JAJSBP3B November 2011 – December 2018 TMP104
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1特長
- 2アプリケーション
- 3概要
- 4改訂履歴
- 5Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6Specifications
- 7Detailed Description
- 8デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 9メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- YFF|4
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.3.2 Command Register
Figure 8 shows the internal register structure of the TMP104. Communications between the registers are transferred through the interface in LSB-first order. The 8-bit Command Register, as shown in Table 3, is used to determine the type of instruction being addressed. These eight bits could either interpret a global instruction or an individual instruction, which is determined by the value of P7. When P7 = 0, the command byte interprets an individual instruction; when P7 = 1, the command byte interprets a global instruction.
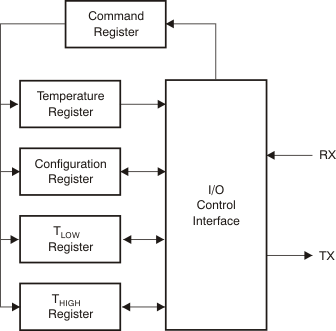 Figure 8. Internal Register Structure
Figure 8. Internal Register Structure Table 3. Command Register Byte
| P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 | P0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLB | IN3/ID3 | IN2/ID2 | IN1/ID1 | IN0/ID0 | P1 | P0 | R/W |