SDLS025D December 1983 – May 2017 SN5400 , SN54LS00 , SN54S00 , SN7400 , SN74LS00 , SN74S00
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings: SN74LS00
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: SNx400
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: SNx4LS00
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: SNx4S00
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics: SNx400
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: SNx4LS00
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics: SNx4S00
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
- PS|8
- DB|14
- N|14
- NS|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PS|8
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
When using multiple bit logic, devices inputs must never float.
Devices with multiple-emitter inputs (SN74 and SN74S series) need special care. Because no voltage greater than 5.5 V must be applied to the inputs (if exceeded, the base-emitter junction at the inputs breaks down), the inputs of these devices must be connected to the supply voltage, VCC, through series resistor, RS (see Figure 5). This resistor must be dimensioned such that the current flowing into the gate or gates, which results from overvoltage, does not exceed 1 mA. However, because the high-level input current of the circuits connected to the gate flows through this resistor, the resistor must be dimensioned so that the voltage drop across it still allows the required high level. Equation 1 and Equation 2 are for dimensioning resistor, RS, and several inputs can be connected to a high level through a single resistor if the following conditions are met.
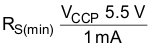
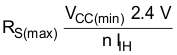
where
- n = number of inputs connected
- IIH = high input current (typical 40 µA)
- VCC(min) = minimum supply voltage, VCC
- VCCP = maximum peak voltage of the supply voltage, VCC (about 7 V)
11.2 Layout Example
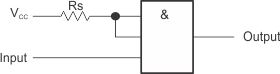 Figure 5. Series Resistor Connected to Unused Inputs of Multiple-Emitter Transistors
Figure 5. Series Resistor Connected to Unused Inputs of Multiple-Emitter Transistors