SBAS705B June 2015 – April 2020 ADS131E08S
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 SPI Interface
- 9.5.2 Data Retrieval
- 9.5.3
SPI Command Definitions
- 9.5.3.1 WAKEUP: Exit STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.2 STANDBY: Enter STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.3 RESET: Reset Registers to Default Values
- 9.5.3.4 START: Start Conversions
- 9.5.3.5 STOP: Stop Conversions
- 9.5.3.6 OFFSETCAL: Channel Offset Calibration
- 9.5.3.7 RDATAC: Start Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.8 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode
- 9.5.3.9 RDATA: Read Data
- 9.5.3.10 RREG: Read from Register
- 9.5.3.11 WREG: Write to Register
- 9.5.3.12 Sending Multibyte Commands
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.6.1.1 ID: ID Control Register (Factory-Programmed, Read-Only) (address = 00h) [reset = D2h]
- 9.6.1.2 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 01h) [reset = 94h]
- 9.6.1.3 CONFIG2: Configuration Register 2 (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.4 CONFIG3: Configuration Register 3 (address = 03h) [reset = E0h]
- 9.6.1.5 FAULT: Fault Detect Control Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 CHnSET: Individual Channel Settings (address = 05h to 0Ch) [reset = 10h]
- 9.6.1.7 FAULT_STATP: Fault Detect Positive Input Status (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.8 FAULT_STATN: Fault Detect Negative Input Status (address = 13h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.9 GPIO: General-Purpose IO Register (address = 14h) [reset = 0Fh]
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PAG|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PAG|64
Orderable Information
9.3.8 Voltage Reference
The ADS131E08S uses an internal voltage reference and does not provide the option of connecting an external reference voltage. Figure 29 shows a simplified block diagram of the internal reference. There are two internal reference voltage options generated with respect to AVSS: 2.4 V and 4 V. Connect VREFN to AVSS.
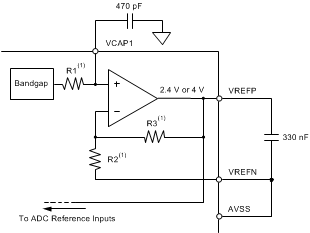
The external band-limiting capacitors, connected to VCAP1 and between the VREFP and VREFN nodes, determine the amount of reference noise contribution. Although limiting the bandwidth through larger capacitor sizes helps keep noise at a minimum, using large capacitors increases the power-up time of the ADC. Using the capacitor values shown in Figure 29 is recommended to optimize the power-up time of the device.
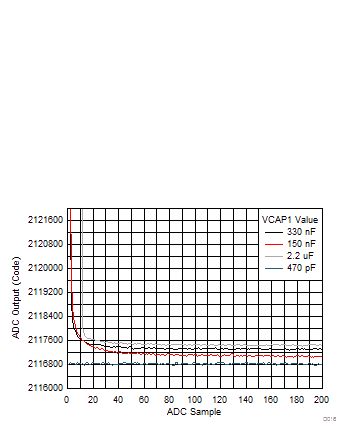
The internal band gap (VCAP1 pin) used to create the internal reference voltage requires a capacitor to filter noise. As a result of limited drive strength, the size of the capacitor on VCAP1 sets the power-up time of the device. Figure 30 shows the accuracy of the first 200 conversion samples with different capacitors on VCAP1 following power-up. Larger capacitors on VCAP1 help filter broadband noise but add to the power-up time. To generate the plot of Figure 30, the ADC input voltage is fixed at 1 V during power-up and the ADC output conversion result is tracked to show the VCAP1 power-up time.
Use the VREF_4V bit in the CONFIG2 register to set the internal reference to either 4 V or 2.4 V. By default, the reference powers up as 4 V for a 5-V system (or ±2.5-V supplies). In a 3-V system (or ±1.5-V supplies), configure the internal reference to 2.4 V immediately following power-up. No damage occurs to the device when the ADS131E08S is set to a 4-V reference when using a 3-V supply system. The internal reference saturates until programmed to 2.4 V.