SLOS842A September 2013 – June 2015 DRV8301-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Buck Converter Characteristics
- 6.7 Current Shunt Amplifier Characteristics
- 6.8 Gate Timing and Protection Characteristics
- 6.9 SPI Timing Requirements (Slave Mode Only)
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCA|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCA|56
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
DCA Package
56-Pin HTSSOP With PowerPAD™
Top View
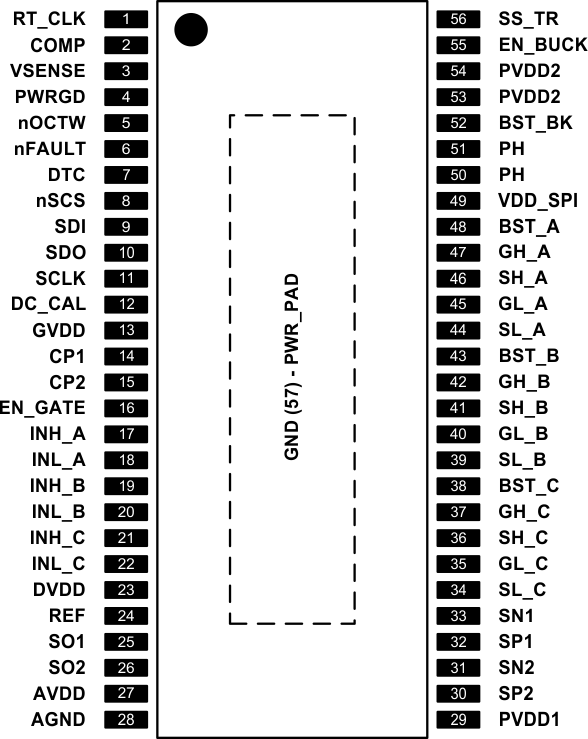
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 28 | P | Analog ground pin |
| AVDD | 27 | P | Internal 6-V supply voltage, AVDD cap should always be installed and connected to AGND. This is an output, but not specified to drive external circuitry. |
| BST_A | 48 | P | Bootstrap capacitor pin for half-bridge A |
| BST_B | 43 | P | Bootstrap capacitor pin for half-bridge B |
| BST_BK | 52 | P | Bootstrap capacitor pin for buck converter |
| BST_C | 38 | P | Bootstrap capacitor pin for half-bridge C |
| COMP | 2 | O | Buck error amplifier output and input to the output switch current comparator. |
| CP1 | 14 | P | Charge pump pin 1, ceramic capacitor should be used between CP1 and CP2 |
| CP2 | 15 | P | Charge pump pin 2, ceramic capacitor should be used between CP1 and CP2 |
| DC_CAL | 12 | I | When DC_CAL is high, device shorts inputs of shunt amplifiers and disconnects loads. DC offset calibration can occur through external microcontroller. |
| DTC | 7 | I | Dead-time adjustment with external resistor to GND |
| DVDD | 23 | P | Internal 3.3-V supply voltage. DVDD capacitor should connect to AGND. This is an output, but not specified to drive external circuitry. |
| EN_BUCK | 55 | I | Enable buck converter. Internal pullup current source. Pull below 1.2 V to disable. Float to enable. Adjust the input undervoltage lockout with two resistors |
| EN_GATE | 16 | I | Enable gate driver and current shunt amplifiers. Control buck through EN_BUCK pin. |
| nFAULT | 6 | O | Fault report indicator. This output is open drain with external pullup resistor required. |
| GH_A | 47 | O | Gate drive output for high-side MOSFET, half-bridge A |
| GH_B | 42 | O | Gate drive output for high-side MOSFET, half-bridge B |
| GH_C | 37 | O | Gate drive output for high-side MOSFET, half-bridge C |
| GL_A | 45 | O | Gate drive output for low-side MOSFET, half-bridge A |
| GL_B | 40 | O | Gate drive output for low-side MOSFET, half-bridge B |
| GL_C | 35 | O | Gate drive output for low-side MOSFET, half-bridge C |
| GVDD | 13 | P | Internal gate driver voltage regulator. GVDD capacitor should connect to GND |
| INH_A | 17 | I | PWM Input signal (high-side), half-bridge A |
| INH_B | 19 | I | PWM Input signal (high-side), half-bridge B |
| INH_C | 21 | I | PWM Input signal (high-side), half-bridge C |
| INL_A | 18 | I | PWM Input signal (low-side), half-bridge A |
| INL_B | 20 | I | PWM Input signal (low-side), half-bridge B |
| INL_C | 22 | I | PWM Input signal (low-side), half-bridge C |
| nOCTW | 5 | O | Overcurrent and over temperature warning indicator. This output is open drain with external pullup resistor required. Programmable output mode through SPI registers. |
| PH | 50 | O | The source of the internal high-side MOSFET of buck converter |
| 51 | |||
| PVDD1 | 29 | P | Power supply pin for gate driver, current shunt amplifier, and SPI communication. PVDD1 is independent of buck power supply, PVDD2. PVDD1 capacitor should connect to GND |
| PVDD2 | 53 | P | Power supply pin for buck converter, PVDD2 capacitor should connect to GND. |
| 54 | |||
| PWRGD | 4 | I | An open-drain output with external pullup resistor required. Asserts low if buck output voltage is low because of thermal shutdown, dropout, overvoltage, or EN_BUCK shut down |
| REF | 24 | I | Reference voltage to set output of shunt amplfiiers with a bias voltage which equals to half of the voltage set on this pin. Connect to ADC reference in microcontroller. |
| RT_CLK | 1 | I | Resistor timing and external clock for buck regulator. Resistor should connect to GND (PowerPAD) with very short trace to reduce the potential clock jitter due to noise. |
| SCLK | 11 | I | SPI clock signal |
| nSCS | 8 | I | SPI chip select |
| SDI | 9 | I | SPI input |
| SDO | 10 | O | SPI output |
| SH_A | 46 | I | High-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge A. High-side VDS measured between this pin and PVDD1. |
| SH_B | 41 | I | High-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge B. High-side VDS measured between this pin and PVDD1. |
| SH_C | 36 | I | High-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge C. High-side VDS measured between this pin and PVDD1. |
| SL_A | 44 | I | Low-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge A. Low-side VDS measured between this pin and SH_A. |
| SL_B | 39 | I | Low-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge B. Low-side VDS measured between this pin and SH_B. |
| SL_C | 34 | I | Low-Side MOSFET source connection, half-bridge C. Low-side VDS measured between this pin and SH_C. |
| SN1 | 33 | I | Input of current amplifier 1 (connecting to negative input of amplifier). |
| SN2 | 31 | I | Input of current amplifier 2 (connecting to negative input of amplifier). |
| SO1 | 25 | O | Output of current amplifier 1 |
| SO2 | 26 | O | Output of current amplifier 2 |
| SP1 | 32 | I | Input of current amplifier 1 (connecting to positive input of amplifier). Recommended to connect to ground side of the sense resistor for the best common-mode rejection. |
| SP2 | 30 | I | Input of current amplifier 2 (connecting to positive input of amplifier). Recommended to connect to ground side of the sense resistor for the best common-mode rejection. |
| SS_TR | 56 | I | Buck soft-start and tracking. An external capacitor connected to this pin sets the output rise time. Because the voltage on this pin overrides the internal reference, it can be used for tracking and sequencing. Cap should connect to GND |
| VDD_SPI | 49 | I | SPI supply pin to support 3.3-V or 5-V logic. Connect to either 3.3 V or 5 V. |
| VSENSE | 3 | I | Buck output voltage sense pin. Inverting node of error amplifier. |
| GND (PWR_PAD) |
57 | P | GND pin. The exposed PowerPAD must be electrically connected to ground plane through soldering to PCB for proper operation and connected to bottom side of PCB through vias for better thermal spreading. |
(1) KEY: I = Input, O = Output, P = Power