SBOS366E August 2006 – January 2021 INA193A-Q1 , INA194A-Q1 , INA195A-Q1 , INA196A-Q1 , INA197A-Q1 , INA198A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Basic Connection
Figure 7-1 shows the basic connection of the INA19xA. The input pins, VIN+ and VIN–, should be connected as closely as possible to the shunt resistor to minimize any resistance in series with the shunt resistance.
Power-supply bypass capacitors are required for stability. Applications with noisy or high-impedance power supplies may require additional decoupling capacitors to reject power-supply noise. Connect bypass capacitors close to the device pins.
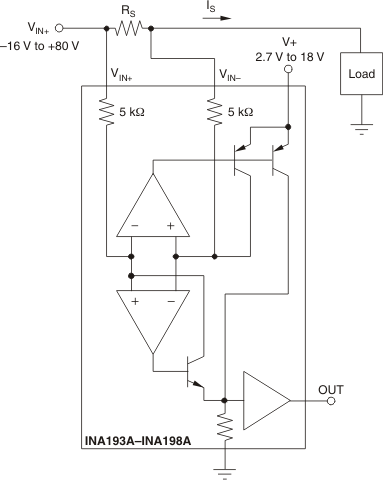 Figure 7-1 INA19xA Basic Connections
Figure 7-1 INA19xA Basic Connections