SNVS334F January 2005 – January 2016 LM2734Z , LM2734Z-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
LM2734Z Design Example 1
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.2 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.5 Boost Diode
- 8.2.1.2.6 Boost Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.7 Output Voltage
- 8.2.1.2.8 Calculating Efficiency, and Junction Temperature
- 8.2.1.2.9 Calculating the LM2734Z Junction Temperature
- 8.2.1.2.10 WSON Package
- 8.2.1.2.11 Package Selection
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 8.2.2 LM2734Z Design Example 2
- 8.2.3 LM2734Z Design Example 3
- 8.2.4 LM2734Z Design Example 4
- 8.2.5 LM2734Z Design Example 5
- 8.2.1
LM2734Z Design Example 1
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
When planning layout there are a few things to consider when trying to achieve a clean, regulated output. The most important consideration when completing the layout is the close coupling of the GND connections of the CIN capacitor and the catch diode D1. These ground ends must be close to one another and be connected to the GND plane with at least two through-holes. Place these components as close to the IC as possible. Next in importance is the location of the GND connection of the COUT capacitor, which must be near the GND connections of CIN and D1.
There must be a continuous ground plane on the bottom layer of a two-layer board except under the switching node island.
The FB pin is a high impedance node and care must be taken to make the FB trace short to avoid noise pickup and inaccurate regulation. The feedback resistors must be placed as close as possible to the IC, with the GND of R2 placed as close as possible to the GND of the IC. The VOUT trace to R1 must be routed away from the inductor and any other traces that are switching.
High AC currents flow through the VIN, SW and VOUT traces, so they must be as short and wide as possible. However, making the traces wide increases radiated noise, so the designer must make this trade-off. Radiated noise can be decreased by choosing a shielded inductor.
The remaining components must also be placed as close as possible to the IC. Please see the AN-1229 SIMPLE SWITCHER® PCB Layout Guidelines Application Note (SNVA054) for further considerations and the LM2734Z demo board as an example of a four-layer layout.
10.2 Layout Examples
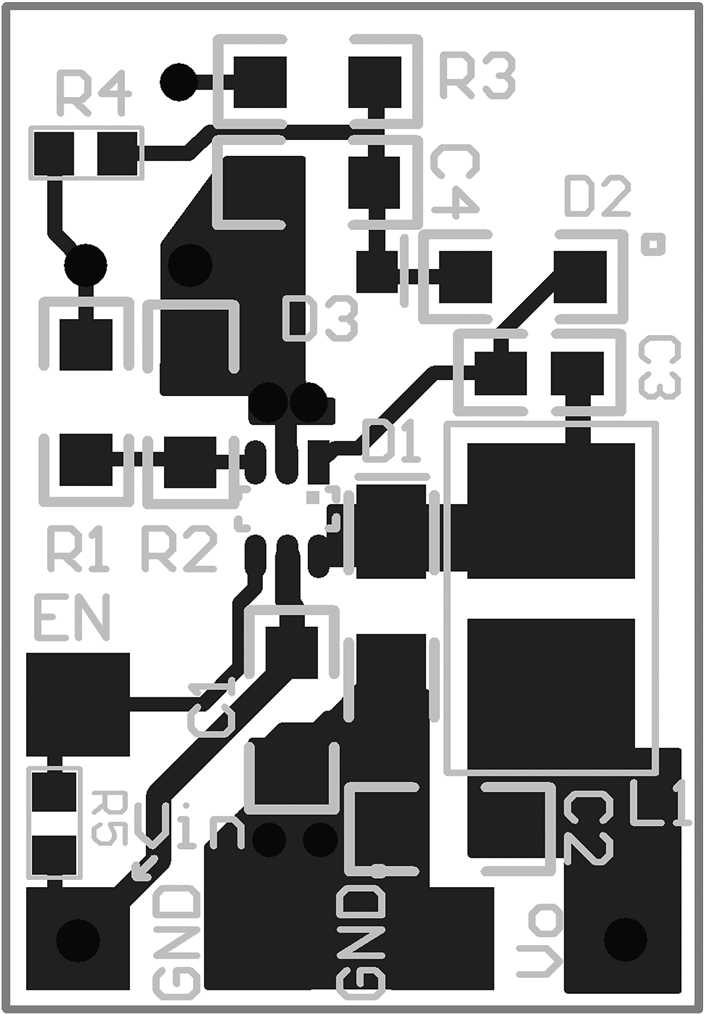 Figure 20. Top Layer
Figure 20. Top Layer
 Figure 22. Internal Plane 1 (GND)
Figure 22. Internal Plane 1 (GND)
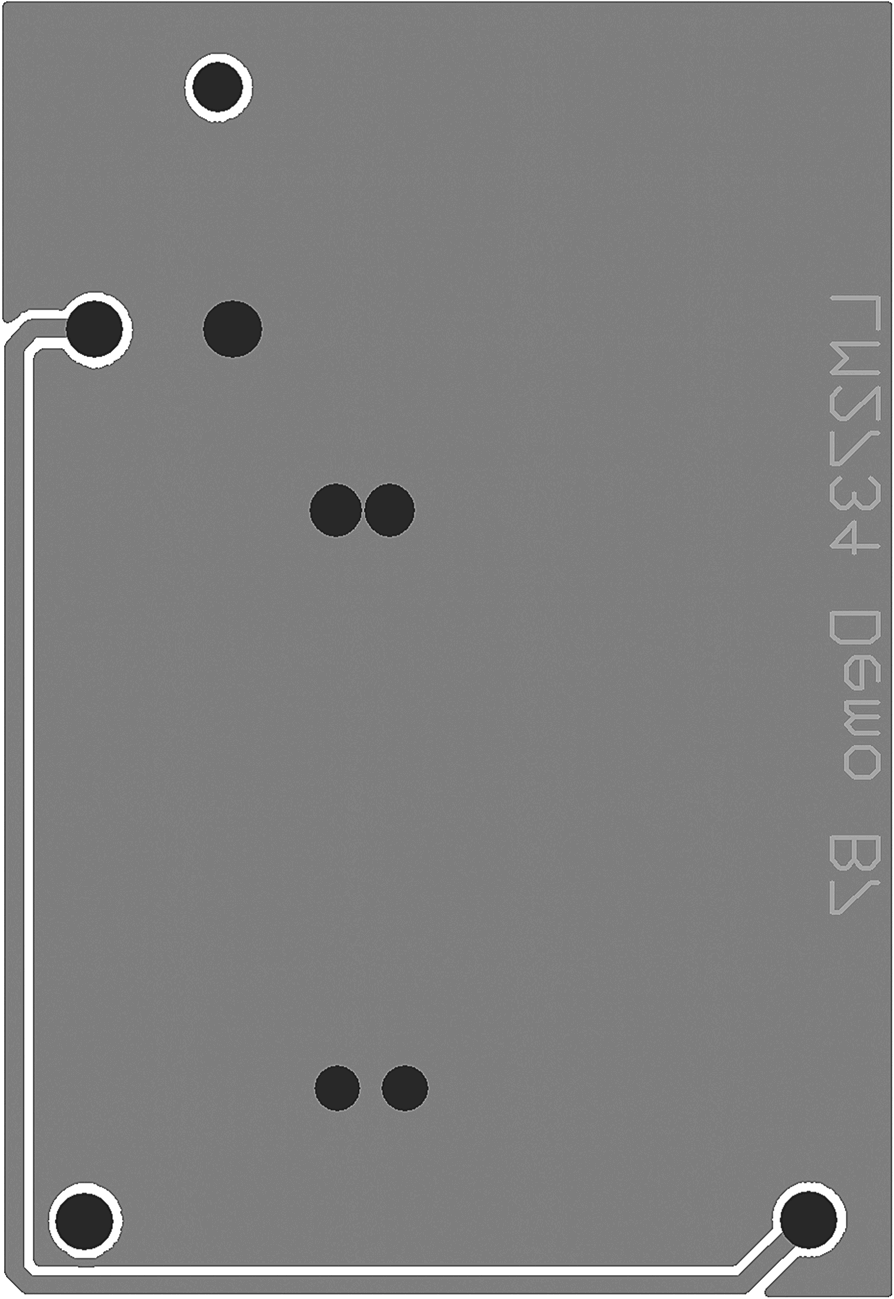 Figure 21. Bottom Layer
Figure 21. Bottom Layer
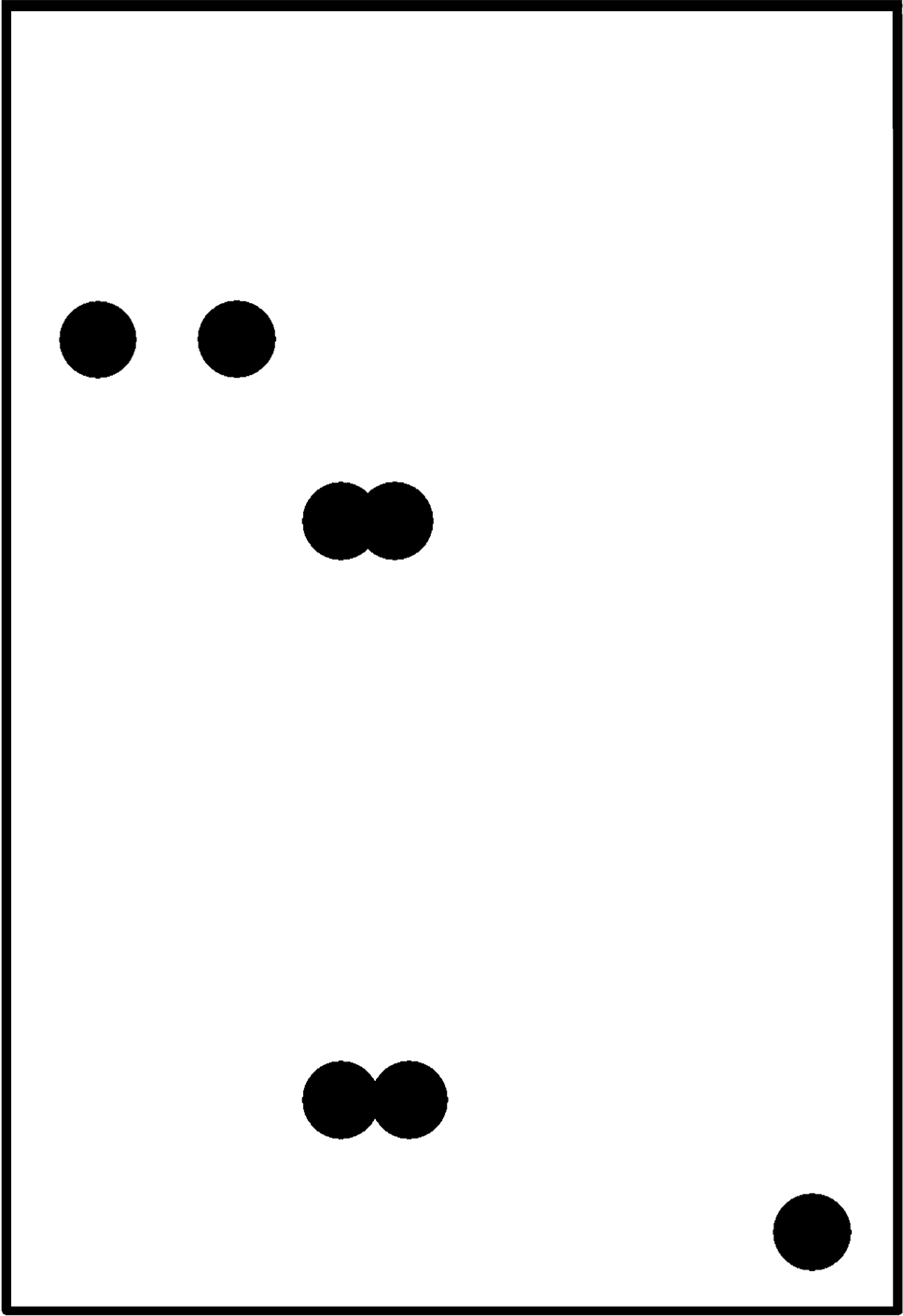 Figure 23. Internal Plane 2 (VIN)
Figure 23. Internal Plane 2 (VIN)