SWRA495K December 2015 – April 2024 CC1310 , CC1350 , CC2620 , CC2630 , CC2640 , CC2640R2F , CC2640R2F-Q1 , CC2642R-Q1 , CC2650 , CC2662R-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Oscillator and Crystal Basics
- 2Overview of Crystal Oscillators for CC devices
- 3Selecting Crystals for the CC devices
- 4PCB Layout of the Crystal
- 5Measuring the Amplitude of the Oscillations of Your Crystal
- 6Crystals for CC13xx, CC26xx and CC23xx
- 7High Performance BAW Oscillator
- 8References
- 9Revision History
1.3 Negative Resistance
Negative resistance (RN) is a parameter of the complete oscillator circuit, including capacitor values, crystal parameters, and the on-chip circuit. The CC devices dynamically adjust the oscillator parameters to ensure sufficient oscillator margin during crystal startup and then relax the margins for steady state to decrease the current consumption. This means that when using a crystal within the requirements outlined in the CC data sheets, proper start-up and steady-state margin is ensured over operating conditions.
Equation 7 approximates the negative resistance and shows that a low CL gives a larger negative resistance.
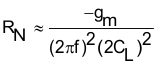
where:
- gmis the transconductance of the active element in the oscillator, and can be approximated as 7 milli-Siemens for the high frequency crystal oscillator and 30 micro-Siemens for the low frequency crystal
- CLis the load capacitance
You can also find the negative resistance of the circuit by introducing a resistor in series with the crystal. To avoid parasitic effects, TI recommends using a 0201 resistor for this task. The threshold of the sum of the extra 0201 external resistance and ESR or the crystal where the oscillator is unable to start up is approximately the same as the circuit negative resistance.