SBOS549C April 2011 – March 2021 OPA2376-Q1 , OPA376-Q1 , OPA4376-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.4 Phantom-Powered Microphone
The circuit shown in Figure 8-4 depicts how a remote microphone amplifier can be powered by a phantom source on the output side of the signal cable. The cable serves double duty, carrying both the differential output signal from and dc power to the microphone amplifier stage.
An OPA2376-Q1 serves as a single-ended input to a differential output amplifier with a 6-dB gain. Common-mode bias for the two op amps is provided by the dc voltage developed across the electret microphone element. A 48-V phantom supply is reduced to 5.1 V by the series 6.8-kΩ resistors on the output side of the cable, and the 4.7-kΩ resistors and zener diode on the input side of the cable. AC coupling blocks the different dc voltage levels from each other on each end of the cable.
An INA163 instrumentation amplifier provides differential inputs and receives the balanced audio signals from the cable.
The INA163 gain may be set from 0 dB to 80 dB by selecting the RG value. The INA163 circuit is typical of the input circuitry used in mixing consoles.
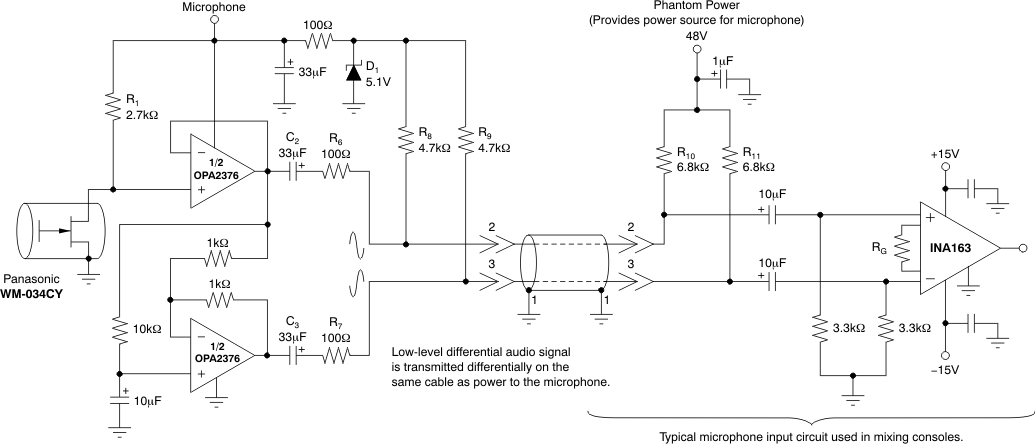 Figure 8-4 Phantom-Powered Electret Microphone
Figure 8-4 Phantom-Powered Electret Microphone