SBOU113A June 2011 – January 2023
- INA226EVM Rev A Model User's Guide and Software Tutorial
- 1Trademarks
- 2Overview
- 3INA226EVM Hardware Setup
- 4INA226EVM Hardware
- 5INA226EVM Software Setup
- 6INA226EVM Software Overview
- 7INA226EVM Documentation
- 8Revision History
6.2.4 Set Configuration Register
The Configuration register must then be set correctly for the software to operate properly. There are two methods used to set the Configuration register. First, the user can manually calculate the desired value and then input that value into the register table, as shown in Equation 1. Alternatively, the user can allow the software to create a recommended window and choose an LSB for the current as shown in Figure 6-7. Both methods accomplish the same goal by using Equation 1, but the method is selected by changing the value in Step 4: Select Configuration Method (as Figure 6-6 and Figure 6-7 show).
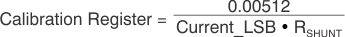
Use Equation 2 to calculate the current LSB by a recommended range in the INA226 data sheet. It is important to note that with either of the methods used, the Current LSB and the Calibration register values are calculated based on the other variable and the RSHUNT value. See the section, Programming the INA226 in the product data sheet for more information on setting the Calibration register value.
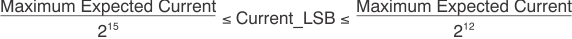
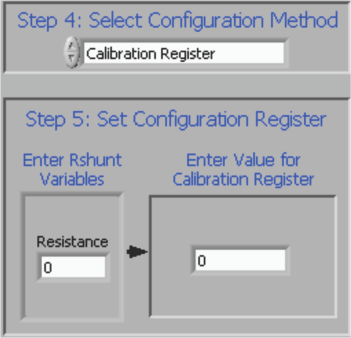 Figure 6-6 Setting the Configuration Register (Calibration Register)
Figure 6-6 Setting the Configuration Register (Calibration Register)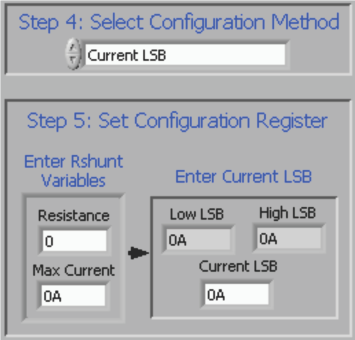 Figure 6-7 Setting the Configuration Register (Current LSB)
Figure 6-7 Setting the Configuration Register (Current LSB)