SCPS201E August 2009 – May 2022 TCA9535
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The pull-up resistors, RP, for the SCL and SDA lines need to be selected appropriately and take into consideration the total capacitance of all targets on the I2C bus. The minimum pull-up resistance is a function of VCC, VOL,(max), and IOL as shown in Equation 5.
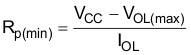
The maximum pull-up resistance is a function of the maximum rise time, tr (300 ns for fast-mode operation, fSCL = 400 kHz) and bus capacitance, Cb as shown in Equation 6.
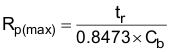
The maximum bus capacitance for an I2C bus must not exceed 400 pF for standard-mode or fast-mode operation. The bus capacitance can be approximated by adding the capacitance of the TCA9535, Ci for SCL or CIO for SDA, the capacitance of wires/connections/traces, and the capacitance of additional targets on the bus. For further details, refer to I2C Pull-up Resistor Calculation application report, SLVA689.