SLVS728D January 2007 – October 2019 TPS2412 , TPS2413
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Definitions
- 8.3.2 TPS2412 vs TPS2413 – MOSFET Control Methods
- 8.3.3 N+1 Power Supply – Typical Connection
- 8.3.4 Input ORing – Typical Connection
- 8.3.5 System Design and Behavior With Transients
- 8.3.6 TPS2412 Regulation-Loop Stability
- 8.3.7 MOSFET Selection and R(RSET)
- 8.3.8 Gate Drive, Charge Pump and C(BYP)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- PW|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1 Definitions
The following descriptions refer to the pinout and the functional block diagram.
A, C: The A pin serves as the simulated diode anode and the C as the cathode. GATE is driven high when V(AC) exceeds 10 mV. Both devices provide a strong GATE pulldown when V(AC) is less than the programmable fast turnoff threshold. The TPS2412 has a soft pulldown when V(AC) is less than 10 mV but above the fast turnoff threshold.
Several internal comparator and amplifier circuits monitor these two pins. The inputs are protected from excess differential voltage by a clamp diode and series resistance. If C falls below A by more than about 0.7 V, a small current flows out of C. Protect the internal circuits with an external clamp if C can be more than 6 V lower than A.
The internal charge pump output, which provides bias power to the comparators and voltage to drive GATE, is referenced to A. Some charge pump current appears on A due to this topology. The A and C pins should be Kelvin connected to the MOSFET source and drain. A and C connections should also be short and low impedance, with special attention to the A connection. Residual noise from the charge pump can be reduced with a bypass capacitor at A if the application permits.
BYP: BYP is the internal charge pump output, and the positive supply voltage for internal comparator circuits and GATE driver. A capacitor must be connected from BYP to A. While the capacitor value is not critical, a 2200-pF ceramic is recommended. Traces to this part must be kept short and low impedance to provide adequate filtering.
CAUTION
Shorting this pin to a voltage below A damages the TPS241x.
GATE: Gate controls the external N channel MOSFET gate. GATE is driven positive with respect to A by a driver operating from the voltage on BYP. A time-limited high current discharge source pulls GATE to GND when the fast turnoff comparator is activated. The high-current discharge is followed by a sustaining pulldown. The turnoff circuits are disabled by the thermal shutdown, leaving a resistive pulldown to keep the gate from floating. The gate connection should be kept low impedance to maximize turnoff current.
GND: This is the input supply reference. GND should have a low impedance connection to the ground plane. It carries several Amperes of rapid-rising discharge current when the external MOSFET is turned off, and also carries significant charge pump currents.
RSET: A resistor connected from this pin to GND sets the fast V(A-C) comparator turnoff threshold. The threshold is slightly positive when the RSET pin is left open. Current drawn by the resistor programs the turnoff voltage to increasing negative values. The TPS2413 must have a negative threshold programmed to avoid an unstable condition at light load. The expression for R(RSET) in terms of the trip voltage, V(OFF), follows.
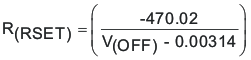
The units of the numerator are (V × V/A). V(OFF) is positive for V(A) greater than V(C), V(OFF) is less than 3 mV, and R(RSET) is in ohms.
RSVD: Connect to ground.
VDD: VDD is the primary supply for the gate drive charge pump and other internal circuits. This pin must be connected a source that is 3 V or greater when the external MOSFET is to be turned on. VDD may be greater or lower than the controlled bus voltage.
A 0.01-μF bypass capacitor, or 10-Ω and a 0.01-μF filter, is recommended because charge pump currents are drawn through VDD.