SNLS787 September 2025 TDP2004-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
- 6Detailed Description
- 7Application and Implementation
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGF|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGF|40
Orderable Information
7.2.1.3 Application Curves
The TDP2004-Q1 is a linear redriver that can be used to extend channel reach of a DP link. The redriver can help to pass compliance by removing ISI deterministic jitter at data rates up to 20Gbps (UHBR20) for DP2.1. Figure 7-3 - Figure 7-6 shows a typical DP 2.1 Tx compliance channel setup along with compliance Eye Diagrams at TP3_EQ with or without redriver. The comparison of eye diagrams show that TDP2004-Q1 can provide signal conditioning by extending horizontal and vertical eye openings that makes a failing eye to pass.
 Figure 7-3 A
Typical 20Gbps (UHBR20) DP 2.1 Tx Compliance Channel
Setup With No Redriver
Figure 7-3 A
Typical 20Gbps (UHBR20) DP 2.1 Tx Compliance Channel
Setup With No Redriver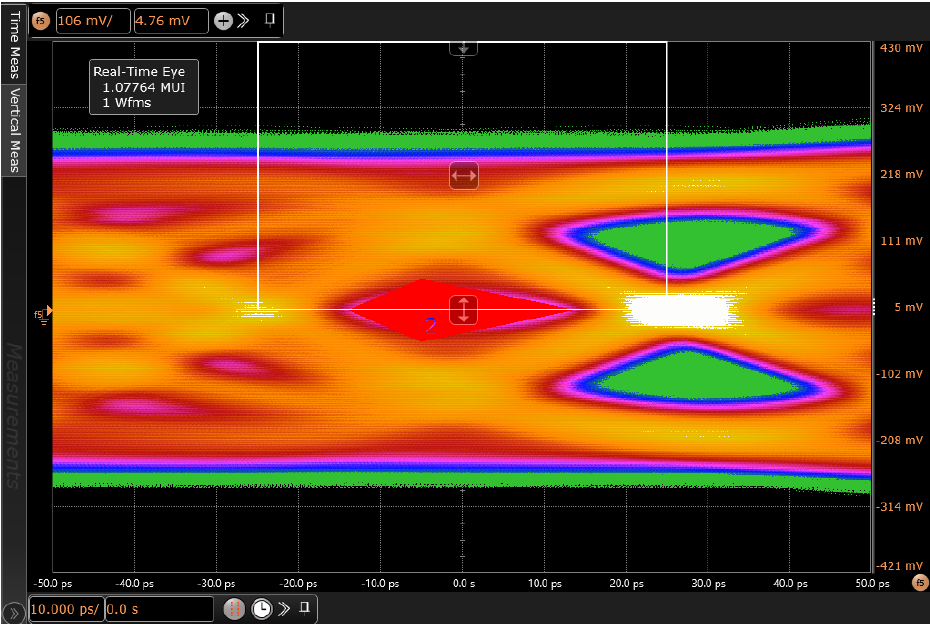 Figure 7-5 DP 2.1
Tx Compliance Eye Diagram at TP3_EQ With No
Redriver
Figure 7-5 DP 2.1
Tx Compliance Eye Diagram at TP3_EQ With No
Redriver Figure 7-4 A
Typical 20Gbps (UHBR20) DP 2.1 Tx Compliance Channel
Setup With Redriver
Figure 7-4 A
Typical 20Gbps (UHBR20) DP 2.1 Tx Compliance Channel
Setup With Redriver Figure 7-6 DP 2.1
Tx Compliance Eye Diagram at TP3_EQ With TDP2004-Q1 for Signal
Conditioning
Figure 7-6 DP 2.1
Tx Compliance Eye Diagram at TP3_EQ With TDP2004-Q1 for Signal
Conditioning