SBOS366E August 2006 – January 2021 INA193A-Q1 , INA194A-Q1 , INA195A-Q1 , INA196A-Q1 , INA197A-Q1 , INA198A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
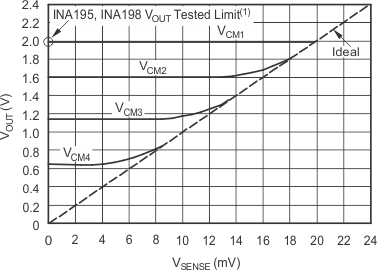
7.4.2.4 Low VSENSE Case 2: VSENSE < 20 mV, 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS
This region of operation is the least accurate for the INA19xA-Q1 family. To achieve the wide input common mode voltage range, these devices use two operational amplifier front ends in parallel. One operational amplifier front end operates in the positive input common mode voltage range, and the other in the negative input region. For this case, neither of these two internal amplifiers dominates and overall loop gain is very low. Within this region, VOUT approaches voltages close to linear operation levels for Normal Case 2. This deviation from linear operation becomes greatest the closer VSENSE approaches 0 V. Within this region, as VSENSE approaches 20 mV, device operation is closer to that described by Normal Case 2. Figure 7-8 illustrates this behavior for the INA195A. The VOUT maximum peak for this case is tested by maintaining a constant VS, setting VSENSE = 0 mV and sweeping VCM from 0 V to VS. The exact VCM at which VOUT peaks during this test varies from part to part, but the VOUT maximum peak is tested to be less than the specified VOUT tested limit.