SNVA037F April 2001 – February 2022 LM3477 , LM3488
3 Hysteretic Mode
As the load current is decreased, the LM3477 will eventually enter a 'hysteretic' mode of operation. When the load current drops below the hysteretic mode threshold, the output voltage rises slightly. The overvoltage protection (OVP) comparator senses this rise and causes the power MOSFET to shut off. As the load pulls current out of the output capacitor, the output voltage drops until it hits the low threshold of the OVP comparator and the part begins switching again. This behavior results in a lower frequency, higher peak-to-peak output voltage ripple than with the normal pulse width modulation scheme. The magnitude of the output voltage ripple is determined by the OVP threshold levels, which are referred to the feedback voltage and are typically 1.25 V to 1.31 V. For more information, see the Electrical Characteristics table in the LM3477 High Efficiency High-Side N-Channel Controller for Switching Regulator Data Sheet. In the case of a 3.3-V output, this translates to a regulated output voltage between 3.27 V and 3.43 V. The hysteretic mode threshold point is a function of RSN and RSL. Figure 3-1 shows the hysteretic threshold versus VIN for the LM3477 evaluation board with and without RSL.
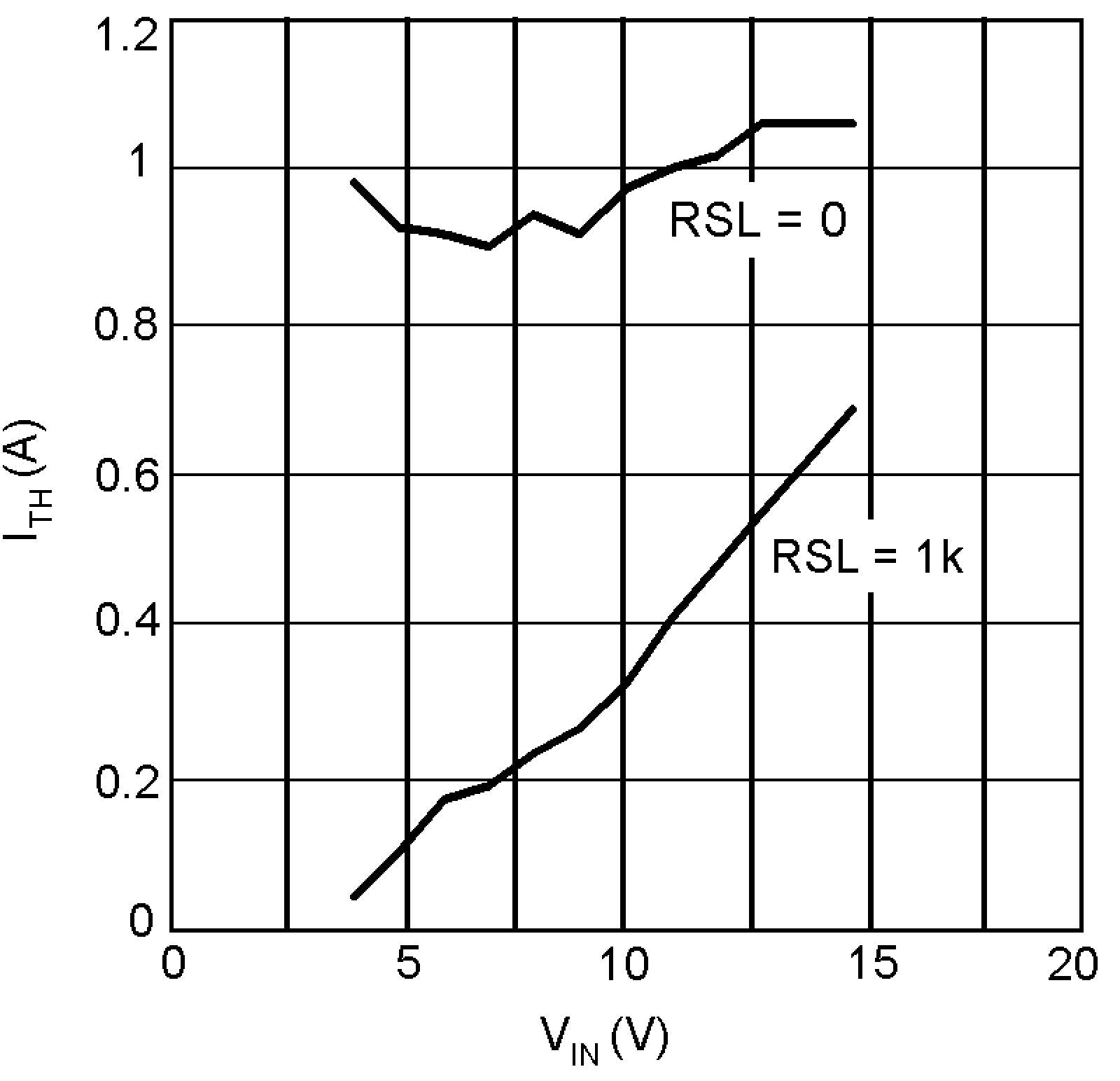 Figure 3-1 ITH vs
VIN
Figure 3-1 ITH vs
VIN