SBOS726A October 2015 – October 2015 TMP107-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Map
- 8.6.1 Temperature Register (address = 0h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.2 Configuration Register (address = 1h) [reset = A000h]
- 8.6.3 High Limit 1 Register (address = 2h) [reset = 7FFCh]
- 8.6.4 Low Limit 1 Register (address = 3h) [reset = 8000h]
- 8.6.5 High Limit 2 Register (address = 4h) [reset = 7FFCh]
- 8.6.6 Low Limit 2 Register (address = 5h) [reset = 8000h]
- 8.6.7 EEPROM n Register (where n = 1 to 8) (addresses = 6h to Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.8 Die ID Register (address = Fh) [reset = 1107h]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Mount the TMP107-Q1 to a PCB as shown in Figure 44. Obtaining acceptable performance with alternate layout schemes is possible, however this layout produces good results and is intended as a guideline.
- Bypass the V+ pin to ground with a low-ESR ceramic bypass-capacitor. The typical recommended bypass capacitance is a 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor with a X5R or X7R dielectric. The optimum placement is closest to the V+ and GND pins of the device. Take care to minimize the loop area formed by the bypass-capacitor connection, the V+ pin, and the GND pin of the IC.
- Use larger copper area pads to reduce self-heating and lower thermal resistance to the environment.
- If possible, use PCB boards with thick copper layers.
- If possible, do not use stain to protect the IC because stain can increase thermal resistance.
11.2 Layout Example
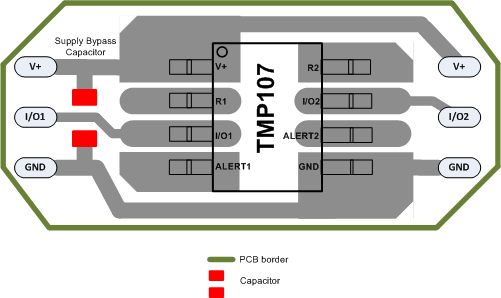 Figure 44. Layout Example
Figure 44. Layout Example