SBASAS1A November 2023 – March 2024 DAC39RF12 , DAC39RFS12
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 SPI and FRI Timing Diagrams
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: Bandwidth and DC Linearity
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: Single Tone Spectra
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics: Dual Tone Spectra
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics: Noise Spectral Density
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics: Linearity Sweeps
- 6.16 Typical Characteristics: Modulated Waveforms
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics: Phase and Amplitude Noise
- 6.18 Typical Characteristics: Power Dissipation and Supply Currents
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 DAC Output Modes
- 7.3.2 DAC Core
- 7.3.3 DEM and Dither
- 7.3.4 Offset Adjustment
- 7.3.5 Clocking Subsystem
- 7.3.6 Digital Signal Processing Blocks
- 7.3.7
JESD204C Interface
- 7.3.7.1 Deviation from JESD204C Standard
- 7.3.7.2 Transport Layer
- 7.3.7.3 Scrambler and Descrambler
- 7.3.7.4 Link Layer
- 7.3.7.5 Physical Layer
- 7.3.7.6 Serdes PLL Control
- 7.3.7.7 Serdes Crossbar
- 7.3.7.8 Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency
- 7.3.7.9 Operation in Subclass 0 Systems
- 7.3.7.10 Link Reset
- 7.3.8 Alarm Generation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.7 JESD204C Interface
The devices uses a JESD204C high-speed serial interface to transfer data from the logic device to the receiving DAC. The device serial lanes are capable of operating with both 8b/10b encoding and 64b/66b encoding. The JESD204C formats using 8b/10b encoding are backwards compatible with existing JESD204B receivers. A maximum of 16 lanes can be used to lower lane rates for interfacing with speed limited logic devices. There are a few differences between 8b/10b and 64b/66b encoding, which is highlighted throughout this section. Figure 7-50 shows a simplified block diagram of the 8b/10b encoded JESD204C interface and Figure 7-51 shows a simplified block diagram of the 64b/66b encoded JESD204C interface.
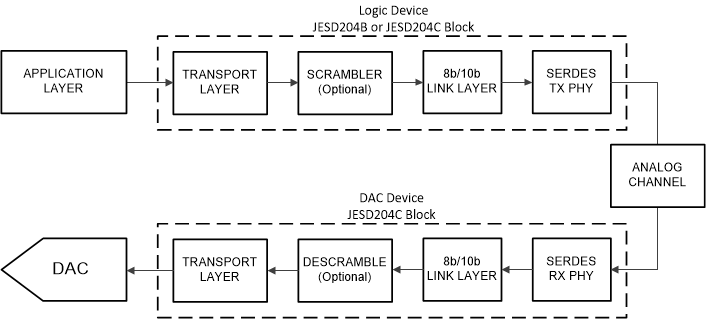 Figure 7-50 Simplified JESD204C Interface Diagram with 8b/10b Encoding
Figure 7-50 Simplified JESD204C Interface Diagram with 8b/10b Encoding Figure 7-51 Simplified JESD204C Interface Diagram with 64b/66b Encoding
Figure 7-51 Simplified JESD204C Interface Diagram with 64b/66b EncodingNot all optional features of JESD204C are supported by the device. The list of features that are supported and the features that are not supported is provided in Table 7-15
| LETTER IDENTIFIER | FEATURE | SUPPORTED BY DEVICE? |
|---|---|---|
| a | 8b/10b link layer | Yes |
| b | 64b/66b link layer | Yes |
| c | 64b/80b link layer | No |
| d | The command channel when using 64b/66b or 64b/80b link layer | No |
| e | Forward error correction (FEC) when using the 64b/66b or 64b/80b link layer | No |
| f | CRC3 when using the 64b/66b or 64b/80b link layer | No |
| g | A physical SYNC pin when using the 8b/10b link layer | Yes |
| h | Subclass 0 | Yes |
| i | Subclass 1 | Yes |
| j | Subclass 2 | No |
| k | Lane alignment within a single link | Yes |
| l | Subclass 1 with support for lane alignment on a multipoint link by means of the MULTIREF signal | No |
| m | SYNC interface timing compatible with JESD204A | Yes |
| n | SYNC interface timing compatible with JESD204B | Yes |
The various signals used in the JESD204C interface and the associated device pin names are summarized briefly in Table 7-16 for reference.
| SIGNAL NAME | DEVICE PIN NAMES | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Data | [15:0]SRX± | High-speed serialized data after 8b/10b or 64b/66b encoding that is received by the SerDes receivers. |
| SYNC | SYNC | Link initialization signal (handshake), toggles low to start code group synchronization (CGS) process. Not used for 64B/66B encoding modes. |
| Device clock | CLK+, CLK– | DAC sampling clock, also used for clocking digital logic and SerDes receivers. |
| SYSREF | SYSREF+, SYSREF– | System timing reference used to deterministically reset the internal local multiframe clock (LMFC) or local extended multiblock clock (LEMC) counters in each JESD204C device |