SLLSFC5C November 2021 – January 2023 ISOUSB211
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power Supply Options
- 8.3.2 Power Up
- 8.3.3 Symmetric Operation, Dual-Role Port and Role-Reversal
- 8.3.4 Connect and Speed Detection
- 8.3.5 Disconnect Detection
- 8.3.6 Reset
- 8.3.7 LS/FS Message Traffic
- 8.3.8 HS Message Traffic
- 8.3.9 Equalization and Pre-emphasis
- 8.3.10 L2 Power Management State (Suspend) and Resume
- 8.3.11 L1 Power Management State (Sleep) and Resume
- 8.3.12 HS Test Mode Support
- 8.3.13 CDP Advertising
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.1.1 Layout Example
The layout example in this section shows
the recommended placement for de-coupling capacitors and ESD protection diodes. A
continuous ground plane is recommended below the D+/D- signal traces. Small
footprint capacitors (0402/0201) are recommended so that these may be placed very
close to the supply pins and corresponding ground pins and connected using the top
layer. There should not be any vias in the routing path between the decoupling
capacitors and the corresponding supply and ground pins. The capacitors on V1P8Vx supplies are
higher in priority when considering placement close to the IC. The ESD
protection diodes should be placed close to the connector with a strong connection
to the ground plane. Pins 4 and 11 for
V1P8V1 and pins 18 and 25 for V1P8V2 are connected
together, but this connection is after the de-coupling capacitors. If more than
2 layers are available in the PCB, this connection should be made in an inner or
bottom layer (ex. Layer 3 or 4) so as to not interrupt the ground plane under
the D+/D- traces. The example shown is for an isolated host or hub, but
similar considerations apply for isolated peripherals also. The 120-μF capacitor on
VBUS only applies to host or hub and should not be used for peripherals. A ferrite
bead, with dc resistance less than 100 mΩ, may be optionally placed on the VBUS
route, after the 100-nF (and 120-μF) capacitors to prevent transients such as ESD
from affecting the rest of the circuits.
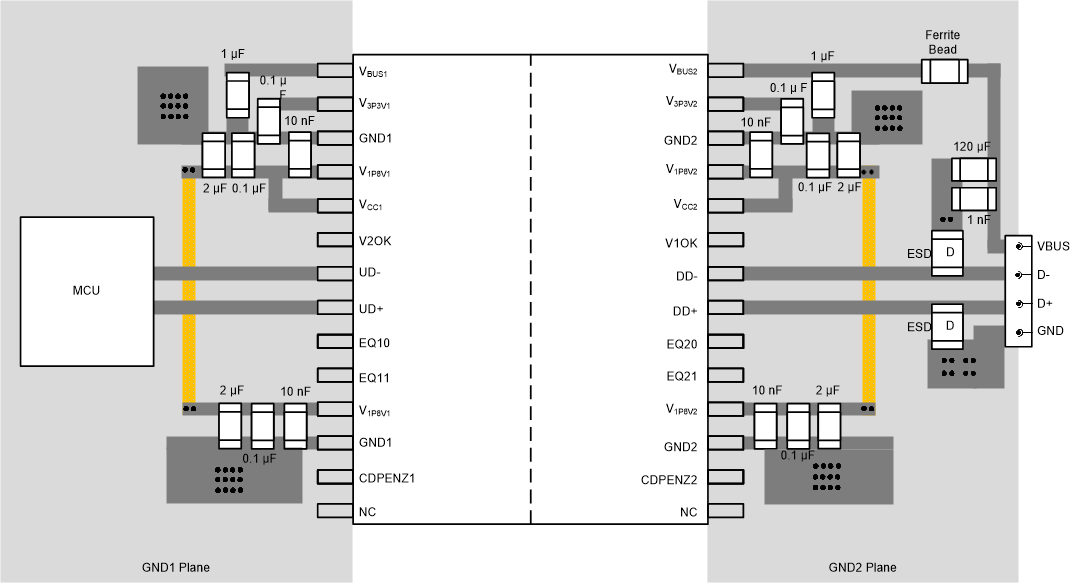 Figure 11-1 Layout Example for
ISOUSB211.
Figure 11-1 Layout Example for
ISOUSB211.
For best performance, it is recommended to minimize the length of D+/D- board traces from the MCU to ISOUSB211, and from ISOUSB211 to the connector. Vias and stubs on D+/D- lines must be avoided. This is especially important for High Speed Operation.
Connect a small plane (for example, 2 mm x 2 mm) to the GND pins on the top layer to improve thermal performance. Connect this to the ground player in the second layer with multiple vias.
 Figure 11-1 Layout Example for
ISOUSB211.
Figure 11-1 Layout Example for
ISOUSB211.