SLUS900E December 2008 – August 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 I2C Read After Backup Mode
- 7.6.2
Normal Register Descriptions
- 7.6.2.1 SECONDS Register (address = 0x00) [reset = 0XXXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.2 MINUTES Register (address = 0x01) [reset = 1XXXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.3 CENT_HOURS Register (address = 0x02) [reset = XXXXXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.4 DAY Register (address = 0x03) [reset = 00000XXXb]
- 7.6.2.5 DATE Register (address = 0x04) [reset = 00XXXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.6 MONTH Register (address = 0x05) [reset = 000XXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.7 YEARS Register (address = 0x06) [reset = XXXXXXXXb]
- 7.6.2.8 CAL_CFG1 Register (address = 0x07) [reset = 10000000b]
- 7.6.2.9 TCH2 Register (address = 0x08) [reset = 10010000b]
- 7.6.2.10 CFG2 Register (address = 0x09) [reset = 10101010b]
- 7.6.3 Special Function Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The VCC pin should be bypassed to GND using a low-ESR ceramic bypass capacitor with a minimum recommended value of 1-µF. This capacitor should be placed as close to the VCC and GND pins as possible with thick trace or ground plane connection to the device GND pin.
Locate the 32.768-kHz crystal oscillator as close as possible to the OSCI and OSCO pins. This will minimize stray capacitance.
10.2 Layout Example
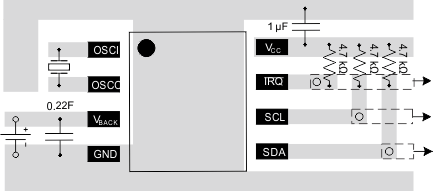 Figure 25. Recommended PCB Layout
Figure 25. Recommended PCB Layout