SLLSF42A March 2018 – May 2018 SN65LVDS93B-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGG|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.1.3 Traces, Vias, and Other PCB Components
A right angle in a trace can cause more radiation. The capacitance increases in the region of the corner, and the characteristic impedance changes. This impedance change causes reflections.
- Avoid right-angle bends in a trace and try to route them at least with two 45° corners. To minimize any impedance change, the best routing would be a round bend (see Figure 20).
- Separate high-speed signals (e.g., clock signals) from low-speed signals and digital from analog signals; again, placement is important.
- To minimize crosstalk not only between two signals on one layer but also between adjacent layers, route them with 90° to each other.
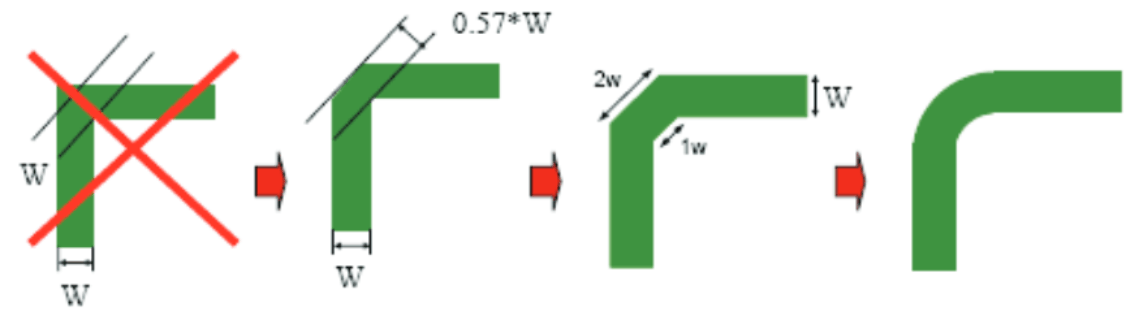 Figure 20. Poor and Good Right Angle Bends
Figure 20. Poor and Good Right Angle Bends