SNLS309I April 2010 – December 2014 LMH1983
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Control of PLL1
- 8.3.2 PLL1 Loop Response Design Equations
- 8.3.3 Control of PLL2 and PLL3
- 8.3.4 Control of PLL4
- 8.3.5 Clock Output Jitter
- 8.3.6 Lock Determination
- 8.3.7 Lock Time Considerations
- 8.3.8 LOR Determination
- 8.3.9 Output Driver Adjustments
- 8.3.10 TOF1 Alignment
- 8.3.11 TOF2 and TOF3 Alignment
- 8.3.12 TOF4 Alignment
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTA|40
Orderable Information
10 Power Supply Recommendations
It is important to ensure that the LMH1983 is provided with an adequate power supply that provides the cleanest voltage to the VDD_IO and VDD supply pins. One potential source of jitter on a multiple clock system such as the LMH1983 is interference among the four PLLs on the chip. To help reduce this effect, each PLL is run from a separate power supply internally on the LMH1983, and each supply has its own internal regulator. These regulators each require their own external bypass as seen in Figure 32 with bypass capacitors.
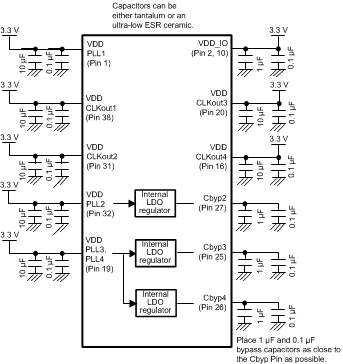 Figure 32. LMH1983 Power Supply Connection Diagram
Figure 32. LMH1983 Power Supply Connection Diagram