SBAS705B June 2015 – April 2020 ADS131E08S
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 SPI Interface
- 9.5.2 Data Retrieval
- 9.5.3
SPI Command Definitions
- 9.5.3.1 WAKEUP: Exit STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.2 STANDBY: Enter STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.3 RESET: Reset Registers to Default Values
- 9.5.3.4 START: Start Conversions
- 9.5.3.5 STOP: Stop Conversions
- 9.5.3.6 OFFSETCAL: Channel Offset Calibration
- 9.5.3.7 RDATAC: Start Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.8 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.9 RDATA: Read Data
- 9.5.3.10 RREG: Read from Register
- 9.5.3.11 WREG: Write to Register
- 9.5.3.12 Sending Multibyte Commands
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.6.1.1 ID: ID Control Register (Factory-Programmed, Read-Only) (address = 00h) [reset = D2h]
- 9.6.1.2 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 01h) [reset = 94h]
- 9.6.1.3 CONFIG2: Configuration Register 2 (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.4 CONFIG3: Configuration Register 3 (address = 03h) [reset = E0h]
- 9.6.1.5 FAULT: Fault Detect Control Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 CHnSET: Individual Channel Settings (address = 05h to 0Ch) [reset = 10h]
- 9.6.1.7 FAULT_STATP: Fault Detect Positive Input Status (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.8 FAULT_STATN: Fault Detect Negative Input Status (address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.9 GPIO: General-Purpose IO Register (address = 14h) [reset = 0Fh]
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PAG|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PAG|64
Orderable Information
9.4.3.3 Continuous Conversion Mode
When the START pin is pulled high or the START command is issued, conversions continue indefinitely until the START pin is taken low or the STOP command is transmitted, as shown in Figure 34. When the START pin is pulled low or the STOP command is issued, the conversion in progress completes and the DRDY output transitions from high to low indicating that the latest data are available. Figure 35 and Table 6 illustrate the timing of where the START pin can be brought low or the STOP command can be sent relative to a completed conversion to halt further conversions. If the START pin is pulled low or if the STOP command is sent after the tDSHD time, then an additional conversion takes place and completes before further conversions are halted. To continuously run the converter without commands, tie the START pin high.
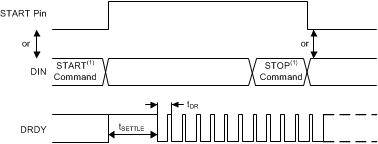
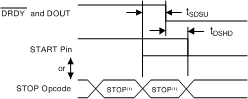
Table 6. Timing Characteristics for Figure 35(1)
| MIN | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| tSDSU | Setup time; set the START pin low or send the STOP command before the DRDY falling edge to halt further conversions | 16 | tCLK |
| tDSHD | Delay time; set the START pin low or send the STOP command to complete the current conversion and halt further conversions | 16 | tCLK |