SPRS947 June 2016 SM320C6748-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
-
3Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 3.1 Pin Diagram
- 3.2
Pin Attributes
- 3.2.1 Device Reset, NMI and JTAG
- 3.2.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.2.3 Real-Time Clock and 32-kHz Oscillator
- 3.2.4 DEEPSLEEP Power Control
- 3.2.5 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 3.2.6 DDR2/mDDR Controller
- 3.2.7 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI)
- 3.2.8 Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU)
- 3.2.9 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0)
- 3.2.10 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM)
- 3.2.11 Boot
- 3.2.12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
- 3.2.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.2.14 Timers
- 3.2.15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP)
- 3.2.16 Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports (McBSP)
- 3.2.17 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0, USB1)
- 3.2.18 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.2.19 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.2.20 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCDC)
- 3.2.21 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
- 3.2.22 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 3.2.23 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
- 3.2.24 Video Port Interface (VPIF)
- 3.2.25 General Purpose Input Output
- 3.2.26 Reserved and No Connect
- 3.2.27 Supply and Ground
- 3.3 Pin Multiplexing
- 3.4 Connections for Unused Pins
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On-Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.6 Thermal Data for GWT Package
- 4.7
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 4.7.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 4.7.2 Power Supply Sequencing
- 4.7.3 Reset Timing
- 4.7.4 Clock Specifications
- 4.7.5 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 4.7.6
Peripherals
- 4.7.6.1 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 4.7.6.2 Enhanced Direct Memory Access Controller (EDMA3)
- 4.7.6.3 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 4.7.6.4
DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller
- 4.7.6.4.1 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- 4.7.6.4.2 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Register Description(s)
- 4.7.6.4.3
DDR2/mDDR Interface
- 4.7.6.4.3.1 DDR2/mDDR Interface Schematic
- 4.7.6.4.3.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR2/mDDR Devices
- 4.7.6.4.3.3 PCB Stackup
- 4.7.6.4.3.4 Placement
- 4.7.6.4.3.5 DDR2/mDDR Keep Out Region
- 4.7.6.4.3.6 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 4.7.6.4.3.7 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 4.7.6.4.3.8 Net Classes
- 4.7.6.4.3.9 DDR2/mDDR Signal Termination
- 4.7.6.4.3.10 VREF Routing
- 4.7.6.4.3.11 DDR2/mDDR CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 4.7.6.4.3.12 DDR2/mDDR Boundary Scan Limitations
- 4.7.6.5 Memory Protection Units
- 4.7.6.6 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD0, MMCSD1)
- 4.7.6.7 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
- 4.7.6.8 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 4.7.6.9 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.7.6.10 Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
- 4.7.6.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C)
- 4.7.6.12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 4.7.6.13 Universal Serial Bus OTG Controller (USB0) [USB2.0 OTG]
- 4.7.6.14 Universal Serial Bus Host Controller (USB1) [USB1.1 OHCI]
- 4.7.6.15 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 4.7.6.16 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 4.7.6.17 LCD Controller (LCDC)
- 4.7.6.18 Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 4.7.6.19 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
- 4.7.6.20 Video Port Interface (VPIF)
- 4.7.6.21 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 4.7.6.22 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
- 4.7.6.23 Timers
- 4.7.6.24 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- 4.7.6.25 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.7.6.26 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 4.7.7 Emulation and Debug
- 5Detailed Description
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- GWT|361
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
3 Terminal Configuration and Functions
Extensive use of pin multiplexing is used to accommodate the largest number of peripheral functions in the smallest possible package. Pin multiplexing is controlled using a combination of hardware configuration at device reset and software programmable register settings. See Section 3.3 for details.
3.1 Pin Diagram
Figure 3-1, Figure 3-2, Figure 3-3, and Figure 3-4 show the bottom view of the GWT package pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D).
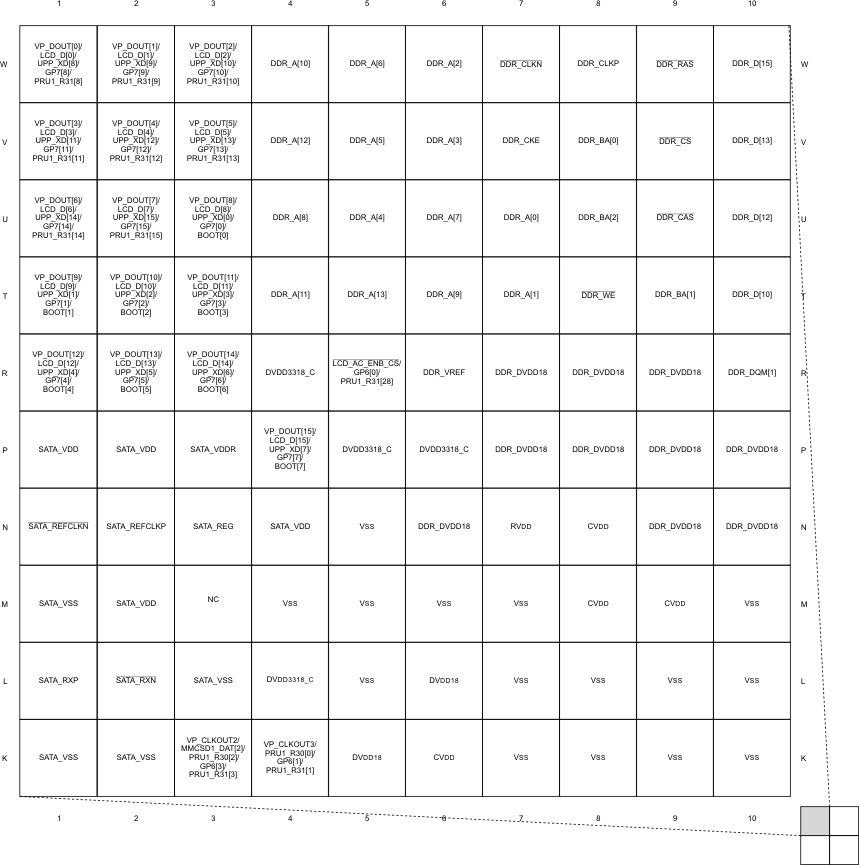 Figure 3-1 Pin Map (Quad A)
Figure 3-1 Pin Map (Quad A)
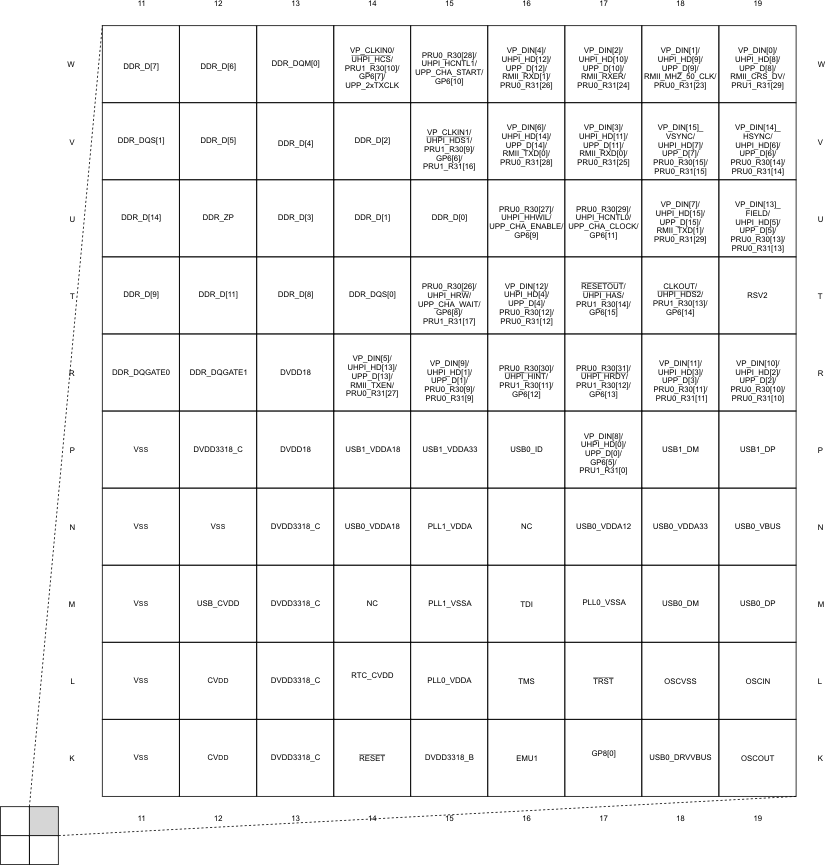 Figure 3-2 Pin Map (Quad B)
Figure 3-2 Pin Map (Quad B)
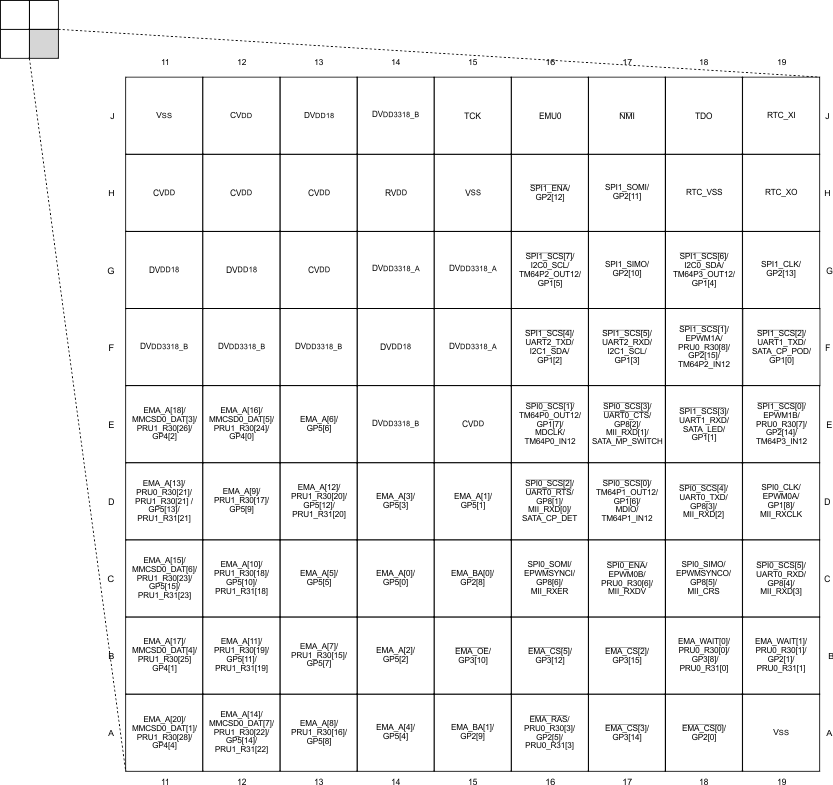 Figure 3-3 Pin Map (Quad C)
Figure 3-3 Pin Map (Quad C)
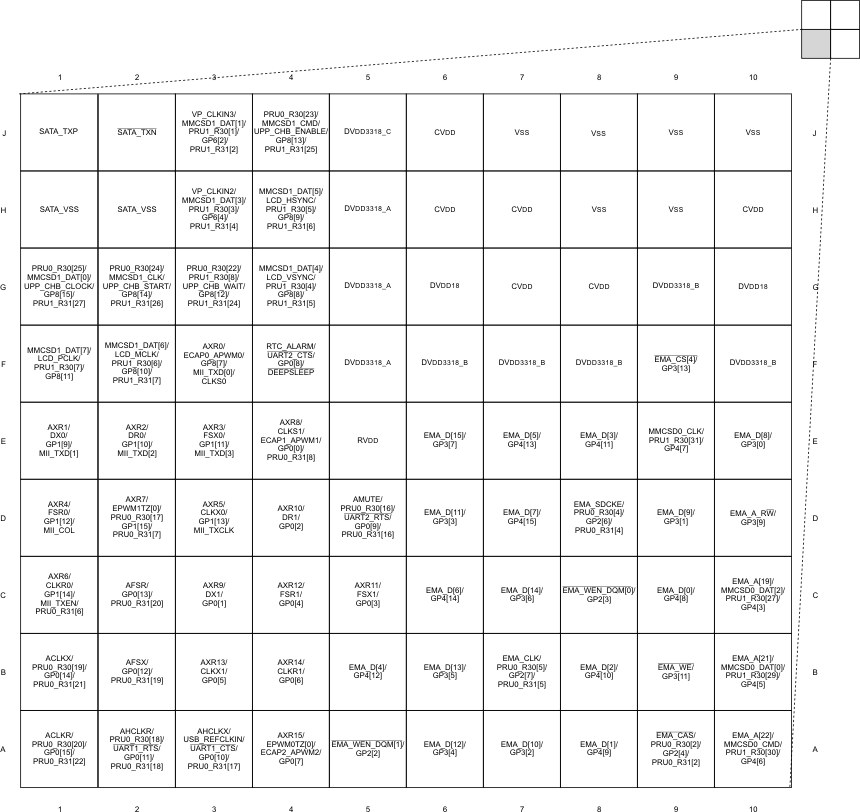 Figure 3-4 Pin Map (Quad D)
Figure 3-4 Pin Map (Quad D)
3.2 Pin Attributes
Table 3-1 to Table 3-27 identify the external signal names, the associated pin/ball numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type (I, O, IO, OZ, or PWR), whether the pin/ball has any internal pullup/pulldown resistors, whether the pin/ball is configurable as an IO in GPIO mode, and a functional pin description.
3.2.1 Device Reset, NMI and JTAG
Table 3-1 Reset, NMI and JTAG Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(4) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| RESET | |||||
| RESET | K14 | I | IPU | B | Device reset input |
| NMI | J17 | I | IPU | B | Non-Maskable Interrupt |
| RESETOUT / UHPI_HAS / PRU1_R30[14] / GP6[15] | T17 | O(3) | CP[21] | C | Reset output |
| JTAG | |||||
| TMS | L16 | I | IPU | B | JTAG test mode select |
| TDI | M16 | I | IPU | B | JTAG test data input |
| TDO | J18 | O | IPU | B | JTAG test data output |
| TCK | J15 | I | IPU | B | JTAG test clock |
| TRST | L17 | I | IPD | B | JTAG test reset |
| EMU0 | J16 | I/O | IPU | B | Emulation pin |
| EMU1 | K16 | I/O | IPU | B | Emulation pin |
Note: For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
Table 3-2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| CLKOUT / UHPI_HDS2 / PRU1_R30[13] / GP6[14] | T18 | O | CP[22] | C | PLL Observation Clock |
| 1.2-V OSCILLATOR | |||||
| OSCIN | L19 | I | — | — | Oscillator input |
| OSCOUT | K19 | O | — | — | Oscillator output |
| OSCVSS | L18 | GND | — | — | Oscillator ground |
| 1.2-V PLL0 | |||||
| PLL0_VDDA | L15 | PWR | — | — | PLL analog VDD (1.2-V filtered supply) |
| PLL0_VSSA | M17 | GND | — | — | PLL analog VSS (for filter) |
| 1.2-V PLL1 | |||||
| PLL1_VDDA | N15 | PWR | — | — | PLL analog VDD (1.2-V filtered supply) |
| PLL1_VSSA | M15 | GND | — | — | PLL analog VSS (for filter) |
Note: For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.3 Real-Time Clock and 32-kHz Oscillator
Table 3-3 Real-Time Clock (RTC) and 1.2-V, 32-kHz Oscillator Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| RTC_XI | J19 | I | — | — | RTC 32-kHz oscillator input |
| RTC_XO | H19 | O | — | — | RTC 32-kHz oscillator output |
| RTC_ALARM / UART2_CTS / GP0[8] / DEEPSLEEP | F4 | O | CP[0] | A | RTC Alarm |
| RTC_CVDD | L14 | PWR | — | — | RTC module core power (isolated from chip CVDD) |
| RTC_Vss | H18 | GND | — | — | Oscillator ground |
Note: For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.4 DEEPSLEEP Power Control
Table 3-4 DEEPSLEEP Power Control Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| RTC_ALARM / UART2_CTS / GP0[8] / DEEPSLEEP | F4 | I | CP[0] | A | DEEPSLEEP power control output |
Note: For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.5 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
Table 3-5 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| EMA_D[15] / GP3[7] | E6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | EMIFA data bus |
| EMA_D[14] / GP3[6] | C7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[13] / GP3[5] | B6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[12] / GP3[4] | A6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[11] / GP3[3] | D6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[10] / GP3[2] | A7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[9] / GP3[1] | D9 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[8] / GP3[0] | E10 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[7] / GP4[15] | D7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[6] / GP4[14] | C6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[5] / GP4[13] | E7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[4] / GP4[12] | B5 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[3] / GP4[11] | E8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[2] / GP4[10] | B8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[1] / GP4[9] | A8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[0] / GP4[8] | C9 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_A[22] / MMCSD0_CMD / PRU1_R30[30] / GP4[6] | A10 | O | CP[18] | B | EMIFA address bus |
| EMA_A[21] / MMCSD0_DAT[0] / PRU1_R30[29] / GP4[5] | B10 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[20] / MMCSD0_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[28] / GP4[4] | A11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[19] / MMCSD0_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[27] / GP4[3] | C10 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[18] / MMCSD0_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[26] / GP4[2] | E11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[17] / MMCSD0_DAT[4] / PRU1_R30[25] / GP4[1] | B11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[16] / MMCSD0_DAT[5] / PRU1_R30[24] / GP4[0] | E12 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[15] / MMCSD0_DAT[6] / PRU1_R30[23] / GP5[15] / PRU1_R31[23] | C11 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[14] / MMCSD0_DAT[7] / PRU1_R30[22] / GP5[14] / PRU1_R31[22] | A12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[13] / PRU0_R30[21] / PRU1_R30[21] / GP5[13] / PRU1_R31[21] | D11 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[12] / PRU1_R30[20] / GP5[12] / PRU1_R31[20] | D13 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[11] / PRU1_R30[19] / GP5[11] / PRU1_R31[19] | B12 | O | CP[19] | B | EMIFA address bus |
| EMA_A[10] / PRU1_R30[18] / GP5[10] / PRU1_R31[18] | C12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[9] / PRU1_R30[17] / GP5[9] | D12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[8] / PRU1_R30[16] / GP5[8] | A13 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[7] / PRU1_R30[15] / GP5[7] | B13 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[6] / GP5[6] | E13 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[5] / GP5[5] | C13 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[4] / GP5[4] | A14 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[3] / GP5[3] | D14 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[2] / GP5[2] | B14 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[1] / GP5[1] | D15 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[0] / GP5[0] | C14 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_BA[0] / GP2[8] | C15 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA bank address |
| EMA_BA[1] / GP2[9] | A15 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CLK / PRU0_R30[5] / GP2[7] / PRU0_R31[5] | B7 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA clock |
| EMA_SDCKE / PRU0_R30[4] / GP2[6] / PRU0_R31[4] | D8 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA SDRAM clock enable |
| EMA_RAS / PRU0_R30[3] / GP2[5] / PRU0_R31[3] | A16 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA SDRAM row address strobe |
| EMA_CAS / PRU0_R30[2] / GP2[4] / PRU0_R31[2] | A9 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA SDRAM column address strobe |
| EMA_CS[0] / GP2[0] | A18 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA SDRAM Chip Select |
| EMA_CS[2] / GP3[15] | B17 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA Async chip select |
| EMA_CS[3] / GP3[14] | A17 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CS[4] / GP3[13] | F9 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CS[5] / GP3[12] | B16 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_A_RW / GP3[9] | D10 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA Async Read/Write control |
| EMA_WE / GP3[11] | B9 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA SDRAM write enable |
| EMA_WEN_DQM[1] / GP2[2] | A5 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA write enable/data mask for EMA_D[15:8] |
| EMA_WEN_DQM[0] / GP2[3] | C8 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA write enable/data mask for EMA_D[7:0] |
| EMA_OE / GP3[10] | B15 | O | CP[16] | B | EMIFA output enable |
| EMA_WAIT[0] / PRU0_R30[0] / GP3[8] / PRU0_R31[0] | B18 | I | CP[16] | B | EMIFA wait input/interrupt |
| EMA_WAIT[1] / PRU0_R30[1] / GP2[1] / PRU0_R31[1] | B19 | I | CP[16] | B |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.6 DDR2/mDDR Controller
Table 3-6 DDR2/mDDR Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| DDR_D[15] | W10 | I/O | IPD | DDR2 SDRAM data bus |
| DDR_D[14] | U11 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[13] | V10 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[12] | U10 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[11] | T12 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[10] | T10 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[9] | T11 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[8] | T13 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[7] | W11 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[6] | W12 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[5] | V12 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[4] | V13 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[3] | U13 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[2] | V14 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[1] | U14 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_D[0] | U15 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[13] | T5 | O | IPD | DDR2 row/column address |
| DDR_A[12] | V4 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[11] | T4 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[10] | W4 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[9] | T6 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[8] | U4 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[7] | U6 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[6] | W5 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[5] | V5 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[4] | U5 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[3] | V6 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[2] | W6 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[1] | T7 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_A[0] | U7 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_CLKP | W8 | O | IPD | DDR2 clock (positive) |
| DDR_CLKN | W7 | O | IPD | DDR2 clock (negative) |
| DDR_CKE | V7 | O | IPD | DDR2 clock enable |
| DDR_WE | T8 | O | IPD | DDR2 write enable |
| DDR_RAS | W9 | O | IPD | DDR2 row address strobe |
| DDR_CAS | U9 | O | IPD | DDR2 column address strobe |
| DDR_CS | V9 | O | IPD | DDR2 chip select |
| DDR_DQM[0] | W13 | O | IPD | DDR2 data mask outputs |
| DDR_DQM[1] | R10 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_DQS[0] | T14 | I/O | IPD | DDR2 data strobe inputs/outputs |
| DDR_DQS[1] | V11 | I/O | IPD | |
| DDR_BA[2] | U8 | O | IPD | DDR2 SDRAM bank address |
| DDR_BA[1] | T9 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_BA[0] | V8 | O | IPD | |
| DDR_DQGATE0 | R11 | O | IPD | DDR2 loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to DDR_DQGATE1 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data. |
| DDR_DQGATE1 | R12 | I | IPD | DDR2 loopback signal for external DQS gating. Route to DDR and back to DDR_DQGATE0 with same constraints as used for DDR clock and data. |
| DDR_ZP | U12 | O | — | DDR2 reference output for drive strength calibration of N and P channel outputs. Tie to ground via 50 ohm resistor @ 5% tolerance. |
| DDR_VREF | R6 | I | — | DDR voltage input for the DDR2/mDDR I/O buffers. Note even in the case of mDDR an external resistor divider connected to this pin is necessary. |
| DDR_DVDD18 | N6, N9, N10, P7, P8, P9, P10, R7, R8, R9 | PWR | — | DDR PHY 1.8V power supply pins |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.7 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI)
Table 3-7 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| SPI0 | |||||
| SPI0_CLK / EPWM0A / GP1[8] / MII_RXCLK | D19 | I/O | CP[7] | A | SPI0 clock |
| SPI0_ENA / EPWM0B / PRU0_R30[6] / MII_RXDV | C17 | I/O | CP[7] | A | SPI0 enable |
| SPI0_SCS[0] / TM64P1_OUT12 / GP1[6] / MDIO / TM64P1_IN12 | D17 | I/O | CP[10] | A | SPI0 chip selects |
| SPI0_SCS[1] / TM64P0_OUT12 / GP1[7] / MDCLK / TM64P0_IN12 | E16 | I/O | CP[10] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[2] / UART0_RTS / GP8[1] / MII_RXD[0] /SATA_CP_DET | D16 | I/O | CP[9] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[3] / UART0_CTS / GP8[2] / MII_RXD[1] / SATA_MP_SWITCH | E17 | I/O | CP[9] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[4] / UART0_TXD / GP8[3] / MII_RXD[2] | D18 | I/O | CP[8] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[5] / UART0_RXD / GP8[4] / MII_RXD[3] | C19 | I/O | CP[8] | A | |
| SPI0_SIMO / EPWMSYNCO / GP8[5] / MII_CRS | C18 | I/O | CP[7] | A | SPI0 data slave-in-master-out |
| SPI0_SOMI / EPWMSYNCI / GP8[6] / MII_RXER | C16 | I/O | CP[7] | A | SPI0 data slave-out-master-in |
| SPI1 | |||||
| SPI1_CLK / GP2[13] | G19 | I/O | CP[15] | A | SPI1 clock |
| SPI1_ENA / GP2[12] | H16 | I/O | CP[15] | A | SPI1 enable |
| SPI1_SCS[0] / EPWM1B / PRU0_R30[7] / GP2[14] / TM64P3_IN12 | E19 | I/O | CP[14] | A | SPI1 chip selects |
| SPI1_SCS[1] / EPWM1A / PRU0_R30[8] / GP2[15] / TM64P2_IN12 | F18 | I/O | CP[14] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[2] / UART1_TXD / SATA_CP_POD / GP1[0] | F19 | I/O | CP[13] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[3] / UART1_RXD / SATA_LED / GP1[1] | E18 | I/O | CP[13] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[4] / UART2_TXD / I2C1_SDA / GP1[2] | F16 | I/O | CP[12] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[5] / UART2_RXD / I2C1_SCL / GP1[3] | F17 | I/O | CP[12] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[6] / I2C0_SDA / TM64P3_OUT12 / GP1[4] | G18 | I/O | CP[11] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[7] / I2C0_SCL / TM64P2_OUT12 / GP1[5] | G16 | I/O | CP[11] | A | |
| SPI1_SIMO / GP2[10] | G17 | I/O | CP[15] | A | SPI1 data slave-in-master-out |
| SPI1_SOMI / GP2[11] | H17 | I/O | CP[15] | A | SPI1 data slave-out-master-in |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.8 Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU)
Table 3-8 Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| PRU0_R30[31] / UHPI_HRDY / PRU1_R30[12] / GP6[13] | R17 | O | CP[23] | C | PRU0 Output Signals |
| PRU0_R30[30] / UHPI_HINT / PRU1_R30[11] / GP6[12] | R16 | O | CP[23] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[29]/ UHPI_HCNTL0 / UPP_CHA_CLOCK / GP6[11] | U17 | O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[28] / UHPI_HCNTL1 / UPP_CHA_START / GP6[10] | W15 | O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[27] / UHPI_HHWIL / UPP_CHA_ENABLE / GP6[9] | U16 | O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[26] / UHPI_HRW / UPP_CHA_WAIT / GP6[8] / PRU1_R31[17] | T15 | O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[25] / MMCSD1_DAT[0] / UPP_CHB_CLOCK / GP8[15] / PRU1_R31[27] | G1 | O | CP30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[24] / MMCSD1_CLK / UPP_CHB_START / GP8[14] / PRU1_R31[26] | G2 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[23] / MMCSD1_CMD / UPP_CHB_ENABLE / GP8[13] / PRU1_R31[25] | J4 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[22] / PRU1_R30[8]UPP_CHB_WAIT / / GP8[12] / PRU1_R31[24] | G3 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| EMA_A[13] / PRU0_R30[21] / PRU1_R30[21] / GP5[13] / PRU1_R31[21] | D11 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| ACLKR / PRU0_R30[20] / GP0[15] / PRU0_R31[22] | A1 | O | CP[0] | A | |
| ACLKX / PRU0_R30[19] / GP0[14] / PRU0_R31[21] | B1 | O | CP[0] | A | |
| AHCLKR / PRU0_R30[18] / UART1_RTS / GP0[11] / PRU0_R31[18] | A2 | O | CP[0] | A | |
| AXR7 / EPWM1TZ[0] / PRU0_R30[17] / GP1[15] / PRU0_R31[7] | D2 | O | CP[4] | A | |
| AMUTE / PRU0_R30[16] / UART2_RTS / GP0[9] / PRU0_R31[16] | D5 | O | CP[0] | A | PRU0 Output Signals |
| VP_DIN[15]_VSYNC / UHPI_HD[7] / UPP_D[7] / PRU0_R30[15] / PRU0_R31[15] | V18 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[14]_HSYNC / UHPI_HD[6] / UPP_D[6] / PRU0_R30[14] / PRU0_R31[14] | V19 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[13]_FIELD / UHPI_HD[5] / UPP_D[5] / PRU0_R30[13] / PRU0_R31[13] | U19 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[12] / UHPI_HD[4] / UPP_D[4] / PRU0_R30[12] / PRU0_R31[12] | T16 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[11] / UHPI_HD[3] / UPP_D[3] / PRU0_R30[11] / PRU0_R31[11] | R18 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[10] / UHPI_HD[2] / UPP_D[2] / PRU0_R30[10] / PRU0_R31[10] | R19 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[9] / UHPI_HD[1] / UPP_D[1] / PRU0_R30[9] / PRU0_R31[9] | R15 | O | CP[27] | C | |
| SPI1_SCS[1] / EPWM1A / PRU0_R30[8] / GP2[15] / TM64P2_IN12 | F18 | O | CP[14] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[0] / EPWM1B / PRU0_R30[7] / GP2[14] / TM64P3_IN12 | E19 | O | CP[14] | A | |
| SPI0_ENA / EPWM0B / PRU0_R30[6] / MII_RXDV | C17 | O | CP[7] | A | |
| EMA_CLK / PRU0_R30[5] / GP2[7] / PRU0_R31[5] | B7 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_SDCKE / PRU0_R30[4] / GP2[6] / PRU0_R31[4] | D8 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_RAS / PRU0_R30[3] / GP2[5] / PRU0_R31[3] | A16 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CAS / PRU0_R30[2] / GP2[4] / PRU0_R31[2] | A9 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[1] / PRU0_R30[1] / GP2[1] / PRU0_R31[1] | B19 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[0] / PRU0_R30[0] / GP3[8] / PRU0_R31[0] | B18 | O | CP[16] | B | |
| VP_DIN[7] / UHPI_HD[15] / UPP_D[15] / RMII_TXD[1] / PRU0_R31[29] | U18 | I | CP[26] | C | PRU0 Input Signals |
| VP_DIN[6] / UHPI_HD[14] / UPP_D[14] / RMII_TXD[0] / PRU0_R31[28] | V16 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[5] / UHPI_HD[13] / UPP_D[13] / RMII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[27] | R14 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[4] / UHPI_HD[12] / UPP_D[12] / RMII_RXD[1] / PRU0_R31[26] | W16 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[3] / UHPI_HD[11] / UPP_D[11] / RMII_RXD[0] / PRU0_R31[25] | V17 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[2] / UHPI_HD[10] / UPP_D[10] / RMII_RXER / PRU0_R31[24] | W17 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[1] / UHPI_HD[9] / UPP_D[9] / RMII_MHZ_50_CLK / PRU0_R31[23] | W18 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| ACLKR / PRU0_R30[20] / GP0[15] / PRU0_R31[22] | A1 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| ACLKX / PRU0_R30[19] / GP0[14] / PRU0_R31[21] | B1 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| AFSR / GP0[13] / PRU0_R31[20] | C2 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| AFSX / GP0[12] / PRU0_R31[19] | B2 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| AHCLKR / PRU0_R30[18] / UART1_RTS / GP0[11] / PRU0_R31[18] | A2 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] | A3 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| AMUTE / PRU0_R30[16] / UART2_RTS / GP0[9] / PRU0_R31[16] | D5 | I | CP[0] | A | |
| VP_DIN[15]_VSYNC / UHPI_HD[7] / UPP_D[7] / PRU0_R30[15] / PRU0_R31[15] | V18 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[14]_HSYNC / UHPI_HD[6] / UPP_D[6] / PRU0_R30[14] / PRU0_R31[14] | V19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[13]_FIELD / UHPI_HD[5] / UPP_D[5] / PRU0_R30[13] / PRU0_R31[13] | U19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[12] / UHPI_HD[4] / UPP_D[4] / PRU0_R30[12] / PRU0_R31[12] | T16 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[11] / UHPI_HD[3] / UPP_D[3] / PRU0_R30[11] / PRU0_R31[11] | R18 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[10] / UHPI_HD[2] / UPP_D[2] / PRU0_R30[10] / PRU0_R31[10] | R19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[9] / UHPI_HD[1] / UPP_D[1] / PRU0_R30[9] / PRU0_R31[9] | R15 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| AXR8 / CLKS1 / ECAP1_APWM1 / GP0[0] / PRU0_R31[8] | E4 | I | CP[3] | A | |
| AXR7 / EPWM1TZ[0] / PRU0_R30[17] / GP1[15] / PRU0_R31[7] | D2 | I | CP[4] | A | |
| AXR6 / CLKR0 / GP1[14] / MII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[6] | C1 | I | CP[5] | A | |
| EMA_CLK / PRU0_R30[5] / GP2[7] / PRU0_R31[5] | B7 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_SDCKE / PRU0_R30[4] / GP2[6] / PRU0_R31[4] | D8 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_RAS / PRU0_R30[3] / GP2[5] / PRU0_R31[3] | A16 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CAS / PRU0_R30[2] / GP2[4] / PRU0_R31[2] | A9 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[1] / PRU0_R30[1] / GP2[1] / PRU0_R31[1] | B19 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[0] / PRU0_R30[0] / GP3[8] / PRU0_R31[0] | B18 | I | CP[16] | B | |
| MMCSD0_CLK / PRU1_R30[31] /GP4[7] | E9 | O | CP[18] | B | PRU1 Output Signals |
| EMA_A[22] / MMCSD0_CMD / PRU1_R30[30] / GP4[6] | A10 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[21] / MMCSD0_DAT[0] / PRU1_R30[29] / GP4[5] | B10 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[20] / MMCSD0_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[28] / GP4[4] | A11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[19] / MMCSD0_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[27] / GP4[3] | C10 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[18] / MMCSD0_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[26] / GP4[2] | E11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[17] / MMCSD0_DAT[4] / PRU1_R30[25] / GP4[1] | B11 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[16] / MMCSD0_DAT[5] / PRU1_R30[24] / GP4[0] | E12 | O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[15] / MMCSD0_DAT[6] / PRU1_R30[23] / GP5[15] / PRU1_R31[23] | C11 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[14] / MMCSD0_DAT[7] / PRU1_R30[22] / GP5[14] / PRU1_R31[22] | A12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[13] / PRU0_R30[21] / PRU1_R30[21] / GP5[13] / PRU1_R31[21] | D11 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[12] / PRU1_R30[20] / GP5[12] / PRU1_R31[20] | D13 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[11] / PRU1_R30[19] / GP5[11] / PRU1_R31[19] | B12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[10] / PRU1_R30[18] / GP5[10] / PRU1_R31[18] | C12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[9] / PRU1_R30[17] / GP5[9] | D12 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[8] / PRU1_R30[16] / GP5[8] | A13 | O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[7] / PRU1_R30[15] / GP5[7] | B13 | O | CP[20] | B | |
| RESETOUT / UHPI_HAS / PRU1_R30[14] / GP6[15] | T17 | O | CP[21] | C | |
| CLKOUT / UHPI_HDS2 / PRU1_R30[13] / GP6[14] | T18 | O | CP[22] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[31] / UHPI_HRDY / PRU1_R30[12] / GP6[13] | R17 | O | CP[23] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[30] / UHPI_HINT / PRU1_R30[11] / GP6[12] | R16 | O | CP[23] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN0 / UHPI_HCS / PRU1_R30[10] / GP6[7] / UPP_2xTXCLK | W14 | O | CP[25] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN1 / UHPI_HDS1 / PRU1_R30[9] / GP6[6] / PRU1_R31[16] | V15 | O | CP[25] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[22] / PRU1_R30[8] / UPP_CHB_WAIT / GP8[12] / PRU1_R31[24] | G3 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[7] / LCD_PCLK / PRU1_R30[7] / GP8[11] | F1 | O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[6] / LCD_MCLK / PRU1_R30[6] / GP8[10] / PRU1_R31[7] | F2 | O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[5] / LCD_HSYNC / PRU1_R30[5] / GP8[9] / PRU1_R31[6] | H4 | O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[4] / LCD_VSYNC / PRU1_R30[4] / GP8[8] / PRU1_R31[5] | G4 | O | CP[31] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN2 / MMCSD1_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[3] / GP6[4] / PRU1_R31[4] | H3 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT2 / MMCSD1_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[2] / GP6[3] / PRU1_R31[3] | K3 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN3 / MMCSD1_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[1] / GP6[2] / PRU1_R31[2] | J3 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT3 / PRU1_R30[0] / GP6[1] / PRU1_R31[1] | K4 | O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_DIN[0] / UHPI_HD[8] / UPP_D[8] / RMII_CRS_DV / PRU1_R31[29] | W19 | I | CP[26] | C | PRU1 Input Signals |
| LCD_AC_ENB_CS / GP6[0] / PRU1_R31[28] | R5 | I | CP[31] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[25] / MMCSD1_DAT[0] / UPP_CHB_CLOCK / GP8[15] / PRU1_R31[27] | G1 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[24] / MMCSD1_CLK / UPP_CHB_START / GP8[14] / PRU1_R31[26] | G2 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[23] / MMCSD1_CMD / UPP_CHB_ENABLE / GP8[13] / PRU1_R31[25] | J4 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[22] / PRU1_R30[8] / UPP_CHB_WAIT / GP8[12] / PRU1_R31[24] | G3 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| EMA_A[15]/MMCSD0_DAT[6]/PRU1_R30[23]/GP5[15]/PRU1_R31[23] | C11 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[14]/MMCSD0_DAT[7]/PRU1_R30[22]/GP5[14]/PRU1_R31[22] | A12 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[13]/PRU0_R30[21]/PRU1_R30[21]/GP5[13]/PRU1_R31[21] | D11 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[12]/PRU1_R30[20]/GP5[12]/PRU1_R31[20] | D13 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[11]/PRU1_R30[19]/GP5[11]/PRU1_R31[19] | B12 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[10]/PRU1_R30[18]/GP5[10]/PRU1_R31[18] | C12 | I | CP[19] | B | |
| PRU0_R30[26] / UHPI_HRW / UPP_CHA_WAIT / GP6[8] / PRU1_R31[17] | T15 | I | CP[24] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN1 / UHPI_HDS1 / PRU1_R30[9] / GP6[6] / PRU1_R31[16] | V15 | I | CP[25] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[7] / LCD_D[7] / UPP_XD[15] / GP7[15] / PRU1_R31[15] | U2 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[6] / LCD_D[6] / UPP_XD[14] / GP7[14] / PRU1_R31[14] | U1 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[5] / LCD_D[5] / UPP_XD[13] / GP7[13] / PRU1_R31[13] | V3 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[4] / LCD_D[4] / UPP_XD[12] / GP7[12] / PRU1_R31[12] | V2 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[3] / LCD_D[3] / UPP_XD[11] / GP7[11] / PRU1_R31[11] | V1 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[2] / LCD_D[2] / UPP_XD[10] / GP7[10] / PRU1_R31[10] | W3 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[1] / LCD_D[1] / UPP_XD[9] / GP7[9] / PRU1_R31[9] | W2 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[0] / LCD_D[0] / UPP_XD[8] / GP7[8] / PRU1_R31[8] | W1 | I | CP[28] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[6] / LCD_MCLK / PRU1_R30[6] / GP8[10] / PRU1_R31[7] | F2 | I | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[5] / LCD_HSYNC / PRU1_R30[5] / GP8[9] / PRU1_R31[6] | H4 | I | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[4] / LCD_VSYNC / PRU1_R30[4] / GP8[8] / PRU1_R31[5] | G4 | I | CP[31] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN2 / MMCSD1_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[3] / GP6[4] / PRU1_R31[4] | H3 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT2 / MMCSD1_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[2] / GP6[3] / PRU1_R31[3] | K3 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN3 / MMCSD1_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[1] / GP6[2] / PRU1_R31[2] | J3 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT3 / PRU1_R30[0] / GP6[1] / PRU1_R31[1] | K4 | I | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_DIN[8] / UHPI_HD[0] / UPP_D[0] / GP6[5] / PRU1_R31[0] | P17 | I | CP[27] | C |
3.2.9 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0)
The eCAP Module pins function as either input captures or auxiliary PWM 32-bit outputs, depending upon how the eCAP module is programmed.
Table 3-9 Enhanced Capture Module (eCAP) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||||
| eCAP0 | ||||||
| AXR0 / ECAP0_APWM0 / GP8[7] / MII_TXD[0] / CLKS0 | F3 | I/O | CP[6] | A | enhanced capture 0 input or auxiliary PWM 0 output |
|
| eCAP1 | ||||||
| AXR8 / CLKS1 / ECAP1_APWM1 / GP0[0] / PRU0_R31[8] | E4 | I/O | CP[3] | A | enhanced capture 1 input or auxiliary PWM 1 output |
|
| eCAP2 | ||||||
| AXR15 / EPWM0TZ[0] / ECAP2_APWM2 / GP0[7] | A4 | I/O | CP[1] | A | enhanced capture 2 input or auxiliary PWM 2 output |
|
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.10 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM)
Table 3-10 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (eHRPWM) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| eHRPWM0 | |||||
| SPI0_CLK / EPWM0A / GP1[8] / MII_RXCLK | D19 | I/O | CP[7] | A | eHRPWM0 A output (with high-resolution) |
| SPI0_ENA / EPWM0B / PRU0_R30[6] / MII_RXDV | C17 | I/O | CP[7] | A | eHRPWM0 B output |
| AXR15 / EPWM0TZ[0] / ECAP2_APWM2 / GP0[7] | A4 | I | CP[1] | A | eHRPWM0 trip zone input |
| SPI0_SOMI / EPWMSYNCI / GP8[6] / MII_RXER | C16 | I | CP[7] | A | eHRPWM0 sync input |
| SPI0_SIMO / EPWMSYNCO / GP8[5] / MII_CRS | C18 | I/O | CP[7] | A | eHRPWM0 sync output |
| eHRPWM1 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[1] / EPWM1A / PRU0_R30[8] / GP2[15] / TM64P2_IN12 | F18 | I/O | CP[14] | A | eHRPWM1 A output (with high-resolution) |
| SPI1_SCS[0] / EPWM1B / PRU0_R30[7] / GP2[14] / TM64P3_IN12 | E19 | I/O | CP[14] | A | eHRPWM1 B output |
| AXR7 / EPWM1TZ[0] / PRU0_R30[17] / GP1[15] / PRU0_R31[7] | D2 | I | CP[4] | A | eHRPWM1 trip zone input |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.11 Boot
Table 3-11 Boot Mode Selection Terminal Functions(3)
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(4) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| VP_DOUT[15] / LCD_D[15] / UPP_XD[7] / GP7[7] / BOOT[7] | P4 | I | CP[29] | C | Boot Mode Selection Pins |
| VP_DOUT[14] / LCD_D[14] / UPP_XD[6] / GP7[6] / BOOT[6] | R3 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[13] / LCD_D[13] / UPP_XD[5] / GP7[5] / BOOT[5] | R2 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[12] / LCD_D[12] / UPP_XD[4] / GP7[4] / BOOT[4] | R1 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[11] / LCD_D[11] / UPP_XD[3] / GP7[3] / BOOT[3] | T3 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[10] / LCD_D[10] / UPP_XD[2] / GP7[2] / BOOT[2] | T2 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[9] / LCD_D[9] / UPP_XD[1] / GP7[1] / BOOT[1] | T1 | I | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[8] / LCD_D[8] / UPP_XD[0] / GP7[0] / BOOT[0] | U3 | I | CP[29] | C |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
Table 3-12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| UART0 | |||||
| SPI0_SCS[5] / UART0_RXD / GP8[4] / MII_RXD[3] | C19 | I | CP[8] | A | UART0 receive data |
| SPI0_SCS[4] / UART0_TXD / GP8[3] / MII_RXD[2] | D18 | O | CP[8] | A | UART0 transmit data |
| SPI0_SCS[2] / UART0_RTS / GP8[1] / MII_RXD[0] / SATA_CP_DET | D16 | O | CP[9] | A | UART0 ready-to-send output |
| SPI0_SCS[3] / UART0_CTS / GP8[2] / MII_RXD[1] / SATA_MP_SWITCH | E17 | I | CP[9] | A | UART0 clear-to-send input |
| UART1 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[3] / UART1_RXD / SATA_LED / GP1[1] | E18 | I | CP[13] | A | UART1 receive data |
| SPI1_SCS[2] / UART1_TXD / SATA_CP_POD / GP1[0] | F19 | O | CP[13] | A | UART1 transmit data |
| AHCLKR / PRU0_R30[18] / UART1_RTS /GP0[11] / PRU0_R31[18] | A2 | O | CP[0] | A | UART1 ready-to-send output |
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] |
A3 | I | CP[0] | A | UART1 clear-to-send input |
| UART2 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[5] / UART2_RXD / I2C1_SCL /GP1[3] | F17 | I | CP[12] | A | UART2 receive data |
| SPI1_SCS[4] / UART2_TXD / I2C1_SDA /GP1[2] | F16 | O | CP[12] | A | UART2 transmit data |
| AMUTE / PRU0_R30[16] / UART2_RTS / GP0[9] / PRU0_R31[16] | D5 | O | CP[0] | A | UART2 ready-to-send output |
| RTC_ALARM / UART2_CTS / GP0[8] / DEEPSLEEP | F4 | I | CP[0] | A | UART2 clear-to-send input |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
Table 3-13 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| I2C0 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[6] / I2C0_SDA / TM64P3_OUT12 / GP1[4] | G18 | I/O | CP[11] | A | I2C0 serial data |
| SPI1_SCS[7] / I2C0_SCL / TM64P2_OUT12 / GP1[5] | G16 | I/O | CP[11] | A | I2C0 serial clock |
| I2C1 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[4] / UART2_TXD / I2C1_SDA / GP1[2] | F16 | I/O | CP[12] | A | I2C1 serial data |
| SPI1_SCS[5] / UART2_RXD / I2C1_SCL / GP1[3] | F17 | I/O | CP[12] | A | I2C1 serial clock |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.14 Timers
Table 3-14 Timers Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||||
| TIMER0 | ||||||
| SPI0_SCS[1] / TM64P0_OUT12 / GP1[7] / MDCLK /TM64P0_IN12 | E16 | I | CP[10] | A | Timer0 lower input | |
| SPI0_SCS[1] / TM64P0_OUT12 / GP1[7] / MDCLK / TM64P0_IN12 | E16 | O | CP[10] | A | Timer0 lower output | |
| TIMER1 (Watchdog) | ||||||
| SPI0_SCS[0] / TM64P1_OUT12 / GP1[6] / MDIO / TM64P1_IN12 | D17 | I | CP[10] | A | Timer1 lower input | |
| SPI0_SCS[0] / TM64P1_OUT12 / GP1[6] / MDIO / TM64P1_IN12 | D17 | O | CP[10] | A | Timer1 lower output | |
| TIMER2 | ||||||
| SPI1_SCS[1] / EPWM1A / PRU0_R30[8] / GP2[15] / TM64P2_IN12 | F18 | I | CP[14] | A | Timer2 lower input | |
| SPI1_SCS[7] / I2C0_SCL / TM64P2_OUT12 / GP1[5] | G16 | O | CP[11] | A | Timer2 lower output | |
| TIMER3 | ||||||
| SPI1_SCS[0] / EPWM1B / PRU0_R30[7] / GP2[14] / TM64P3_IN12 | E19 | I | CP[14] | A | Timer3 lower input | |
| SPI1_SCS[6] / I2C0_SDA / TM64P3_OUT12 / GP1[4] | G18 | O | CP[11] | A | Timer3 lower output | |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP)
Table 3-15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||||
| McASP0 | ||||||
| AXR15 / EPWM0TZ[0] / ECAP2_APWM2 / GP0[7] | A4 | I/O | CP[1] | A | McASP0 serial data | |
| AXR14 / CLKR1 / GP0[6] | B4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR13 / CLKX1 / GP0[5] | B3 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR12 / FSR1 / GP0[4] | C4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR11 / FSX1 / GP0[3] | C5 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR10 / DR1 / GP0[2] | D4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR9 / DX1 / GP0[1] | C3 | I/O | CP[2] | A | ||
| AXR8 / CLKS1 / ECAP1_APWM1 / GP0[0] / PRU0_R31[8] | E4 | I/O | CP[3] | A | ||
| AXR7 / EPWM1TZ[0] / PRU0_R30[17] / GP1[15] / PRU0_R31[7] | D2 | I/O | CP[4] | A | ||
| AXR6 / CLKR0 / GP1[14] / MII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[6] | C1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR5 / CLKX0 / GP1[13] / MII_TXCLK | D3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR4 / FSR0 / GP1[12] / MII_COL | D1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR3 / FSX0 / GP1[11] / MII_TXD[3] | E3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR2 / DR0 / GP1[10] / MII_TXD[2] | E2 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR1 / DX0 / GP1[9] / MII_TXD[1] | E1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | ||
| AXR0 / ECAP0_APWM0 / GP8[7]/ MII_TXD[0] / CLKS0 | F3 | I/O | CP[6] | A | ||
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] | A3 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 transmit master clock | |
| ACLKX / PRU0_R30[19] / GP0[14] / PRU0_R31[21] | B1 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 transmit bit clock | |
| AFSX / GP0[12] / PRU0_R31[19] | B2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 transmit frame sync | |
| AHCLKR / PRU0_R30[18] / UART1_RTS / GP0[11] / PRU0_R31[18] | A2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 receive master clock | |
| ACLKR / PRU0_R30[20] / GP0[15] / PRU0_R31[22] | A1 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 receive bit clock | |
| AFSR / GP0[13] / PRU0_R31[20] | C2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 receive frame sync | |
| AMUTE / PRU0_R30[16] / UART2_RTS / GP0[9] / PRU0_R31[16] | D5 | I/O | CP[0] | A | McASP0 mute output | |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.16 Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports (McBSP)
Table 3-16 Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports (McBSPs) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(1) |
DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||||
| McBSP0 | ||||||
| AXR0 / ECAP0_APWM0 / GP8[7] / MII_TXD[0] / CLKS0 | F3 | I | CP[6] | A | McBSP0 sample rate generator clock input | |
| AXR6 / CLKR0 / GP1[14] / MII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[6] | C1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 receive clock | |
| AXR4 / FSR0 / GP1[12] / MII_COL | D1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 receive frame sync | |
| AXR2 / DR0 / GP1[10] / MII_TXD[2] | E2 | I | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 receive data | |
| AXR5 / CLKX0 / GP1[13] / MII_TXCLK | D3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 transmit clock | |
| AXR3 / FSX0 / GP1[11] / MII_TXD[3] | E3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 transmit frame sync | |
| AXR1 / DX0 / GP1[9] / MII_TXD[1] | E1 | O | CP[5] | A | McBSP0 transmit data | |
| McBSP1 | ||||||
| AXR8 / CLKS1 / ECAP1_APWM1 / GP0[0] / PRU0_R31[8] | E4 | I | CP[3] | A | McBSP1 sample rate generator clock input | |
| AXR14 / CLKR1 / GP0[6] | B4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 receive clock | |
| AXR12 / FSR1 / GP0[4] | C4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 receive frame sync | |
| AXR10 / DR1 / GP0[2] | D4 | I | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 receive data | |
| AXR13 / CLKX1 / GP0[5] | B3 | I/O | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 transmit clock | |
| AXR11 / FSX1 / GP0[3] | C5 | I/O | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 transmit frame sync | |
| AXR9 / DX1 / GP0[1] | C3 | O | CP[2] | A | McBSP1 transmit data | |
3.2.17 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0, USB1)
Table 3-17 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| USB0 2.0 OTG (USB0) | |||||
| USB0_DM | M18 | A | IPD | — | USB0 PHY data minus |
| USB0_DP | M19 | A | IPD | — | USB0 PHY data plus |
| USB0_VDDA33 | N18 | PWR | — | — | USB0 PHY 3.3-V supply |
| USB0_ID | P16 | A | — | — | USB0 PHY identification (mini-A or mini-B plug) |
| USB0_VBUS | N19 | A | — | — | USB0 bus voltage |
| USB0_DRVVBUS | K18 | 0 | IPD | B | USB0 controller VBUS control output. |
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] | A3 | I | CP[0] | A | USB_REFCLKIN. Optional clock input |
| USB0_VDDA18 | N14 | PWR | — | — | USB0 PHY 1.8-V supply input |
| USB0_VDDA12 | N17 | A | — | — | USB0 PHY 1.2-V LDO output for bypass cap For proper device operation, this pin must always be connected via a 0.22-μF capacitor to VSS (GND), even if USB0 is not being used. |
| USB_CVDD | M12 | PWR | — | — | USB0 and USB1 core logic 1.2-V supply input |
| USB1 1.1 OHCI (USB1) | |||||
| USB1_DM | P18 | A | — | — | USB1 PHY data minus |
| USB1_DP | P19 | A | — | — | USB1 PHY data plus |
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] | A3 | I | CP[0] | A | USB_REFCLKIN. Optional clock input |
| USB1_VDDA33 | P15 | PWR | — | — | USB1 PHY 3.3-V supply |
| USB1_VDDA18 | P14 | PWR | — | — | USB1 PHY 1.8-V supply |
| USB_CVDD | M12 | PWR | — | — | USB0 and USB1 core logic 1.2-V supply input |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.18 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
Table 3-18 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| MII | |||||
| AXR6 / CLKR0 / GP1[14] / MII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[6] | C1 | O | CP[5] | A | EMAC MII Transmit enable output |
| AXR5 / CLKX0 / GP1[13] / MII_TXCLK | D3 | I | CP[5] | A | EMAC MII Transmit clock input |
| AXR4 / FSR0 / GP1[12] / MII_COL | D1 | I | CP[5] | A | EMAC MII Collision detect input |
| AXR3 / FSX0 / GP1[11] / MII_TXD[3] | E3 | O | CP[5] | A | EMAC MII transmit data |
| AXR2 / DR0 / GP1[10] / MII_TXD[2] | E2 | O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR1 / DX0 / GP1[9] / MII_TXD[1] | E1 | O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR0 / ECAP0_APWM0 / GP8[7] / MII_TXD[0] / CLKS0 | F3 | O | CP[6] | A | |
| SPI0_SOMI / EPWMSYNCI / GP8[6] / MII_RXER | C16 | I | CP[7] | A | EMAC MII receive error input |
| SPI0_SIMO / EPWMSYNCO / GP8[5] / MII_CRS | C18 | I | CP[7] | A | EMAC MII carrier sense input |
| SPI0_CLK / EPWM0A / GP1[8] / MII_RXCLK | D19 | I | CP[7] | A | EMAC MII receive clock input |
| SPI0_ENA / EPWM0B / PRU0_R30[6] / MII_RXDV | C17 | I | CP[7] | A | EMAC MII receive data valid input |
| SPI0_SCS[5] /UART0_RXD / GP8[4] / MII_RXD[3] | C19 | I | CP[8] | A | EMAC MII receive data |
| SPI0_SCS[4] /UART0_TXD / GP8[3] / MII_RXD[2] | D18 | I | CP[8] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[3] / UART0_CTS / GP8[2] / MII_RXD[1] / SATA_MP_SWITCH | E17 | I | CP[9] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[2] / UART0_RTS / GP8[1] / MII_RXD[0] / SATA_CP_DET | D16 | I | CP[9] | A | |
| RMII | |||||
| VP_DIN[1] / UHPI_HD[9] / UPP_D[9] / RMII_MHZ_50_CLK / PRU0_R31[23] | W18 | I/O | CP[26] | C | EMAC 50-MHz clock input or output |
| VP_DIN[2] / UHPI_HD[10] / UPP_D[10] / RMII_RXER / PRU0_R31[24] | W17 | I | CP[26] | C | EMAC RMII receiver error |
| VP_DIN[3] / UHPI_HD[11] / UPP_D[11] / RMII_RXD[0] / PRU0_R31[25] | V17 | I | CP[26] | C | EMAC RMII receive data |
| VP_DIN[4] / UHPI_HD[12] / UPP_D[12] / RMII_RXD[1] /PRU0_R31[26] | W16 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[0] / UHPI_HD[8] / UPP_D[8] / RMII_CRS_DV / PRU1_R31[29] | W19 | I | CP[26] | C | EMAC RMII carrier sense data valid |
| VP_DIN[5] / UHPI_HD[13] / UPP_D[13] / RMII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[27] | R14 | O | CP[26] | C | EMAC RMII transmit enable |
| VP_DIN[6] / UHPI_HD[14] / UPP_D[14] / RMII_TXD[0] / PRU0_R31[28] | V16 | O | CP[26] | C | EMAC RMII transmit data |
| VP_DIN[7] / UHPI_HD[15] / UPP_D[15] / RMII_TXD[1] / PRU0_R31[29] | U18 | O | CP[26] | C | |
| MDIO | |||||
| SPI0_SCS[0] / TM64P1_OUT12 / GP1[6] / MDIO / TM64P1_IN12 | D17 | I/O | CP[10] | A | MDIO serial data |
| SPI0_SCS[1] / TM64P0_OUT12 / GP1[7] / MDCLK / TM64P0_IN12 | E16 | O | CP[10] | A | MDIO clock |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.19 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
Table 3-19 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| MMCSD0 | |||||
| MMCSD0_CLK / PRU1_R30[31] /GP4[7] | E9 | O | CP[18] | B | MMCSD0 Clock |
| EMA_A[22] / MMCSD0_CMD / PRU1_R30[30] / GP4[6] | A10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | MMCSD0 Command |
| EMA_A[14] / MMCSD0_DAT[7] / PRU1_R30[22] / GP5[14] / PRU1_R31[22] | A12 | I/O | CP[19] | B | MMC/SD0 data |
| EMA_A[15] / MMCSD0_DAT[6] / PRU1_R30[23] / GP5[15] / PRU1_R31[23] | C11 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[16] / MMCSD0_DAT[5] / PRU1_R30[24] / GP4[0] | E12 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[17] / MMCSD0_DAT[4] / PRU1_R30[25] / GP4[1] | B11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[18] / MMCSD0_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[26] / GP4[2] | E11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[19] / MMCSD0_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[27] / GP4[3] | C10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[20] / MMCSD0_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[28] / GP4[4] | A11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[21] / MMCSD0_DAT[0] / PRU1_R30[29] / GP4[5] | B10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| MMCSD1 | |||||
| PRU0_R30[24] / MMCSD1_CLK / UPP_CHB_START / GP8[14] / PRU1_R31[26]/ | G2 | O | CP[30] | C | MMCSD1 Clock |
| PRU0_R30[23] / MMCSD1_CMD / UPP_CHB_ENABLE / GP8[13] / PRU1_R31[25] | J4 | I/O | CP[30] | C | MMCSD1 Command |
| MMCSD1_DAT[7] / LCD_PCLK / PRU1_R30[7] / GP8[11] | F1 | I/O | CP[31] | C | MMC/SD1 data |
| MMCSD1_DAT[6] / LCD_MCLK / PRU1_R30[6] / GP8[10] / PRU1_R31[7] | F2 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[5] / LCD_HSYNC / PRU1_R30[5] / GP8[9] / PRU1_R31[6] | H4 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[4] / LCD_VSYNC / PRU1_R30[4] / GP8[8] / PRU1_R31[5] | G4 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN2 / MMCSD1_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[3] / GP6[4] / PRU1_R31[4] | H3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT2 / MMCSD1_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[2] / GP6[3] / PRU1_R31[3] | K3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN3 / MMCSD1_DAT[1]/ PRU1_R30[1] / GP6[2] / PRU1_R31[2] | J3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[25] / MMCSD1_DAT[0] / UPP_CHB_CLOCK / GP8[15]/ PRU1_R31[27] | G1 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.20 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCDC)
Table 3-20 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCDC) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| VP_DOUT[15] / LCD_D[15] / UPP_XD[7] / GP7[7] / BOOT[7] | P4 | I/O | CP[29] | C | LCD data bus |
| VP_DOUT[14] / LCD_D[14] / UPP_XD[6] / GP7[6] / BOOT[6] | R3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[13] / LCD_D[13] / UPP_XD[5] / GP7[5] / BOOT[5] | R2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[12] / LCD_D[12] / UPP_XD[4] / GP7[4] / BOOT[4] | R1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[11] / LCD_D[11] / UPP_XD[3] / GP7[3] / BOOT[3] | T3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[10] / LCD_D[10] / UPP_XD[2] / GP7[2] / BOOT[2] | T2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[9] / LCD_D[9] / UPP_XD[1] / GP7[1] / BOOT[1] | T1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[8] / LCD_D[8] / UPP_XD[0] / GP7[0] / BOOT[0] | U3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[7] / LCD_D[7] / UPP_XD[15] / GP7[15] / PRU1_R31[15] | U2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[6] / LCD_D[6] / UPP_XD[14] / GP7[14] / PRU1_R31[14] | U1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[5] / LCD_D[5] / UPP_XD[13] / GP7[13] / PRU1_R31[13] | V3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[4] / LCD_D[4] / UPP_XD[12] / GP7[12] / PRU1_R31[12] | V2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[3] / LCD_D[3] / UPP_XD[11] / GP7[11] / PRU1_R31[11] | V1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[2] / LCD_D[2] / UPP_XD[10] / GP7[10] / PRU1_R31[10] | W3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[1] / LCD_D[1] / UPP_XD[9] / GP7[9] / PRU1_R31[9] | W2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[0] / LCD_D[0] / UPP_XD[8] / GP7[8] / PRU1_R31[8] | W1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[7] / LCD_PCLK / PRU1_R30[7] / GP8[11] | F1 | O | CP[31] | C | LCD pixel clock |
| MMCSD1_DAT[5] / LCD_HSYNC / PRU1_R30[5] / GP8[9] / PRU1_R31[6] | H4 | O | CP[31] | C | LCD horizontal sync |
| MMCSD1_DAT[4] / LCD_VSYNC / PRU1_R30[4] / GP8[8] / PRU1_R31[5] | G4 | O | CP[31] | C | LCD vertical sync |
| LCD_AC_ENB_CS / GP6[0] / PRU1_R31[28] | R5 | O | CP[31] | C | LCD AC bias enable chip select |
| MMCSD1_DAT[6] / LCD_MCLK / PRU1_R30[6] / GP8[10] / PRU1_R31[7] | F2 | O | CP[31] | C | LCD memory clock |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.21 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
Table 3-21 Serial ATA Controller (SATA) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| SATA_RXP | L1 | I | — | — | SATA receive data (positive) |
| SATA_RXN | L2 | I | — | — | SATA receive data (negative) |
| SATA_TXP | J1 | O | — | — | SATA transmit data (positive) |
| SATA_TXN | J2 | O | — | — | SATA transmit data (negative) |
| SATA_REFCLKP | N2 | I | — | — | SATA PHY reference clock (positive) |
| SATA_REFCLKN | N1 | I | — | — | SATA PHY reference clock (negative) |
| SPI0_SCS[3] / UART0_CTS / GP8[2] / MII_RXD[1] / SATA_MP_SWITCH | E17 | I | CP[9] | A | SATA mechanical presence switch input |
| SPI0_SCS[2] / UART0_RTS / GP8[1] / MII_RXD[0] / SATA_CP_DET | D16 | I | CP[9] | A | SATA cold presence detect input |
| SPI1_SCS[2] / UART1_TXD / SATA_CP_POD / GP1[0] | F19 | O | CP[13] | A | SATA cold presence power-on output |
| SPI1_SCS[3] / UART1_RXD / SATA_LED / GP1[1] | E18 | O | CP[13] | A | SATA LED control output |
| SATA_REG | N3 | A | — | — | SATA PHY PLL regulator output. Requires an external 0.1uF filter capacitor. |
| SATA_VDDR | P3 | PWR | — | — | SATA PHY 1.8V internal regulator supply |
| SATA_VDD | M2, P1, P2, N4 | PWR | — | — | SATA PHY 1.2V logic supply |
| SATA_VSS | H1, H2, K1, K2, L3, M1 | GND | — | — | SATA PHY ground reference |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.22 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
Table 3-22 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| VP_DIN[7] / UHPI_HD[15] / UPP_D[15] / RMII_TXD[1] / PRU0_R31[29] | U18 | I/O | CP[26] | C | UHPI data bus |
| VP_DIN[6] / UHPI_HD[14] / UPP_D[14] / RMII_TXD[0] / PRU0_R31[28] | V16 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[5] / UHPI_HD[13] / UPP_D[13] / RMII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[27] | R14 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[4] / UHPI_HD[12] / UPP_D[12] / RMII_RXD[1] / PRU0_R31[26] | W16 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[3] / UHPI_HD[11] / UPP_D[11] / RMII_RXD[0] / PRU0_R31[25] | V17 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[2] / UHPI_HD[10] / UPP_D[10] / RMII_RXER / PRU0_R31[24] | W17 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[1] / UHPI_HD[9] / UPP_D[9] / RMII_MHZ_50_CLK / PRU0_R31[23] | W18 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[0] / UHPI_HD[8] / UPP_D[8] / RMII_CRS_DV / PRU1_R31[29] | W19 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[15]_VSYNC / UHPI_HD[7] / UPP_D[7] / PRU0_R30[15] / PRU0_R31[15] | V18 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[14]_HSYNC / UHPI_HD[6] / UPP_D[6] / PRU0_R30[14] / PRU0_R31[14] | V19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[13]_FIELD / UHPI_HD[5] / UPP_D[5] / PRU0_R30[13] / PRU0_R31[13] | U19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[12] / UHPI_HD[4] / UPP_D[4] / PRU0_R30[12] / PRU0_R31[12] | T16 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[11] / UHPI_HD[3] / UPP_D[3] / PRU0_R30[11] / PRU0_R31[11] | R18 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[10] / UHPI_HD[2] / UPP_D[2] / PRU0_R30[10] / PRU0_R31[10] | R19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[9] / UHPI_HD[1] / UPP_D[1] / PRU0_R30[9] / PRU0_R31[9] | R15 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[8] / UHPI_HD[0] / UPP_D[0] / GP6[5] / PRU1_R31[0] | P17 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[29] / UHPI_HCNTL0 / UPP_CHA_CLOCK / GP6[11] | U17 | I | CP[24] | C | UHPI access control |
| PRU0_R30[28] / UHPI_HCNTL1 / UPP_CHA_START / GP6[10] | W15 | I | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[27] / UHPI_HHWIL / UPP_CHA_ENABLE / GP6[9] | U16 | I | CP[24] | C | UHPI half-word identification control |
| PRU0_R30[26] / UHPI_HRW / UPP_CHA_WAIT / GP6[8]/PRU1_R31[17] | T15 | I | CP[24] | C | UHPI read/write |
| VP_CLKIN0 / UHPI_HCS / PRU1_R30[10] / GP6[7] / UPP_2xTXCLK | W14 | I | CP[25] | C | UHPI chip select |
| VP_CLKIN1 / UHPI_HDS1 / PRU1_R30[9] / GP6[6] / PRU1_R31[16] | V15 | I | CP[25] | C | UHPI data strobe |
| CLKOUT / UHPI_HDS2 / PRU1_R30[13] / GP6[14] | T18 | I | CP[22] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[30] / UHPI_HINT / PRU1_R30[11] / GP6[12] | R16 | O | CP[23] | C | UHPI host interrupt |
| PRU0_R30[31] / UHPI_HRDY / PRU1_R30[12] /GP6[13] | R17 | O | CP[23] | C | UHPI ready |
| RESETOUT / UHPI_HAS / PRU1_R30[14] / GP6[15] | T17 | I | CP[21] | C | UHPI address strobe |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.23 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
Table 3-23 Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| VP_CLKIN0 / UHPI_HCS /PRU1_R30[10] / GP6[7] / UPP_2xTXCLK | W14 | I | CP[25] | C | uPP 2x transmit clock input |
| PRU0_R30[25] /MMCSD1_DAT[0] / UPP_CHB_CLOCK / GP8[15]/PRU1_R31[27] | G1 | I/O | CP[30] | C | uPP channel B clock |
| PRU0_R30[24]/ MMCSD1_CLK / UPP_CHB_START / GP8[14] / PRU1_R31[26] | G2 | I/O | CP[30] | C | uPP channel B start |
| PRU0_R30[23] / MMCSD1_CMD / UPP_CHB_ENABLE / GP8[13]/PRU1_R31[25] | J4 | I/O | CP[30] | C | uPP channel B enable |
| PRU0_R30[22] / PRU1_R30[8] / UPP_CHB_WAIT / GP8[12]/ PRU1_R31[24] | G3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | uPP channel B wait |
| PRU0_R30[29] /UHPI_HCNTL0 / UPP_CHA_CLOCK / GP6[11] | U17 | I/O | CP[24] | C | uPP channel A clock |
| PRU0_R30[28] / UHPI_HCNTL1 / UPP_CHA_START / GP6[10] | W15 | I/O | CP[24] | C | uPP channel A start |
| PRU0_R30[27] / UHPI_HHWIL / UPP_CHA_ENABLE / GP6[9] | U16 | I/O | CP[24] | C | uPP channel A enable |
| PRU0_R30[26] /UHPI_HRW / UPP_CHA_WAIT / GP6[8] / PRU1_R31[17] | T15 | I/O | CP[24] | C | uPP channel A wait |
| VP_DOUT[7] / LCD_D[7] / UPP_XD[15] / GP7[15] / PRU1_R31[15] | U2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | uPP data bus |
| VP_DOUT[6] / LCD_D[6] / UPP_XD[14] / GP7[14] / PRU1_R31[14] | U1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[5] / LCD_D[5] / UPP_XD[13] / GP7[13] / PRU1_R31[13] | V3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[4] / LCD_D[4] / UPP_XD[12] / GP7[12] / PRU1_R31[12] | V2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[3] / LCD_D[3] / UPP_XD[11] / GP7[11] / PRU1_R31[11] | V1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[2] / LCD_D[2] / UPP_XD[10] / GP7[10] / PRU1_R31[10] | W3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[1] / LCD_D[1] / UPP_XD[9] / GP7[9] / PRU1_R31[9] | W2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[0] / LCD_D[0] / UPP_XD[8] / GP7[8] / PRU1_R31[8] | W1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[15] / LCD_D[15] / UPP_XD[7] / GP7[7] / BOOT[7] | P4 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[14] / LCD_D[14] / UPP_XD[6] / GP7[6] / BOOT[6] | R3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[13] / LCD_D[13] / UPP_XD[5] / GP7[5] / BOOT[5] | R2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[12] / LCD_D[12] / UPP_XD[4] / GP7[4] / BOOT[4] | R1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[11] / LCD_D[11] / UPP_XD[3] / GP7[3] / BOOT[3] | T3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[10] / LCD_D[10] / UPP_XD[2] / GP7[2] / BOOT[2] | T2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[9] / LCD_D[9] / UPP_XD[1] / GP7[1] / BOOT[1] | T1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[8] / LCD_D[8] / UPP_XD[0] / GP7[0] / BOOT[0] | U3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DIN[7] / UHPI_HD[15] / UPP_D[15] / RMII_TXD[1] / PRU0_R31[29] | U18 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[6] / UHPI_HD[14] / UPP_D[14] / RMII_TXD[0] / PRU0_R31[28] | V16 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[5] / UHPI_HD[13] / UPP_D[13] / RMII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[27] | R14 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[4] / UHPI_HD[12] / UPP_D[12] / RMII_RXD[1] / PRU0_R31[26] | W16 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[3] / UHPI_HD[11] / UPP_D[11] / RMII_RXD[0] / PRU0_R31[25] | V17 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[2] / UHPI_HD[10] / UPP_D[10] / RMII_RXER / PRU0_R31[24] | W17 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[1] / UHPI_HD[9] / UPP_D[9] / RMII_MHZ_50_CLK / PRU0_R31[23] | W18 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[0] / UHPI_HD[8] / UPP_D[8] / RMII_CRS_DV / PRU1_R31[29] | W19 | I/O | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[15]_VSYNC / UHPI_HD[7] / UPP_D[7]/PRU0_R30[15] / PRU0_R31[15] | V18 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[14]_HSYNC / UHPI_HD[6] / UPP_D[6]/ PRU0_R30[14] / PRU0_R31[14] | V19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[13]_FIELD / UHPI_HD[5] / UPP_D[5] /PRU0_R30[13] / PRU0_R31[13] | U19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[12] / UHPI_HD[4] / UPP_D[4]/ PRU0_R30[12] / PRU0_R31[12] | T16 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[11] / UHPI_HD[3] / UPP_D[3]/ PRU0_R30[11] / PRU0_R31[11] | R18 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[10] / UHPI_HD[2] / UPP_D[2]/ PRU0_R30[10] / PRU0_R31[10] | R19 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[9] / UHPI_HD[1] / UPP_D[1]/ PRU0_R30[9] / PRU0_R31[9] | R15 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[8] / UHPI_HD[0] / UPP_D[0] / GP6[5] / PRU1_R31[0] | P17 | I/O | CP[27] | C |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.24 Video Port Interface (VPIF)
Table 3-24 Video Port Interface (VPIF) Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| VIDEO INPUT | |||||
| VP_CLKIN0 / UHPI_HCS / PRU1_R30[10] / GP6[7] / UPP_2xTXCLK | W14 | I | CP[25] | C | VPIF capture channel 0 input clock |
| VP_CLKIN1 / UHPI_HDS1/PRU1_R30[9] / GP6[6] / PRU1_R31[16] | V15 | I | CP[25] | C | VPIF capture channel 1 input clock |
| VP_DIN[15]_VSYNC / UHPI_HD[7] / UPP_D[7] / PRU0_R30[15] / PRU0_R31[15] | V18 | I | CP[27] | C | VPIF capture data bus |
| VP_DIN[14]_HSYNC / UHPI_HD[6] / UPP_D[6] / RU0_R30[14] / PRU0_R31[14] | V19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[13]_FIELD / UHPI_HD[5] / UPP_D[5] / PRU0_R30[13] / PRU0_R31[13] | U19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[12] / UHPI_HD[4] / UPP_D[4] / PRU0_R30[12] / PRU0_R31[12] | T16 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[11] / UHPI_HD[3] / UPP_D[3] / PRU0_R30[11] / PRU0_R31[11] | R18 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[10] / UHPI_HD[2] / UPP_D[2] / PRU0_R30[10] / PRU0_R31[10] | R19 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[9] / UHPI_HD[1] / UPP_D[1] / PRU0_R30[9] / PRU0_R31[9] | R15 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[8] / UHPI_HD[0] / UPP_D[0] / GP6[5] / PRU1_R31[0] | P17 | I | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_DIN[7] / UHPI_HD[15] / UPP_D[15] / RMII_TXD[1] / PRU0_R31[29] | U18 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[6] / UHPI_HD[14] / UPP_D[14] / RMII_TXD[0] / PRU0_R31[28] | V16 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[5] / UHPI_HD[13] / UPP_D[13] / RMII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[27] | R14 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[4] / UHPI_HD[12] / UPP_D[12] / RMII_RXD[1] / PRU0_R31[26] | W16 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[3] / UHPI_HD[11] / UPP_D[11] / MII_RXD[0] / PRU0_R31[25] | V17 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[2] / UHPI_HD[10] / UPP_D[10] / RMII_RXER / PRU0_R31[24] | W17 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[1] / UHPI_HD[9] / UPP_D[9] / RMII_MHZ_50_CLK / PRU0_R31[23] | W18 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VP_DIN[0] / UHPI_HD[8] / UPP_D[8] / RMII_CRS_DV / PRU1_R31[29] | W19 | I | CP[26] | C | |
| VIDEO OUTPUT | |||||
| VP_CLKIN2 / MMCSD1_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[3] / GP6[4] / PRU1_R31[4] | H3 | I | CP[30] | C | VPIF display channel 2 input clock |
| VP_CLKOUT2 / MMCSD1_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[2] / GP6[3] / PRU1_R31[3] | K3 | O | CP[30] | C | VPIF display channel 2 output clock |
| VP_CLKIN3 / MMCSD1_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[1] / GP6[2] / PRU1_R31[2] | J3 | I | CP[30] | C | VPIF display channel 3 input clock |
| VP_CLKOUT3 / PRU1_R30[0] / GP6[1] / PRU1_R31[1] | K4 | O | CP[30] | C | VPIF display channel 3 output clock |
| VP_DOUT[15] / LCD_D[15] / UPP_XD[7] / GP7[7] / BOOT[7] | P4 | O | CP[29] | C | VPIF display data bus |
| VP_DOUT[14] / LCD_D[14] / UPP_XD[6] / GP7[6] / BOOT[6] | R3 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[13] / LCD_D[13] / UPP_XD[5] / GP7[5] / BOOT[5] | R2 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[12] / LCD_D[12] / UPP_XD[4] / GP7[4] / BOOT[4] | R1 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[11] / LCD_D[11] / UPP_XD[3] / GP7[3] / BOOT[3] | T3 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[10] / LCD_D[10] / UPP_XD[2] / GP7[2] / BOOT[2] | T2 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[9] / LCD_D[9] / UPP_XD[1] / GP7[1] / BOOT[1] | T1 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[8] / LCD_D[8] / UPP_XD[0] / GP7[0] / BOOT[0] | U3 | O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[7] / LCD_D[7] / UPP_XD[15] / GP7[15] / PRU1_R31[15] | U2 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[6] / LCD_D[6] / UPP_XD[14] / GP7[14] / PRU1_R31[14] | U1 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[5] / LCD_D[5] / UPP_XD[13] / GP7[13] / PRU1_R31[13] | V3 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[4] / LCD_D[4] / UPP_XD[12] / GP7[12] / PRU1_R31[12] | V2 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[3] / LCD_D[3] / UPP_XD[11] / GP7[11] / PRU1_R31[11] | V1 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[2] / LCD_D[2] / UPP_XD[10] / GP7[10] / PRU1_R31[10] | W3 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[1] / LCD_D[1] / UPP_XD[9] / GP7[9] / PRU1_R31[9] | W2 | O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[0] / LCD_D[0] / UPP_XD[8] / GP7[8] / PRU1_R31[8] | W1 | O | CP[28] | C | |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.25 General Purpose Input Output
Table 3-25 General Purpose Input Output Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | PULL(2) | POWER GROUP(3) |
DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| GP0 | |||||
| ACLKR / PRU0_R30[20] / GP0[15] / PRU0_R31[22] | A1 | I/O | CP[0] | A | GPIO Bank 0 |
| ACLKX / PRU0_R30[19] / GP0[14] / PRU0_R31[21] | B1 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AFSR / GP0[13] / PRU0_R31[20] | C2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AFSX / GP0[12] / PRU0_R31[19] | B2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AHCLKR / PRU0_R30[18] / UART1_RTS / GP0[11] / PRU0_R31[18] | A2 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AHCLKX / USB_REFCLKIN / UART1_CTS / GP0[10] / PRU0_R31[17] | A3 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AMUTE / PRU0_R30[16] / UART2_RTS / GP0[9] / PRU0_R31[16] | D5 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| RTC_ALARM / UART2_CTS / GP0[8] / DEEPSLEEP | F4 | I/O | CP[0] | A | |
| AXR15 / EPWM0TZ[0] / ECAP2_APWM2 / GP0[7] | A4 | I/O | CP[1] | A | |
| AXR14 / CLKR1 / GP0[6] | B4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR13 / CLKX1 / GP0[5] | B3 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR12 / FSR1 / GP0[4] | C4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR11 / FSX1 / GP0[3] | C5 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR10 / DR1 / GP0[2] | D4 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR9 / DX1 / GP0[1] | C3 | I/O | CP[2] | A | |
| AXR8 / CLKS1 / ECAP1_APWM1 /GP0[0] / PRU0_R31[8] | E4 | I/O | CP[3] | A | |
| GP1 | |||||
| AXR7 / EPWM1TZ[0] / PRU0_R30[17] / GP1[15] / PRU0_R31[7] | D2 | I/O | CP[4] | A | GPIO Bank 1 |
| AXR6 / CLKR0 / GP1[14] / MII_TXEN / PRU0_R31[6] | C1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR5 / CLKX0 / GP1[13] / MII_TXCLK | D3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR4 / FSR0 / GP1[12] / MII_COL | D1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR3 / FSX0 / GP1[11] / MII_TXD[3] | E3 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR2 / DR0 / GP1[10] / MII_TXD[2] | E2 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| AXR1 / DX0 / GP1[9] / MII_TXD[1] | E1 | I/O | CP[5] | A | |
| SPI0_CLK / EPWM0A / GP1[8] / MII_RXCLK | D19 | I/O | CP[7] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[1] / TM64P0_OUT12 / GP1[7] / MDCLK / TM64P0_IN12 | E16 | I/O | CP[10] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[0] / TM64P1_OUT12 / GP1[6] / MDIO / TM64P1_IN12 | D17 | I/O | CP[10] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[7] / I2C0_SCL / TM64P2_OUT12 / GP1[5] | G16 | I/O | CP[11] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[6] / I2C0_SDA / TM64P3_OUT12 / GP1[4] | G18 | I/O | CP[11] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[5] / UART2_RXD / I2C1_SCL / GP1[3] | F17 | I/O | CP[12] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[4] / UART2_TXD / I2C1_SDA / GP1[2] | F16 | I/O | CP[12] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[3] / UART1_RXD / SATA_LED / GP1[1] | E18 | I/O | CP[13] | A | |
| SPI1_SCS[2] / UART1_TXD / SATA_CP_POD / GP1[0] | F19 | I/O | CP[13] | A | |
| GP2 | |||||
| SPI1_SCS[1] / EPWM1A / PRU0_R30[8] / GP2[15] / TM64P2_IN12 | F18 | I/O | CP[14] | A | GPIO Bank 2 |
| SPI1_SCS[0] / EPWM1B / PRU0_R30[7] / GP2[14] / TM64P3_IN12 | E19 | I/O | CP[14] | A | |
| SPI1_CLK / GP2[13] | G19 | I/O | CP[15] | A | |
| SPI1_ENA / GP2[12] | H16 | I/O | CP[15] | A | |
| SPI1_SOMI / GP2[11] | H17 | I/O | CP[15] | A | |
| SPI1_SIMO / GP2[10] | G17 | I/O | CP[15] | A | |
| EMA_BA[1] / GP2[9] | A15 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_BA[0] / GP2[8] | C15 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CLK / PRU0_R30[5] / GP2[7] / PRU0_R31[5] | B7 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_SDCKE / PRU0_R30[4] / GP2[6] / PRU0_R31[4] | D8 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_RAS / PRU0_R30[3] / GP2[5] / PRU0_R31[3] | A16 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CAS / PRU0_R30[2] / GP2[4] / PRU0_R31[2] | A9 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WEN_DQM[0] / GP2[3] | C8 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WEN_DQM[1] / GP2[2] | A5 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[1] / PRU0_R30[1] / GP2[1] / PRU0_R31[1] | B19 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CS[0] / GP2[0] | A18 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| GP3 | |||||
| EMA_CS[2] / GP3[15] | B17 | I/O | CP[16] | B | GPIO Bank 3 |
| EMA_CS[3] / GP3[14] | A17 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CS[4] / GP3[13] | F9 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_CS[5] / GP3[12] | B16 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WE / GP3[11] | B9 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_OE / GP3[10] | B15 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_A_RW / GP3[9] | D10 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_WAIT[0] / PRU0_R30[0] / GP3[8] / PRU0_R31[0] | B18 | I/O | CP[16] | B | |
| EMA_D[15] / GP3[7] | E6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[14] / GP3[6] | C7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[13] / GP3[5] | B6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[12] / GP3[4] | A6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[11] / GP3[3] | D6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[10] / GP3[2] | A7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[9] / GP3[1] | D9 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[8] / GP3[0] | E10 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| GP4 | |||||
| EMA_D[7] / GP4[15] | D7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | GPIO Bank 4 |
| EMA_D[6] / GP4[14] | C6 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[5] / GP4[13] | E7 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[4] / GP4[12] | B5 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[3] / GP4[11] | E8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[2] / GP4[10] | B8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[1] / GP4[9] | A8 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| EMA_D[0] / GP4[8] | C9 | I/O | CP[17] | B | |
| MMCSD0_CLK / PRU1_R30[31] / GP4[7] | E9 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[22] / MMCSD0_CMD / PRU1_R30[30] / GP4[6] | A10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[21] / MMCSD0_DAT[0] / PRU1_R30[29] / GP4[5] | B10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[20] / MMCSD0_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[28] / GP4[4] | A11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[19] / MMCSD0_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[27] / GP4[3] | C10 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[18] / MMCSD0_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[26] / GP4[2] | E11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[17] / MMCSD0_DAT[4] / PRU1_R30[25] / GP4[1] | B11 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| EMA_A[16] / MMCSD0_DAT[5] / PRU1_R30[24] / GP4[0] | E12 | I/O | CP[18] | B | |
| GP5 | |||||
| EMA_A[15] / MMCSD0_DAT[6] / PRU1_R30[23] / GP5[15] / PRU1_R31[23] | C11 | I/O | CP[19] | B | GPIO Bank 5 |
| EMA_A[14] / MMCSD0_DAT[7] / PRU1_R30[22] / GP5[14] / PRU1_R31[22] | A12 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[13] / PRU0_R30[21] / PRU1_R30[21] / GP5[13] / PRU1_R31[21] | D11 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[12] / PRU1_R30[20] / GP5[12] / PRU1_R31[20] | D13 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[11] / PRU1_R30[19] / GP5[11] / PRU1_R31[19] | B12 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[10] / PRU1_R30[18] / GP5[10] / PRU1_R31[18] | C12 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[9] / PRU1_R30[17] / GP5[9] | D12 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[8] / PRU1_R30[16] / GP5[8] | A13 | I/O | CP[19] | B | |
| EMA_A[7] / PRU1_R30[15] / GP5[7] | B13 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[6] / GP5[6] | E13 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[5] / GP5[5] | C13 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[4] / GP5[4] | A14 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[3] / GP5[3] | D14 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[2] / GP5[2] | B14 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[1] / GP5[1] | D15 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| EMA_A[0] / GP5[0] | C14 | I/O | CP[20] | B | |
| GP6 | |||||
| RESETOUT / UHPI_HAS / PRU1_R30[14] / GP6[15] | T17 | I/O | CP[21] | C | GPIO Bank 6 |
| CLKOUT / UHPI_HDS2 / PRU1_R30[13] / GP6[14] | T18 | I/O | CP[22] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[31] / UHPI_HRDY / PRU1_R30[12] / GP6[13] | R17 | I/O | CP[23] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[30] / UHPI_HINT / PRU1_R30[11] / GP6[12] | R16 | I/O | CP[23] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[29] / UHPI_HCNTL0 / UPP_CHA_CLOCK / GP6[11] | U17 | I/O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[28] / UHPI_HCNTL1 / UPP_CHA_START / GP6[10] | W15 | I/O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[27] / UHPI_HHWIL / UPP_CHA_ENABLE / GP6[9] | U16 | I/O | CP[24] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[26] / UHPI_HRW / UPP_CHA_WAIT/GP6[8] / PRU1_R31[17] | T15 | I/O | CP[24] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN0 / UHPI_HCS / PRU1_R30[10] GP6[7] / UPP_2xTXCLK | W14 | I/O | CP[25] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN1 / UHPI_HDS1 / PRU1_R30[9] / GP6[6] / PRU1_R31[16] | V15 | I/O | CP[25] | C | |
| VP_DIN[8] / UHPI_HD[0] / UPP_D[0] / GP6[5] / PRU1_R31[0] | P17 | I/O | CP[27] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN2 / MMCSD1_DAT[3] / PRU1_R30[3] / GP6[4] / PRU1_R31[4] | H3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT2 / MMCSD1_DAT[2] / PRU1_R30[2] / GP6[3] / PRU1_R31[3] | K3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKIN3 / MMCSD1_DAT[1] / PRU1_R30[1] / GP6[2] / PRU1_R31[2] | J3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| VP_CLKOUT3 / PRU1_R30[0] / GP6[1] / PRU1_R31[1] | K4 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| LCD_AC_ENB_CS / GP6[0] / PRU1_R31[28] | R5 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| GP7 | |||||
| VP_DOUT[7] / LCD_D[7] / UPP_XD[15] / GP7[15] / PRU1_R31[15] | U2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | GPIO Bank 7 |
| VP_DOUT[6] / LCD_D[6] / UPP_XD[14] / GP7[14] / PRU1_R31[14] | U1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[5] / LCD_D[5] / UPP_XD[13] / GP7[13] / PRU1_R31[13] | V3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[4] / LCD_D[4] / UPP_XD[12] / GP7[12] / PRU1_R31[12] | V2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[3] / LCD_D[3] / UPP_XD[11] / GP7[11] / PRU1_R31[11] | V1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[2] / LCD_D[2] / UPP_XD[10] / GP7[10] / PRU1_R31[10] | W3 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[1] / LCD_D[1] / UPP_XD[9] / GP7[9] / PRU1_R31[9] | W2 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[0] / LCD_D[0] / UPP_XD[8] / GP7[8] / PRU1_R31[8] | W1 | I/O | CP[28] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[15] / LCD_D[15] / UPP_XD[7] / GP7[7] / BOOT[7] | P4 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[14] / LCD_D[14] / UPP_XD[6] / GP7[6] / BOOT[6] | R3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[13] / LCD_D[13] / UPP_XD[5] / GP7[5]/ BOOT[5] | R2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[12] / LCD_D[12] / UPP_XD[4] / GP7[4] / BOOT[4] | R1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[11] / LCD_D[11] / UPP_XD[3] / GP7[3] / BOOT[3] | T3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[10] / LCD_D[10] / UPP_XD[2] / GP7[2] / BOOT[2] | T2 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[9] / LCD_D[9] / UPP_XD[1] / GP7[1] / BOOT[1] | T1 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| VP_DOUT[8] / LCD_D[8] / UPP_XD[0] / GP7[0] / BOOT[0] | U3 | I/O | CP[29] | C | |
| GP8 | |||||
| PRU0_R30[25] / MMCSD1_DAT[0] / UPP_CHB_CLOCK / GP8[15] / PRU1_R31[27] | G1 | I/O | CP30] | C | GPIO Bank 8 |
| PRU0_R30[24] / MMCSD1_CLK / UPP_CHB_START / GP8[14] / PRU1_R31[26] | G2 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[23] / MMCSD1_CMD / UPP_CHB_ENABLE / GP8[13] / PRU1_R31[25] | J4 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| PRU0_R30[22] / PRU1_R30[8] / UPP_CHB_WAIT / GP8[12] / PRU1_R31[24] | G3 | I/O | CP[30] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[7] / LCD_PCLK / PRU1_R30[7] / GP8[11] | F1 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[6] / LCD_MCLK / PRU1_R30[6] / GP8[10] / PRU1_R31[7] | F2 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[5] / LCD_HSYNC / PRU1_R30[5] / GP8[9] / PRU1_R31[6] | H4 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| MMCSD1_DAT[4] / LCD_VSYNC / PRU1_R30[4] / GP8[8] / PRU1_R31[5] | G4 | I/O | CP[31] | C | |
| AXR0 / ECAP0_APWM0 / GP8[7] / MII_TXD[0] / CLKS0 | F3 | I/O | CP[6] | A | |
| SPI0_SOMI / EPWMSYNCI / GP8[6] / MII_RXER | C16 | I/O | CP[7] | A | |
| SPI0_SIMO / EPWMSYNCO / GP8[5] / MII_CRS | C18 | I/O | CP[7] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[5] / UART0_RXD / GP8[4] / MII_RXD[3] | C19 | I/O | CP[8] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[4] / UART0_TXD / GP8[3] / MII_RXD[2] | D18 | I/O | CP[8] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[3] / UART0_CTS / GP8[2] / MII_RXD[1] / SATA_MP_SWITCH | E17 | I/O | CP[9] | A | |
| SPI0_SCS[2] / UART0_RTS / GP8[1] / MII_RXD[0] / SATA_CP_DET | D16 | I/O | CP[9] | A | |
| GP8[0](5) | K17 | I/O | IPD | B | |
Note: The pin type shown refers to the input, output or high-impedance state of the pin function when configured as the signal name highlighted in bold. All multiplexed signals may enter a high-impedance state when the configured function is input-only or the configured function supports high-Z operation. All GPIO signals can be used as input or output. For multiplexed pins where functions have different types (ie., input versus output), the table reflects the pin function direction for that particular peripheral.
3.2.26 Reserved and No Connect
Table 3-26 Reserved and No Connect Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| RSV2 | T19 | PWR | Reserved. For proper device operation, this pin must be tied either directly to CVDD or left unconnected (do not connect to ground). |
| NC | M3, M14, N16 | Pin M3 should be left unconnected (do not connect to power or ground) Pins M14 and N16 may be left unconnected or connected to ground (VSS) |
3.2.27 Supply and Ground
Table 3-27 Supply and Ground Terminal Functions
| SIGNAL | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CVDD (Core supply) | E15, G7, G8, G13, H6, H7, H10, H11, H12, H13, J6, J12, K6, K12, L12, M8, M9, N8 | PWR | Variable (1.3 V - 1 V) core supply voltage pins |
| RVDD (Internal RAM supply) | E5, H14, N7 | PWR | 1.2-V internal ram supply voltage pins (for 375 MHz versions) |
| DVDD18 (I/O supply) | F14, G6, G10, G11, G12, J13, K5, L6, P13, R13 | PWR | 1.8-V I/O supply voltage pins. DVDD18 must be powered even if all of the DVDD3318_x supplies are operated at 3.3 V. |
| DVDD3318_A (I/O supply) | F5, F15, G5, G14, G15, H5 | PWR | 1.8-V or 3.3-V dual-voltage LVCMOS I/O supply voltage pins, Group A |
| DVDD3318_B (I/O supply) | E14, F6, F7, F8, F10, F11, F12, F13, G9, J14, K15 | PWR | 1.8-V or 3.3-V dual-voltage LVCMOS I/O supply voltage pins, Group B |
| DVDD3318_C (I/O supply) | J5, K13, L4, L13, M13, N13, P5, P6, P12, R4 | PWR | 1.8-V or 3.3-V dual-voltage LVCMOS I/O supply voltage pins, Group C |
| VSS (Ground) | A19, H8, H9, H15, J7, J8, J9, J10, J11, K7, K8, K9, K10, K11, L5, L7, L8, L9, L10, L11, M4, M5, M6, M7, M10, M11, N5, N11, N12, P11 | GND | Ground pins. |
| USB0_VDDA33 | N18 | PWR | USB0 PHY 3.3-V supply |
| USB0_VDDA18 | N14 | PWR | USB0 PHY 1.8-V supply input |
| USB0_VDDA12 | N17 | A | USB0 PHY 1.2-V LDO output for bypass cap |
| USB_CVDD | M12 | PWR | USB0 core logic 1.2-V supply input |
| USB1_VDDA33 | P15 | PWR | USB1 PHY 3.3-V supply |
| USB1_VDDA18 | P14 | PWR | USB1 PHY 1.8-V supply |
| SATA_VDD | M2, N4, P1, P2 | PWR | SATA PHY 1.2-V logic supply |
| SATA_VSS | H1, H2, K1, K2, L3, M1 | GND | SATA PHY ground reference |
| DDR_DVDD18 | N6, N9, N10, P7, P8, P9, P10, R7, R8, R9 | PWR | DDR PHY 1.8-V power supply pins |
3.3 Pin Multiplexing
Device level pin multiplexing is controlled by registers PINMUX0 - PINMUX19 in the SYSCFG module. See Table 5-5 for .
For the device family, pin multiplexing can be controlled on a pin-by-pin basis. Each pin that is multiplexed with several different functions has a corresponding 4-bit field in one of the PINMUX registers.
Pin multiplexing selects which of several peripheral pin functions controls the pin's IO buffer output data and output enable values only. The default pin multiplexing control for almost every pin is to select 'none' of the peripheral functions in which case the pin's IO buffer is held tri-stated.
Note that the input from each pin is always routed to all of the peripherals that share the pin; the PINMUX registers have no effect on input from a pin.
3.4 Connections for Unused Pins
All signals multiplexed with multiple functions may be used as an alternate function if a given peripheral is not used. Unused non-multiplexed signals and some other specific signals should be handled as specified in the tables below.
If NMI is unused, it should be pulled-high externally through a 10-kΩ resistor to supply DVDD3318_B.
Table 3-28 Unused USB0 and USB1 Signal Configurations
| SIGNAL NAME | Configuration (When USB0 and USB1 are not used) | Configuration (When only USB1 is not used) |
|---|---|---|
| USB0_DM | No Connect | Use as USB0 function |
| USB0_DP | No Connect | Use as USB0 function |
| USB0_ID | No Connect | Use as USB0 function |
| USB0_VBUS | No Connect | Use as USB0 function |
| USB0_DRVVBUS | No Connect | Use as USB0 function |
| USB0_VDDA33 | No Connect | 3.3V |
| USB0_VDDA18 | No Connect | 1.8V |
| USB0_VDDA12 | Internal USB PHY output connected to an external 0.22-μF filter capacitor | |
| USB1_DM | No Connect | VSS or No Connect |
| USB1_DP | No Connect | VSS or No Connect |
| USB1_VDDA33 | No Connect | No Connect |
| USB1_VDDA18 | No Connect | No Connect |
| USB_REFCLKIN | No Connect or other peripheral function | Use for USB0 or other peripheral function |
| USB_CVDD | 1.2V | 1.2V |
Table 3-29 Unused SATA Signal Configuration
| SIGNAL NAME | Configuration |
|---|---|
| SATA_RXP | No Connect |
| SATA_RXN | No Connect |
| SATA_TXP | No Connect |
| SATA_TXN | No Connect |
| SATA_REFCLKP | No Connect |
| SATA_REFCLKN | No Connect |
| SATA_MP_SWITCH | May be used as GPIO or other peripheral function |
| SATA_CP_DET | May be used as GPIO or other peripheral function |
| SATA_CP_POD | May be used as GPIO or other peripheral function |
| SATA_LED | May be used as GPIO or other peripheral function |
| SATA_REG | No Connect |
| SATA_VDDR | No Connect |
| SATA_VDD | Prior to silicon revision 2.0, this supply must be connected to a static 1.2V nominal supply. For silicon revision 2.0 and later, this supply may be left unconnected for additional power conservation. |
| SATA_VSS | VSS |
Table 3-30 Unused RTC Signal Configuration
| SIGNAL NAME | Configuration |
|---|---|
| RTC_XI | May be held high (CVDD) or low |
| RTC_XO | No Connect |
| RTC_ALARM | May be used as GPIO or other peripheral function |
| RTC_CVDD | Connect to CVDD |
| RTC_VSS | VSS |
Table 3-31 Unused DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Signal Configuration
| SIGNAL NAME | Configuration (1) |
|---|---|
| DDR_D[15:0] | No Connect |
| DDR_A[13:0] | No Connect |
| DDR_CLKP | No Connect |
| DDR_CLKN | No Connect |
| DDR_CKE | No Connect |
| DDR_WE | No Connect |
| DDR_RAS | No Connect |
| DDR_CAS | No Connect |
| DDS_CS | No Connect |
| DDR_DQM[1:0] | No Connect |
| DDR_DQS[1:0] | No Connect |
| DDR_BA[2:0] | No Connect |
| DDR_DQGATE0 | No Connect |
| DDR_DQGATE1 | No Connect |
| DDR_ZP | No Connect |
| DDR_VREF | No Connect |
| DDR_DVDD18 | No Connect |