SLVSB19D February 2012 – March 2015 DRV8834
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematic
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
-
Dual-H-Bridge Current-Control Motor Driver
- Capable of Driving Two DC Motors or One Stepper Motor
- Two Control Modes:
- Built-In Indexer Logic With Simple STEP/DIRECTION Control and Up to
1/32-Step Microstepping - PHASE/ENABLE Control, With the Ability to Drive External References for > 1/32-Step Microstepping
- Built-In Indexer Logic With Simple STEP/DIRECTION Control and Up to
- Output Current 1.5-A Continuous, 2.2-A Peak per H-Bridge (at VM = 5 V, 25°C)
- Low RDS(ON): 305-mΩ HS + LS
(at VM = 5 V, 25°C) - Wide Power Supply Voltage Range:
2.5 V to 10.8 V - Dynamic tBLANK and Mixed Decay Modes for Smooth Microstepping
- PWM Winding Current Regulation and Limiting
- Thermally Enhanced Surface-Mount Package
2 Applications
- Battery-Powered Toys
- POS Printers
- Video Security Cameras
- Office Automation Machines
- Gaming Machines
- Robotics
3 Description
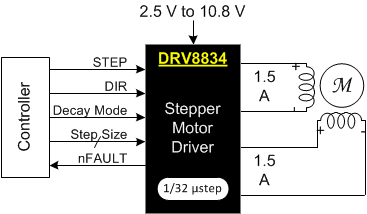
The DRV8834 provides a flexible motor driver solution for toys, printers, cameras, and other mechatronic applications. The device has two H-bridge drivers, and is intended to drive a bipolar stepper motor or two DC motors.
The output driver block of each H-bridge consists of N-channel power MOSFETs configured as an H-bridge to drive the motor windings. Each H-bridge includes circuitry to regulate or limit the winding current.
With proper PCB design, each H-bridge of the DRV8834 can driving up to 1.5-A RMS (or DC) continuously, at 25°C with a VM supply of 5 V. The device can support peak currents of up to 2.2 A per bridge. Current capability is reduced slightly at lower VM voltages.
Internal shutdown functions with a fault output pin are provided for overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, undervoltage lockout and overtemperature. A low-power sleep mode is also provided.
The DRV8834 is packaged in a 24-pin HTSSOP or VQFN package with PowerPAD™ (Eco-friendly: RoHS & no Sb/Br).
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| DRV8834 | HTSSOP (24) | 7.80 mm × 4.40 mm |
| VQFN (24) | 4.00 mm × 4.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
4 Simplified Schematic