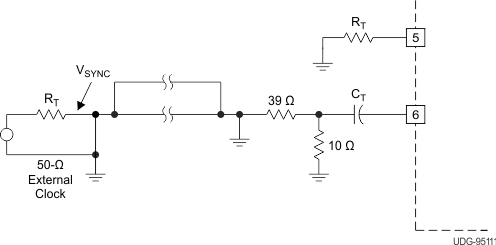 Figure 7-2 General Oscillator Synchronization
Figure 7-2 General Oscillator Synchronization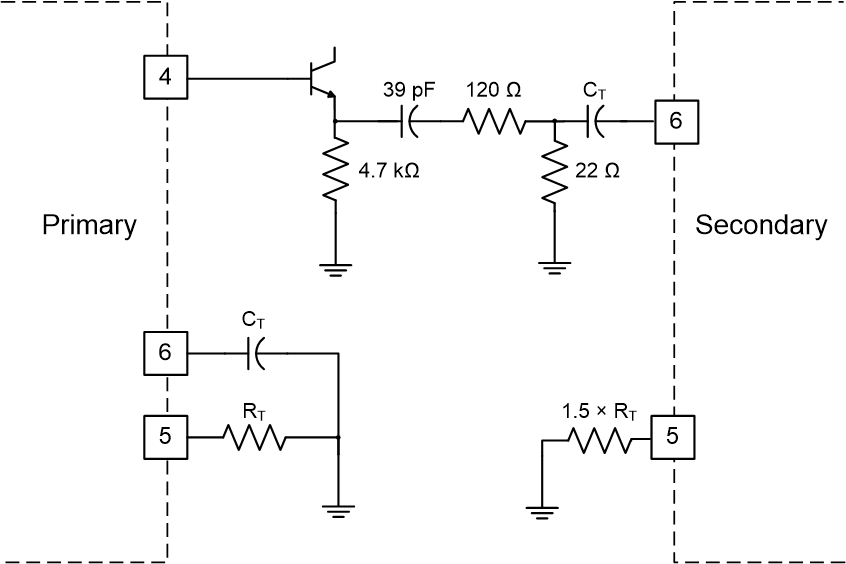 Figure 7-3 Two Unit
Interface
Figure 7-3 Two Unit
Interface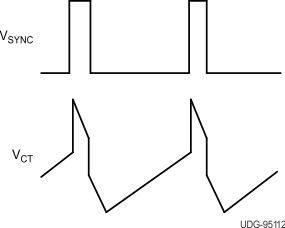 Figure 7-4 Operational Waveforms
Figure 7-4 Operational Waveforms