SBAS683B August 2014 – May 2020 ADS1120-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Multiplexer
- 8.3.2 Low-Noise PGA
- 8.3.3 Modulator
- 8.3.4 Digital Filter
- 8.3.5 Output Data Rate
- 8.3.6 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.7 Clock Source
- 8.3.8 Excitation Current Sources
- 8.3.9 Low-Side Power Switch
- 8.3.10 Sensor Detection
- 8.3.11 System Monitor
- 8.3.12 Offset Calibration
- 8.3.13 Power Supplies
- 8.3.14 Temperature Sensor
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.2 Analog Input Filtering
Analog input filtering serves two purposes: first, to limit the effect of aliasing during the sampling process and second, to reduce external noise from being a part of the measurement.
As with any sampled system, aliasing can occur if proper antialias filtering is not in place. Aliasing occurs when frequency components are present in the input signal that are higher than half the sampling frequency of the ADC (also known as the Nyquist frequency). These frequency components are folded back and show up in the actual frequency band of interest below half the sampling frequency. Note that inside a ΔΣ ADC, the input signal is sampled at the modulator frequency f(MOD) and not at the output data rate. The filter response of the digital filter repeats at multiples of the sampling frequency (f(MOD)), as shown in Figure 73. Signals or noise up to a frequency where the filter response repeats are attenuated to a certain amount by the digital filter depending on the filter architecture. Any frequency components present in the input signal around the modulator frequency or multiples thereof are not attenuated and alias back into the band of interest, unless attenuated by an external analog filter.
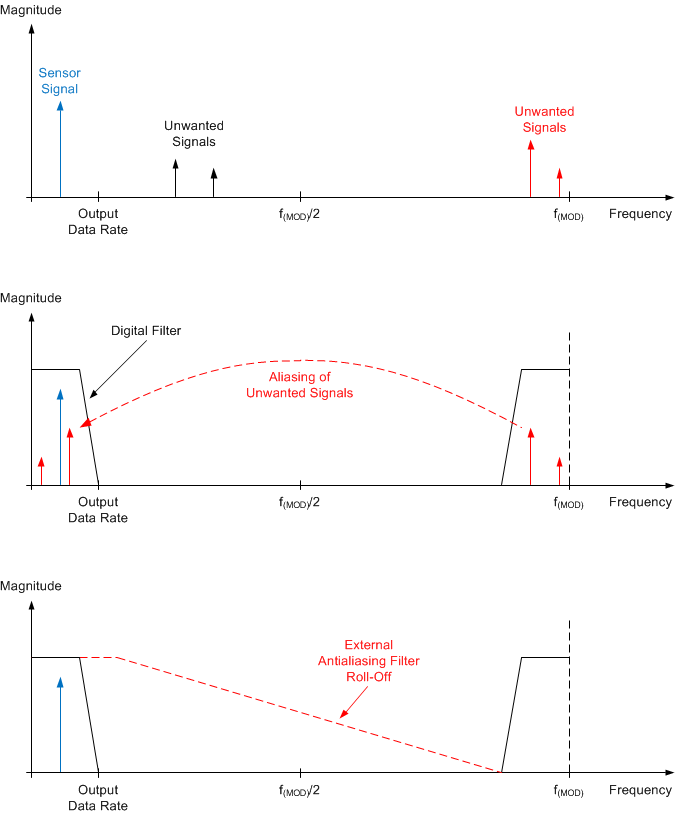 Figure 73. Effect of Aliasing
Figure 73. Effect of Aliasing Many sensor signals are inherently bandlimited; for example, the output of a thermocouple has a limited rate of change. In this case the sensor signal does not alias back into the pass-band when using a ΔΣ ADC. However, any noise pick-up along the sensor wiring or the application circuitry can potentially alias into the pass-band. Power line-cycle frequency and harmonics are one common noise source. External noise can also be generated from electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI) sources, such as nearby motors and cellular phones. Another noise source typically exists on the printed circuit board (PCB) itself in the form of clocks and other digital signals. Analog input filtering helps remove unwanted signals from affecting the measurement result.
A first-order resistor-capacitor (RC) filter is (in most cases) sufficient to either totally eliminate aliasing, or to reduce the effect of aliasing to a level within the noise floor of the sensor. Ideally, any signal beyond f(MOD) / 2 is attenuated to a level below the noise floor of the ADC. The digital filter of the ADS1120-Q1 attenuates signals to a certain degree, as illustrated in the filter response plots in the Digital Filter section. In addition, noise components are usually smaller in magnitude than the actual sensor signal. Therefore, using a first-order RC filter with a cutoff frequency set at the output data rate or 10x higher is generally a good starting point for a system design.
Internal to the device, prior to the PGA inputs, is an EMI filter as illustrated in Figure 39. The cutoff frequency of this filter is approximately 31.8 MHz, which helps reject high-frequency interferences.