SBAS817C November 2017 – November 2019 ADS8166 , ADS8167 , ADS8168
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Interface and Hardware Configuration Registers
- 7.6.1.1 REG_ACCESS Register (address = 00h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.2 PD_CNTL Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.3 SDI_CNTL Register (address = 008h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.4 SDO_CNTL1 Register (address = 0Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.5 SDO_CNTL2 Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.6 SDO_CNTL3 Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.7 SDO_CNTL4 Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.8 DATA_CNTL Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1.9 PARITY_CNTL Register (address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.2 Device Calibration Registers
- 7.6.3 Analog Input Configuration Registers
- 7.6.4
Channel Sequence Configuration Registers Map
- 7.6.4.1 DEVICE_CFG Register (address = 1Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.2 CHANNEL_ID Register (address = 1Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.3 SEQ_START Register (address = 1Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.4 SEQ_ABORT Register (address = 1Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.5 ON_THE_FLY_CFG Register (address = 2Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.6 AUTO_SEQ_CFG1 Register (address = 80h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.7 AUTO_SEQ_CFG2 Register (address = 82h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.8
Custom Channel Sequencing Mode Registers
- 7.6.4.8.1 CCS_START_INDEX Register (address = 88h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.8.2 CCS_END_INDEX Register (address = 89h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.8.3 CCS_SEQ_LOOP Register (address = 8Bh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.8.4 CCS_CHID_INDEX_m Registers (address = 8C, 8E, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 9A, 9C, 9E, A0, A2, A4, A6, A8, and AAh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4.8.5 REPEAT_INDEX_m Registers (address = 8D, 8F, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99, 9B, 9D, 9F, A1, A3, A5, A7, A9, and ABh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5
Digital Window Comparator Configuration Registers Map
- 7.6.5.1 ALERT_CFG Register (address = 2Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.2 HI_TRIG_AINx[15:0] Register (address = 4Dh to 30h) [reset = 0000h]
- 7.6.5.3 LO_TRIG_AINx[15:0] Register (address = 71h to 54h) [reset = 0000h]
- 7.6.5.4 HYSTERESIS_AINx[7:0] Register (address = 4Fh to 33h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.5 ALERT_LO_STATUS Register (address = 78h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.6 ALERT_HI_STATUS Register (address = 79h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.7 ALERT_STATUS Register (address = 7Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.8 CURR_ALERT_LO_STATUS Register (address = 7Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.9 CURR_ALERT_HI_STATUS Register (address = 7Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5.10 CURR_ALERT_STATUS Register (address = 7Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.1
Interface and Hardware Configuration Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
at AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 1.65 V to 5.5 V, REFIO configured as output pin, and maximum throughput (unless otherwise noted)
| Typical DNL = ±0.15 LSB |
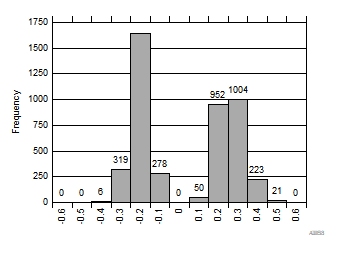
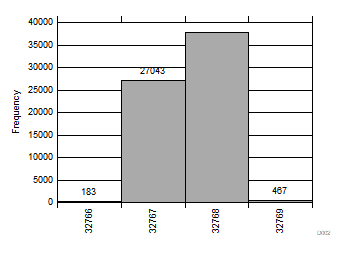
| 2250 devices |
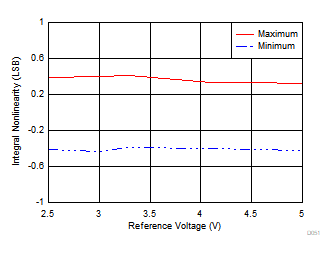
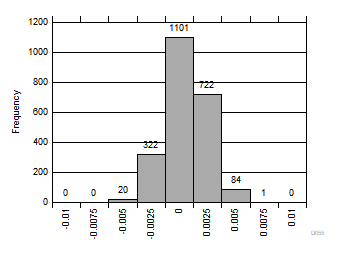
| 2250 devices |

| With the appropriate REF_SEL[2:0]; see the OFST_CAL register |
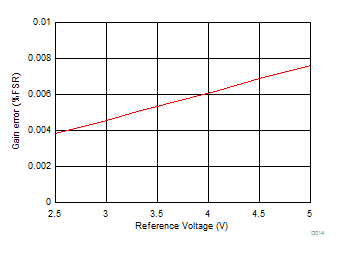
| EN_MARG = 0b |
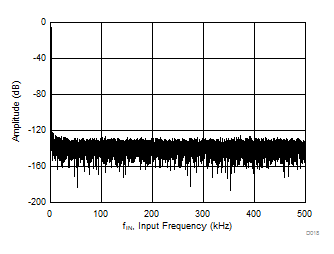
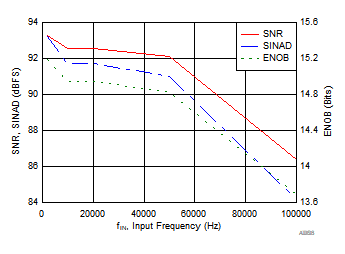
| fIN = 2 kHz, SNR = 93.8 dB, THD = –112.7 dB |
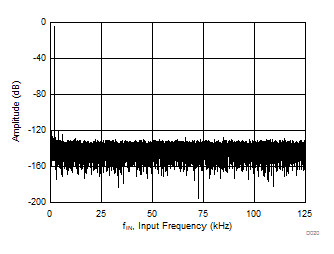
| fIN = 2 kHz, SNR = 93.8 dB, THD = –111.4 dB |

| fIN = 2 kHz |
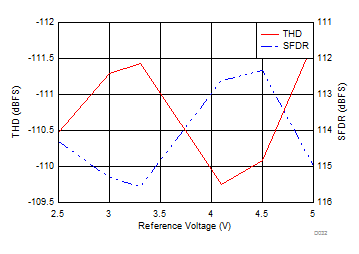
| fIN = 2 kHz |

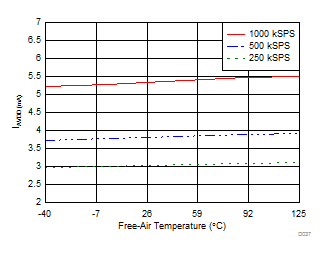
| AVDD = 5 V |
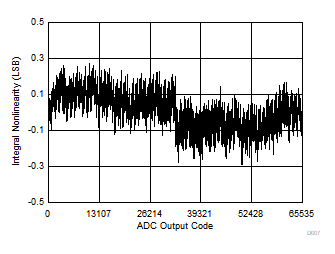
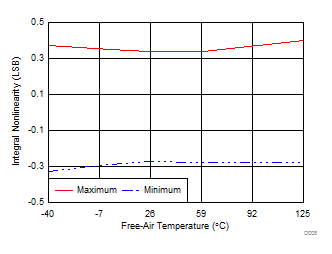
| Typical INL = ±0.3 LSB |
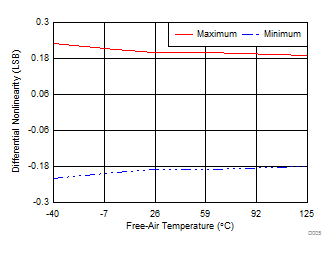

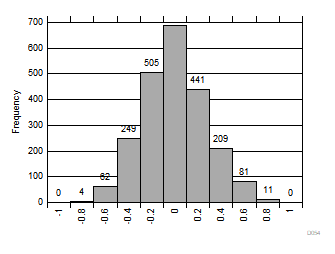
| 2250 devices |
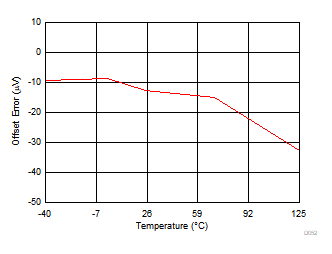
| REF_SEL[2:0] = 000b |

| EN_MARG = 0b |
| Standard deviation = 0.51 LSB |
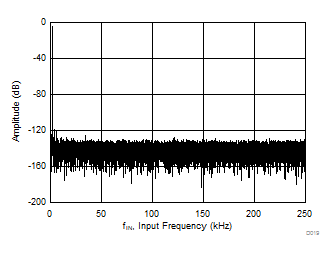
| fIN = 2 kHz, SNR = 93.8 dB, THD = –112.4 dB |
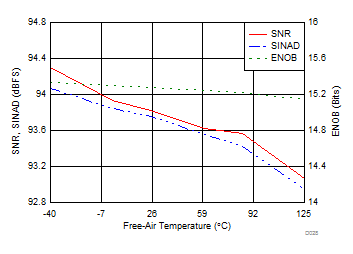
| fIN = 2 kHz |
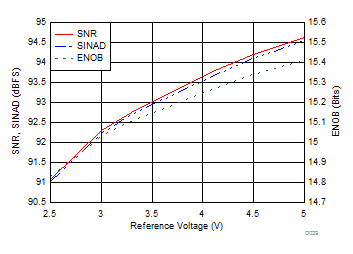
| fIN = 2 kHz |