JAJSI75A April 2018 – November 2019 TPS57112C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.4.2 Enable Functionality and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.4.3 Slow-Start or Tracking Pin
- 8.4.4 Sequencing
- 8.4.5 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 8.4.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.4.7 Frequency Shift
- 8.4.8 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 8.4.9 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 8.4.10 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 8.4.11 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 8.4.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4.13 Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
- 8.4.14 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 8.4.15 Small-Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 9.2.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 9.2.2.5 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 9.2.2.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.7 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistor Selection
- 9.2.2.8 Compensation
- 9.2.2.9 Power-Dissipation Estimate
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTE|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTE|16
発注情報
8.4.13 Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
Figure 31 shows an equivalent model for the TPS57112C-Q1 control loop, which one can model in a circuit simulation program to check frequency response and dynamic load response. The error amplifier is a transconductance amplifier with a gm of 245 μS. One can model the error amplifier using an ideal voltage-controlled current source. Resistor R0 and capacitor C0 model the open-loop gain and frequency response of the amplifier. The 1-mV ac voltage source between nodes a and b effectively breaks the control loop for the frequency-response measurements. Plotting a over c vs frequency shows the small-signal response of the frequency compensation. Plotting a over b vs frequency shows the small-signal response of the overall loop. One can check the dynamic loop response by replacing R(L) with a current source with the appropriate load-step amplitude and step rate in a time-domain analysis.
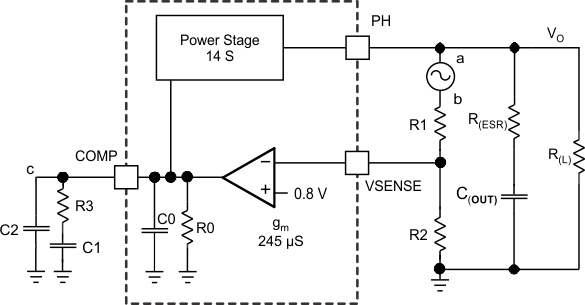 Figure 31. Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
Figure 31. Small-Signal Model for Loop Response